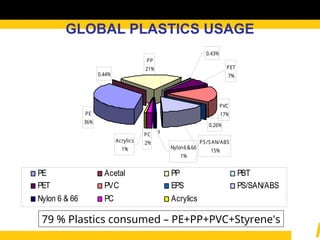
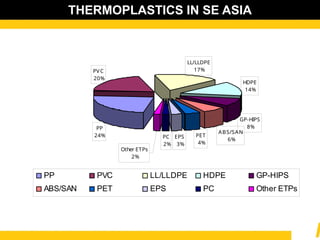
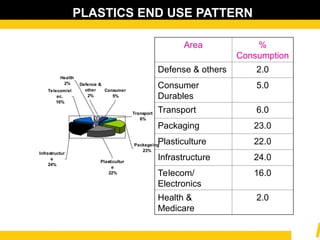
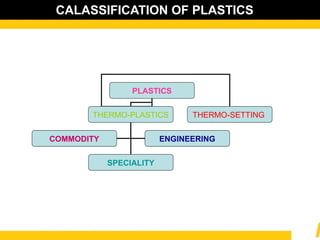
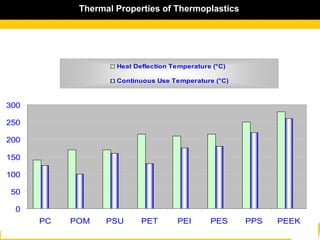
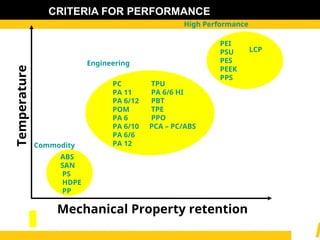
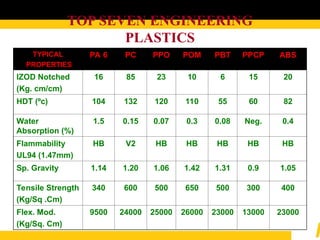
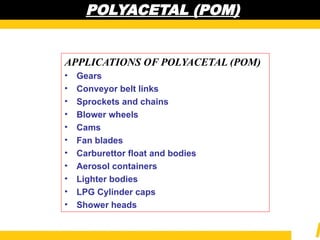
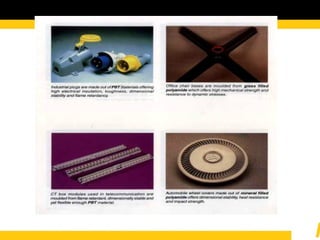
The document details the usage and characteristics of various engineering plastics in modern automotive applications, highlighting the significant presence of materials such as polypropylene, polyethylene, and polyamide among others. It discusses the mechanical and thermal properties of these plastics, their classifications, and specific applications in industries like automotive, telecommunications, and healthcare. Additionally, it addresses the processing technologies and advantages these materials offer, including lightweight solutions and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing.