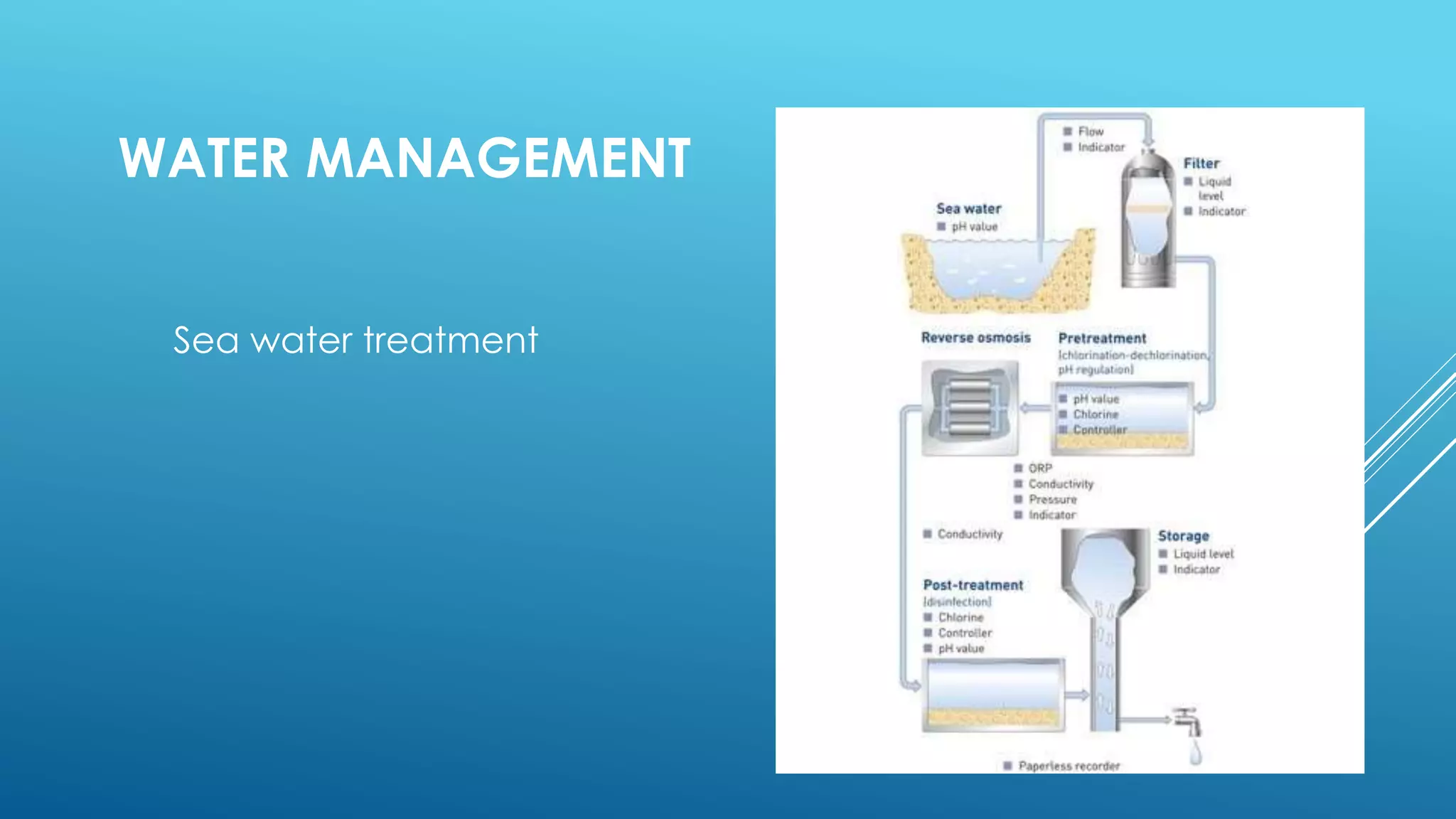
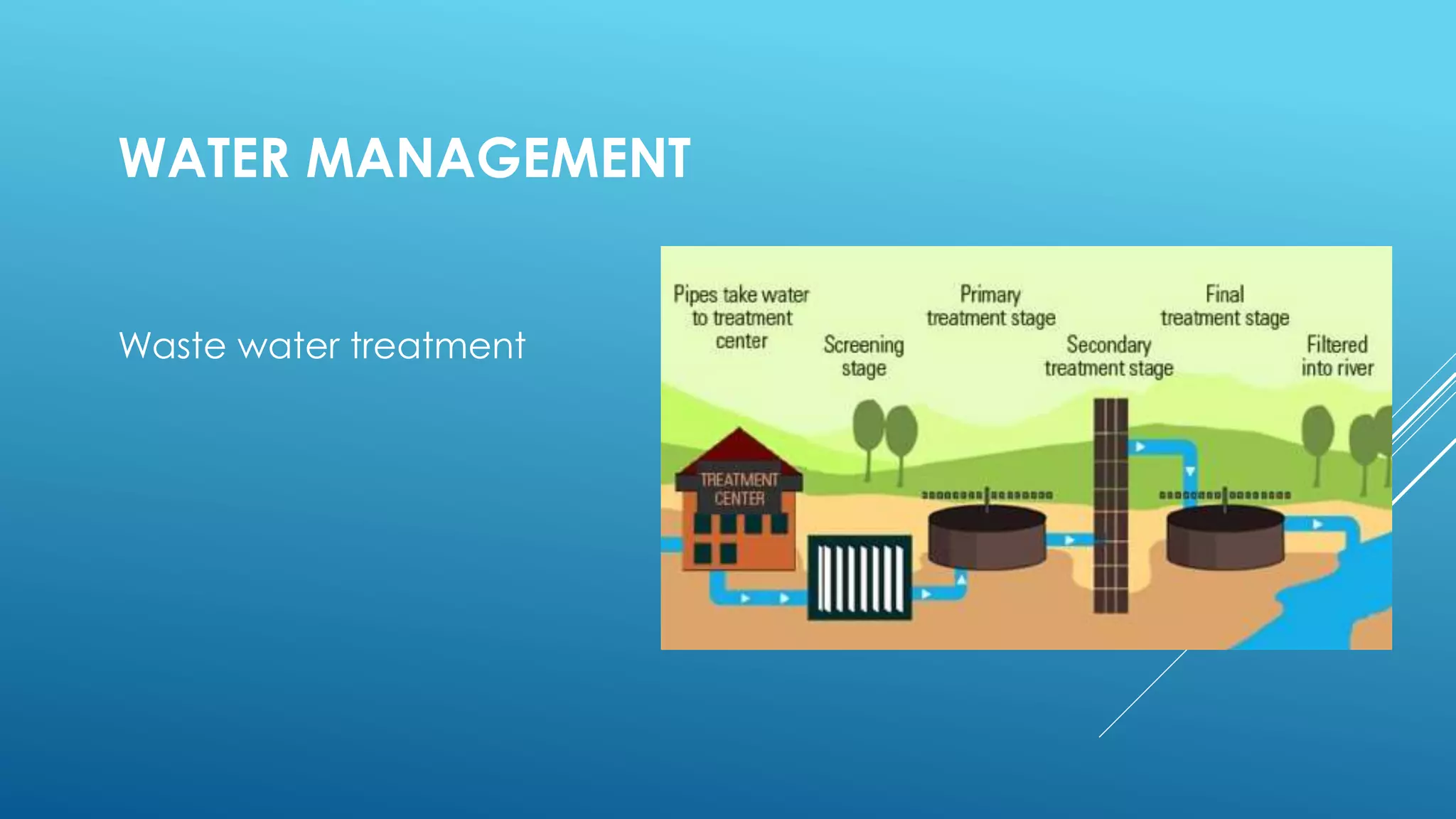
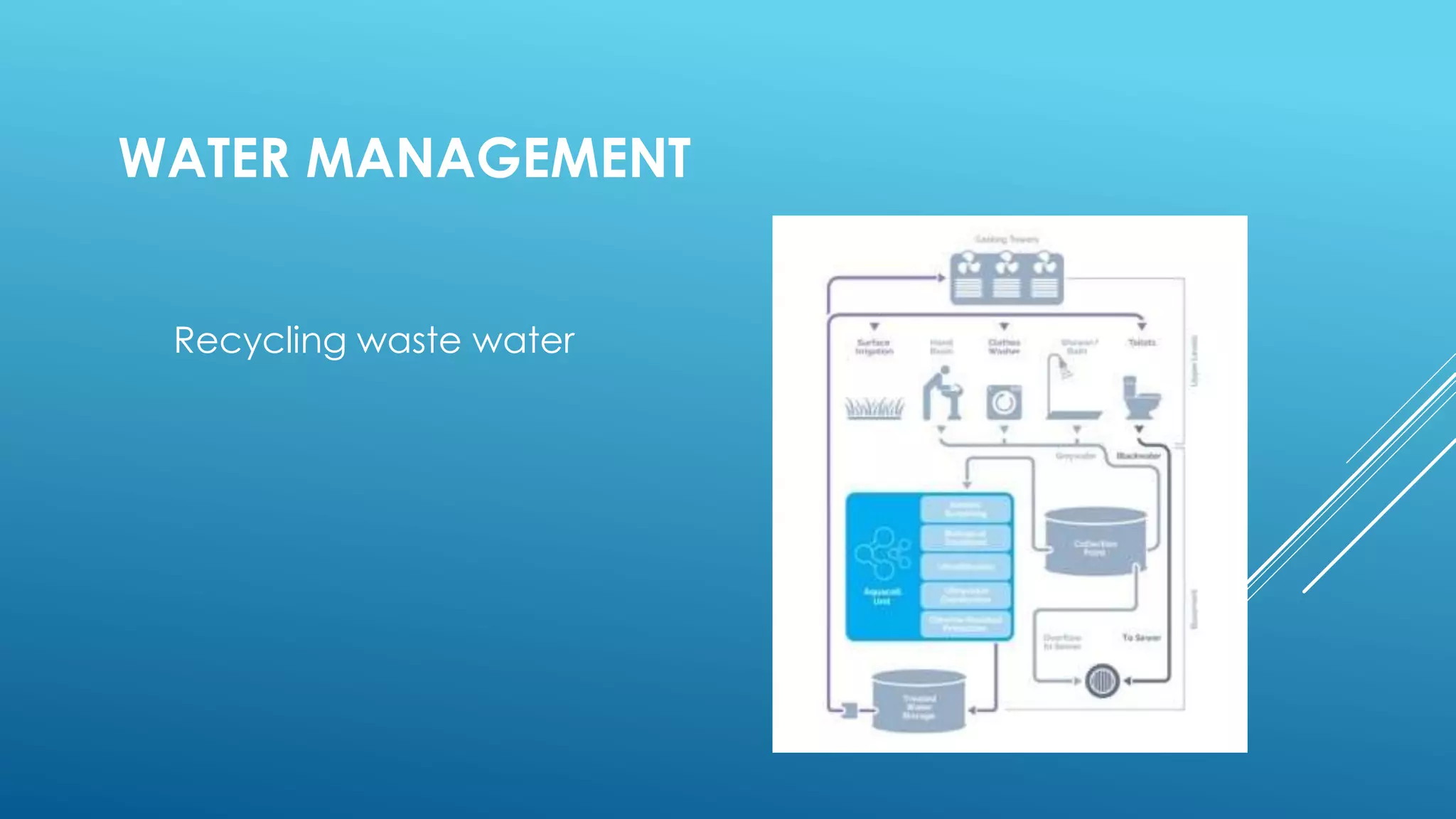
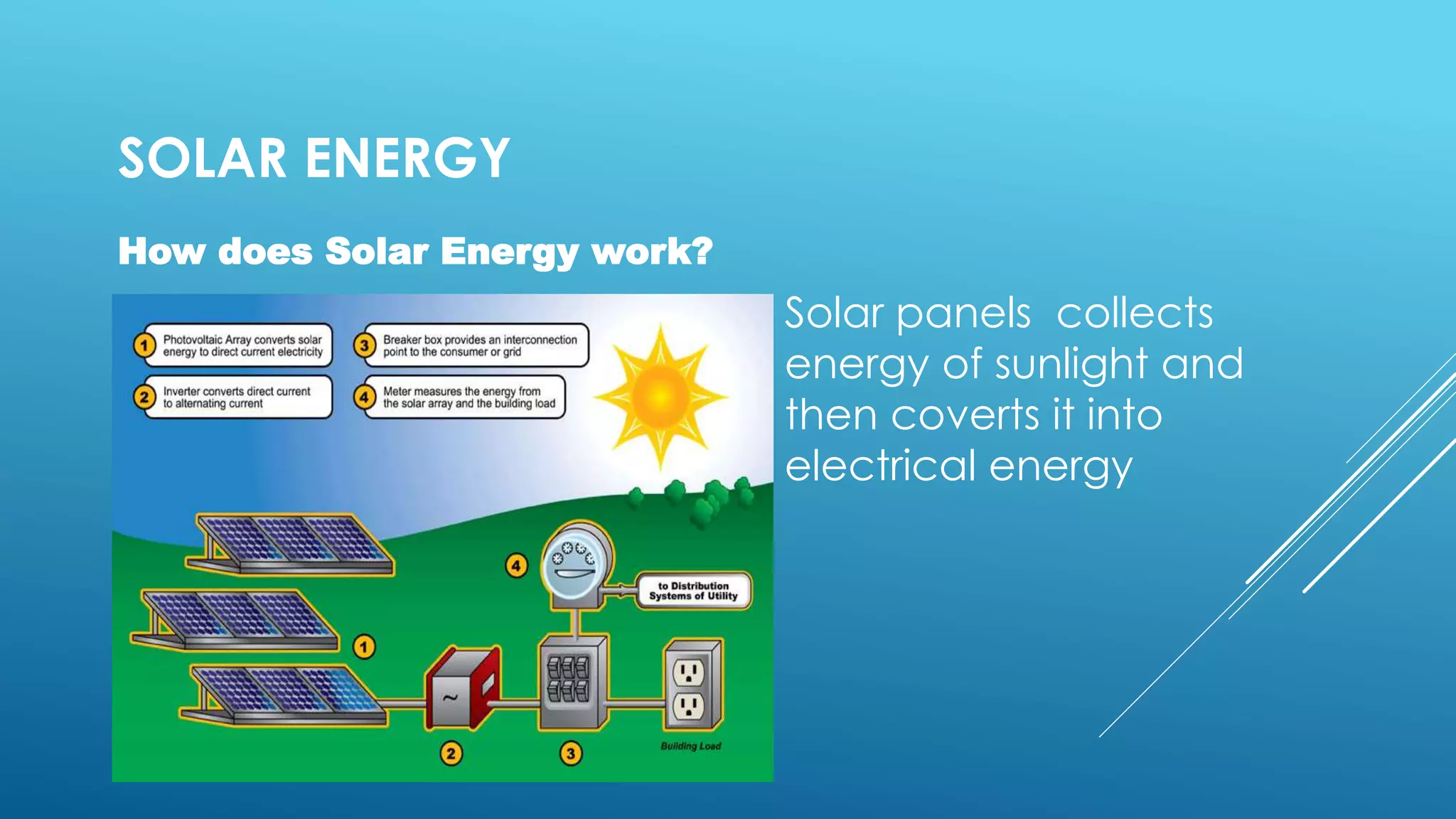
The document discusses security technologies and waste, water, and disaster management strategies for future cities. It examines biometric scanners like fingerprint, iris, and voice recognition for security. It also discusses using drones and facial recognition for surveillance. For waste management, it describes sorting waste and using incineration to generate energy from waste. It outlines water treatment and recycling processes. For disaster relief, it recommends earthquake-resistant building features like reinforced foundations, walls, and joints.