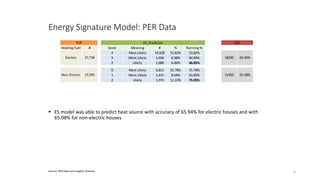
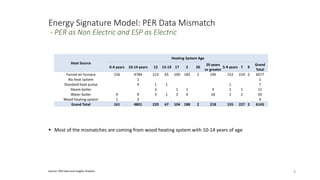
The document discusses the energy signature model for electric and non-electric houses, highlighting the differences in their consumption patterns across seasons. Electric houses show a higher winter peak and a steeper slope in energy use compared to non-electric houses, which have a more balanced yearly consumption and summer peaks. The model demonstrates a predictive accuracy of 94.35% for electric houses and 81.57% for non-electric houses based on a range of components related to energy consumption.