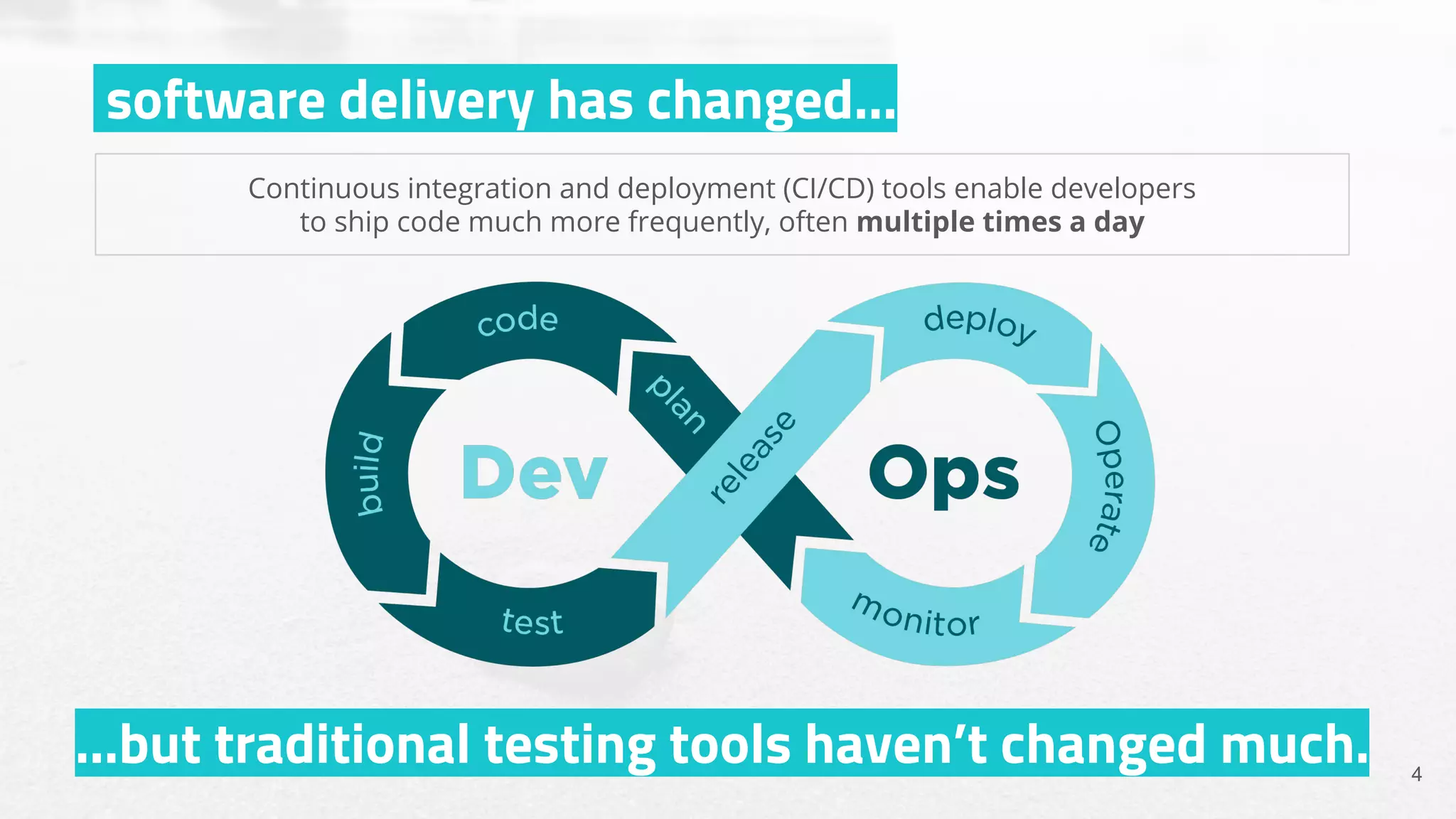
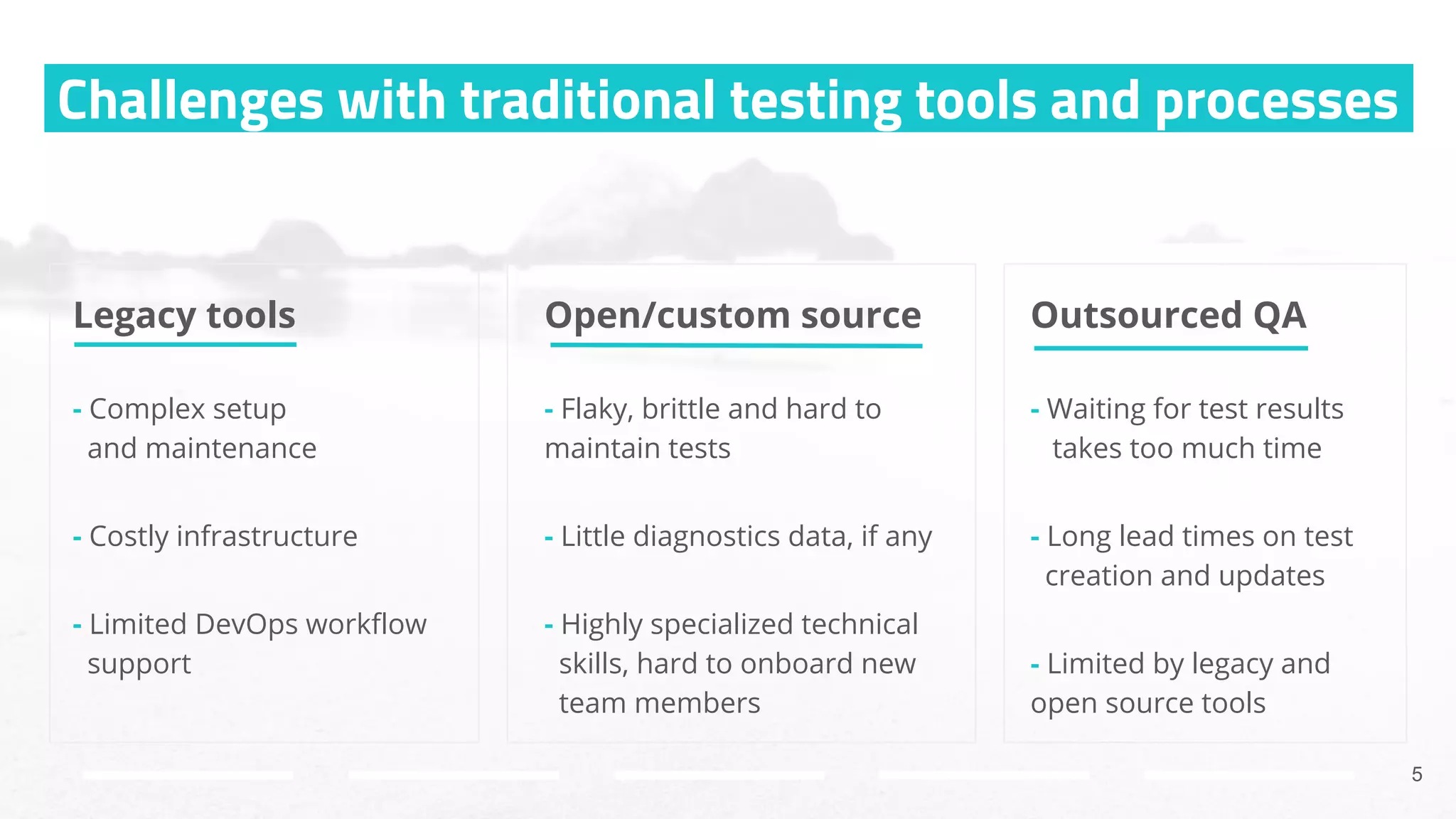
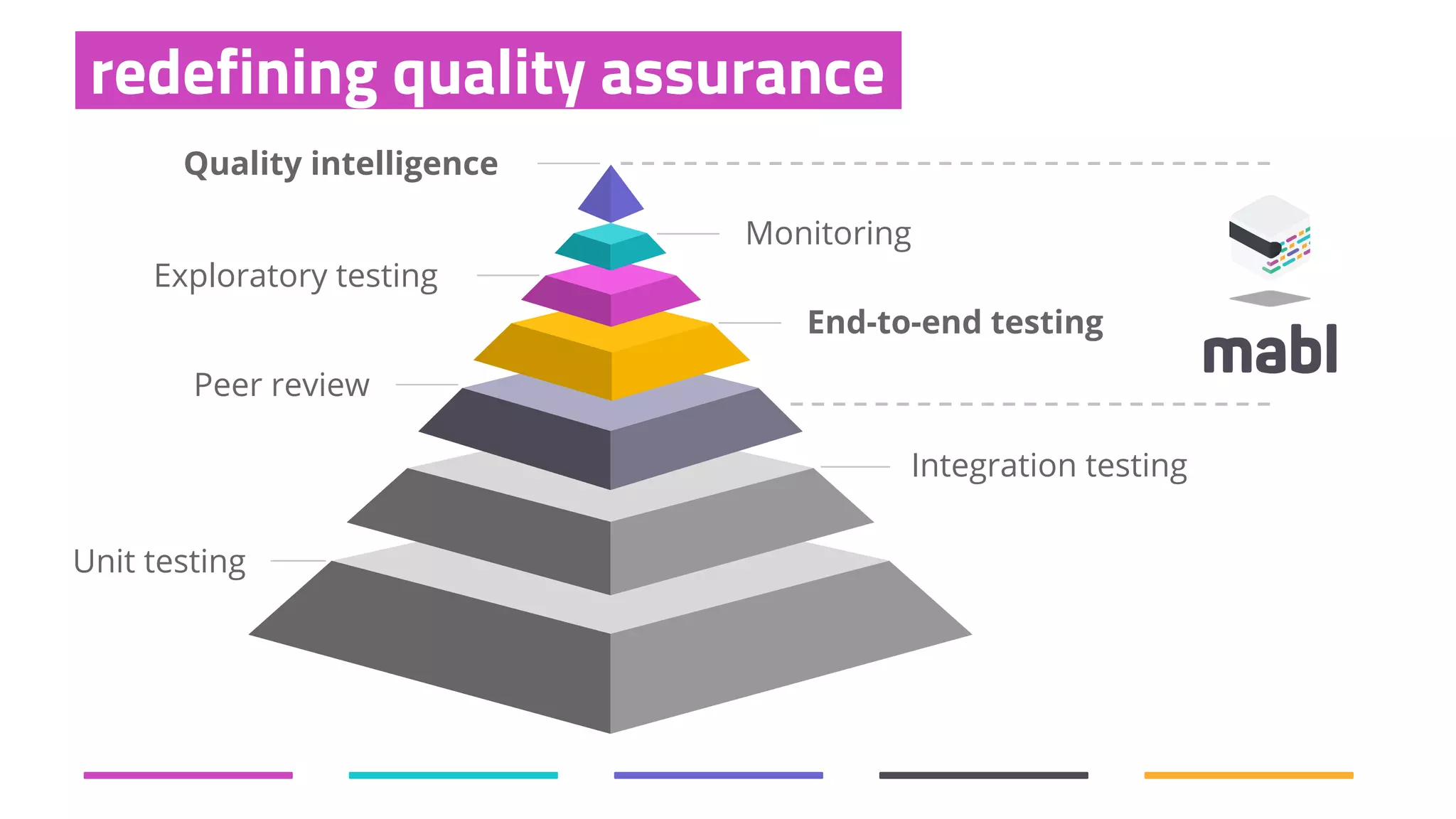
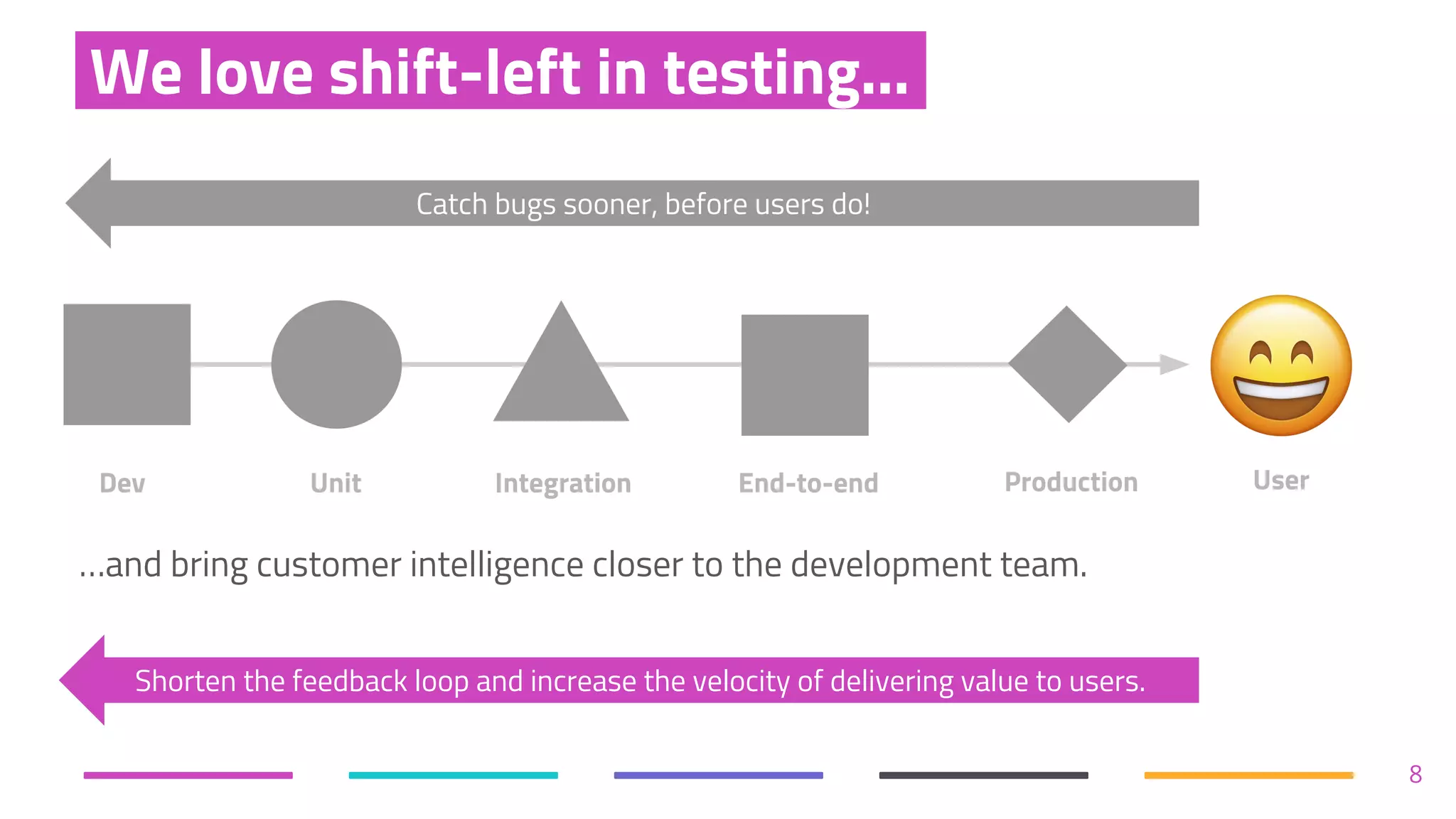
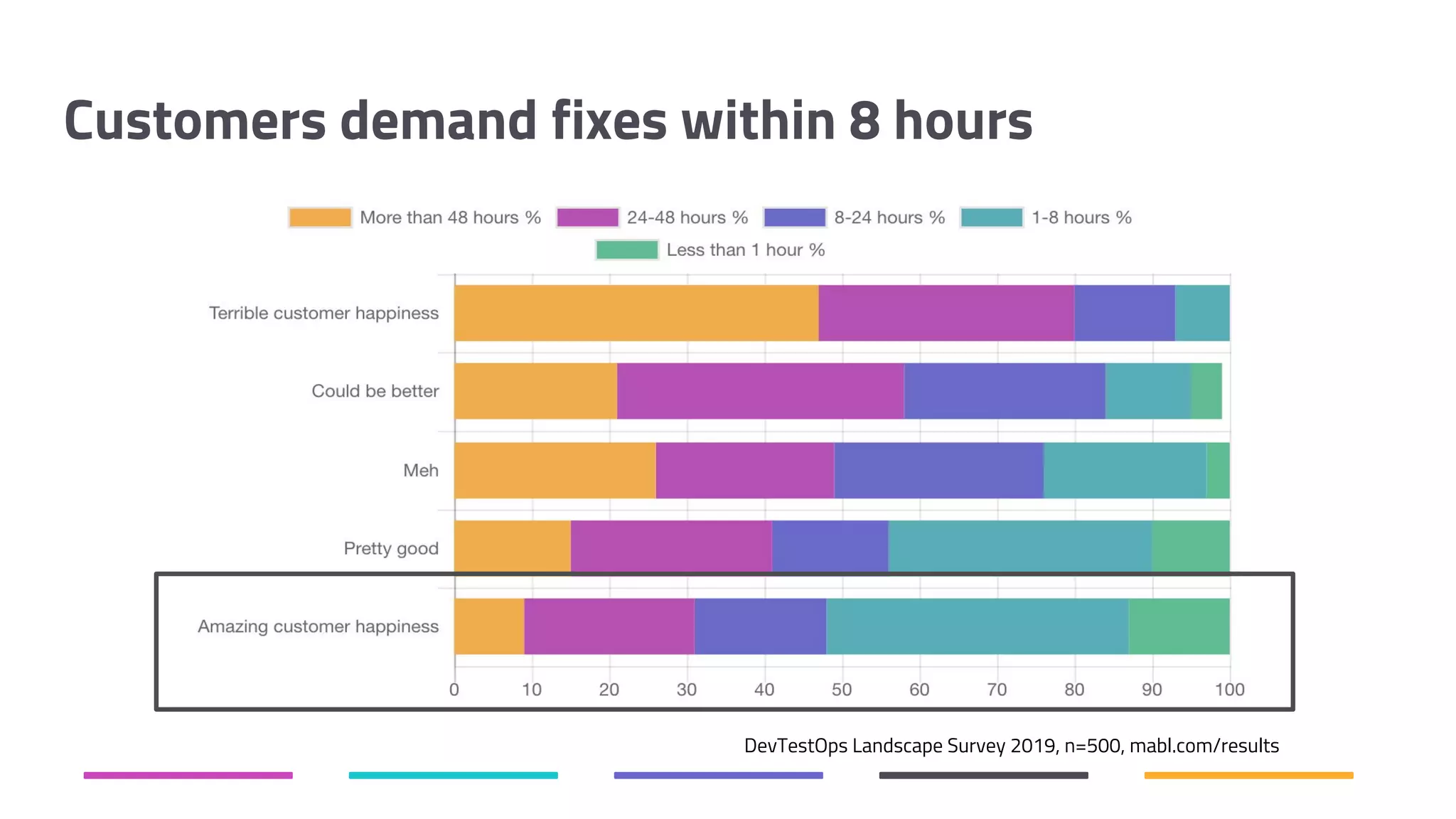
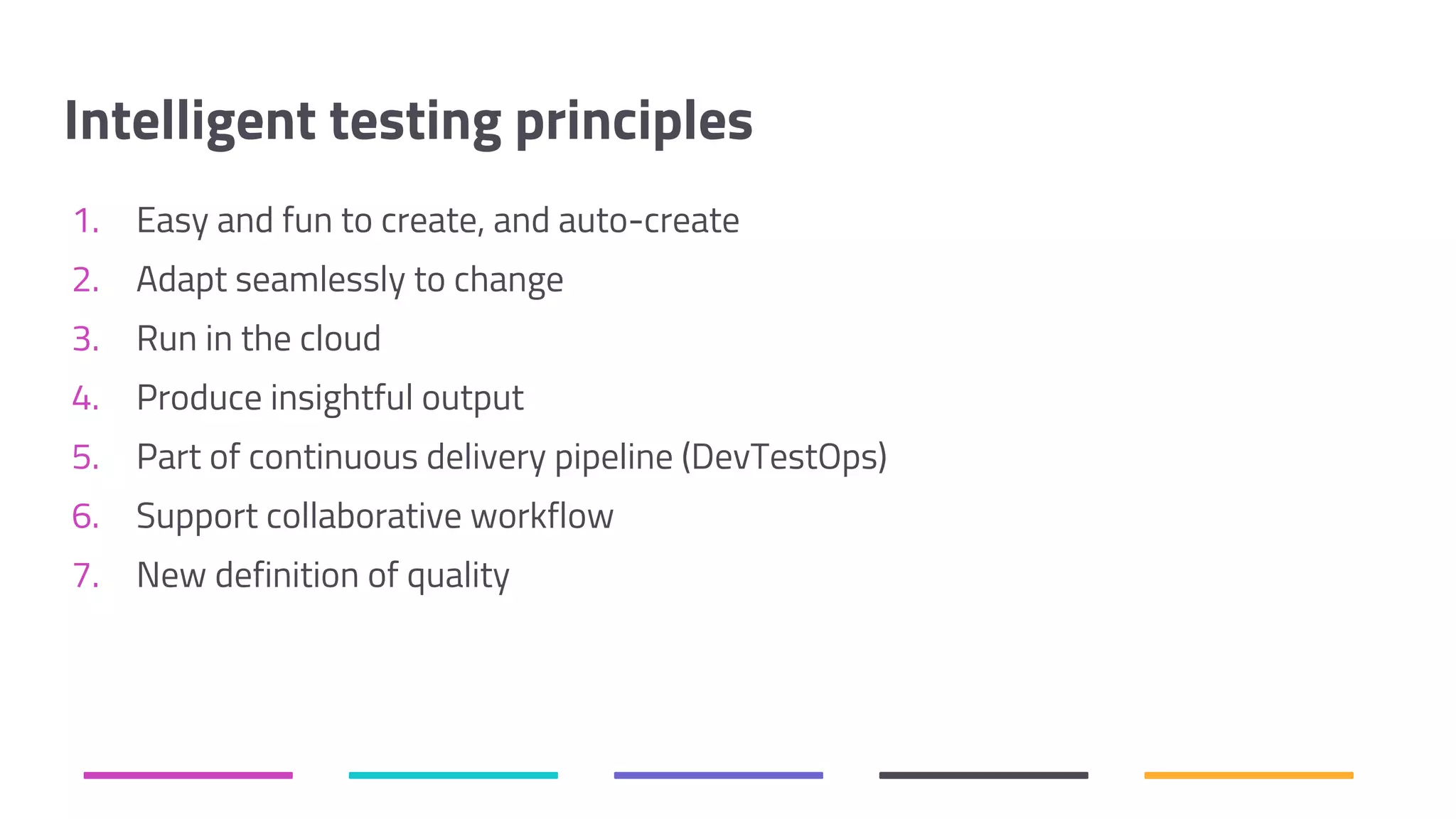
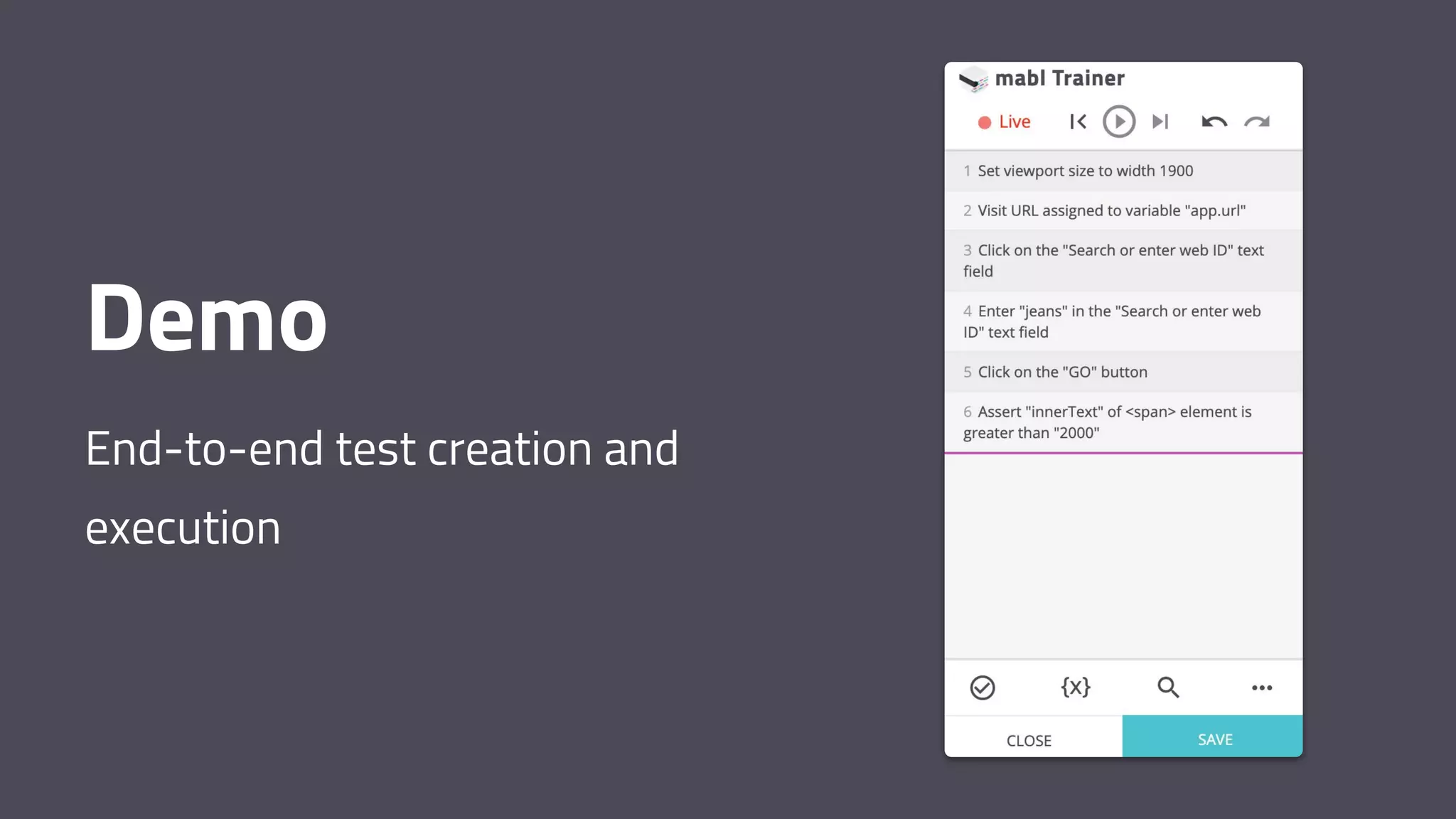
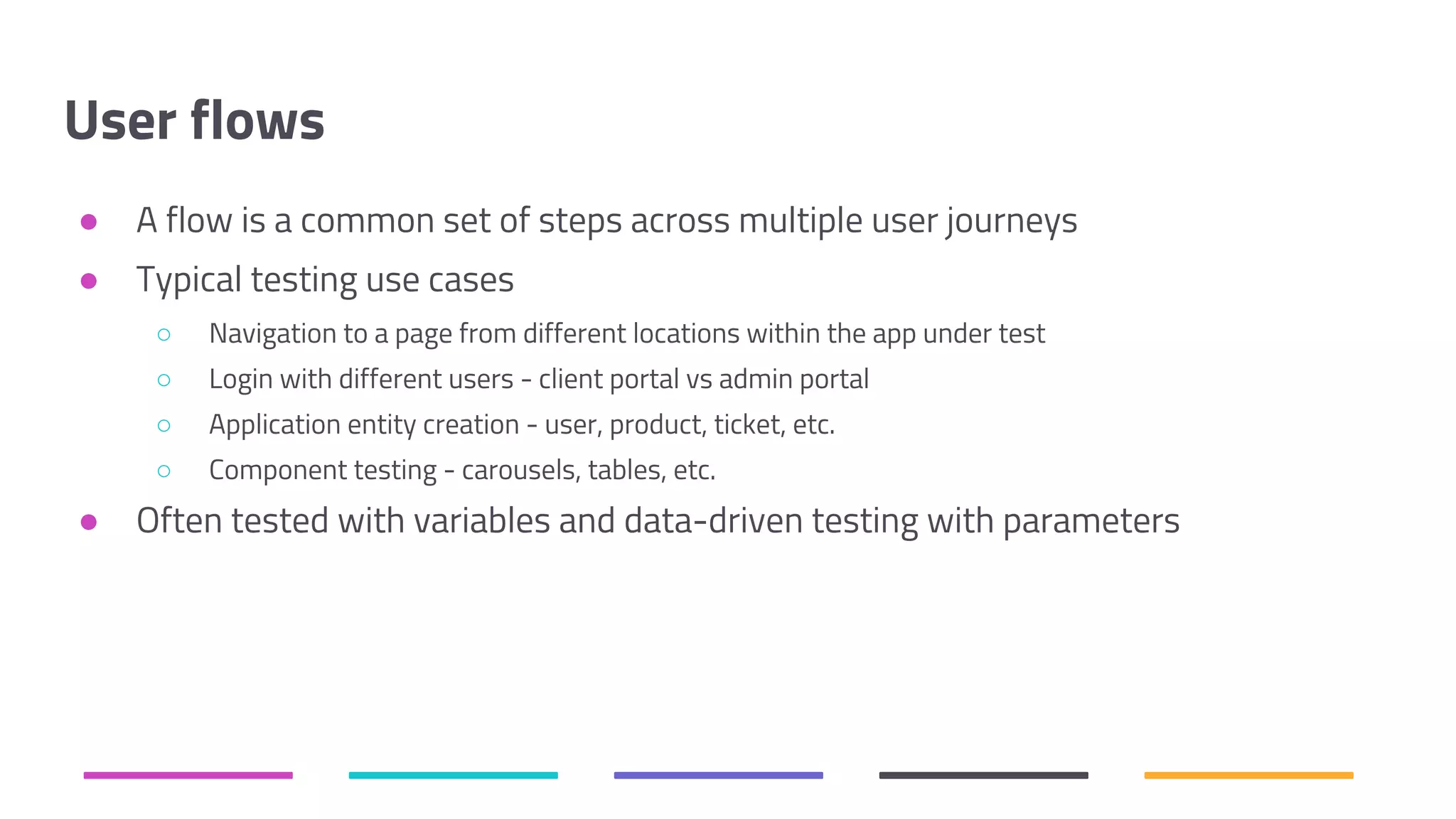
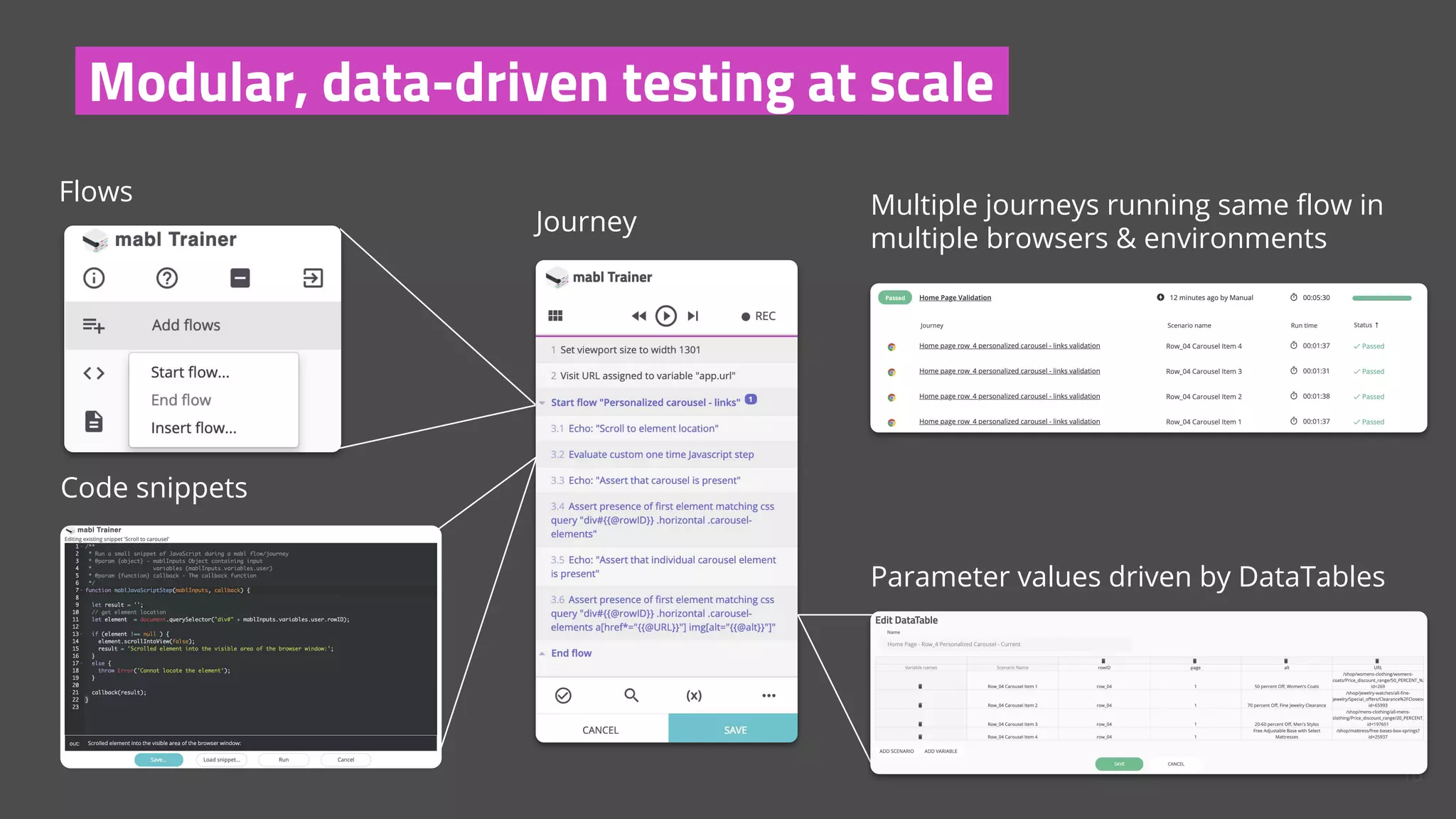
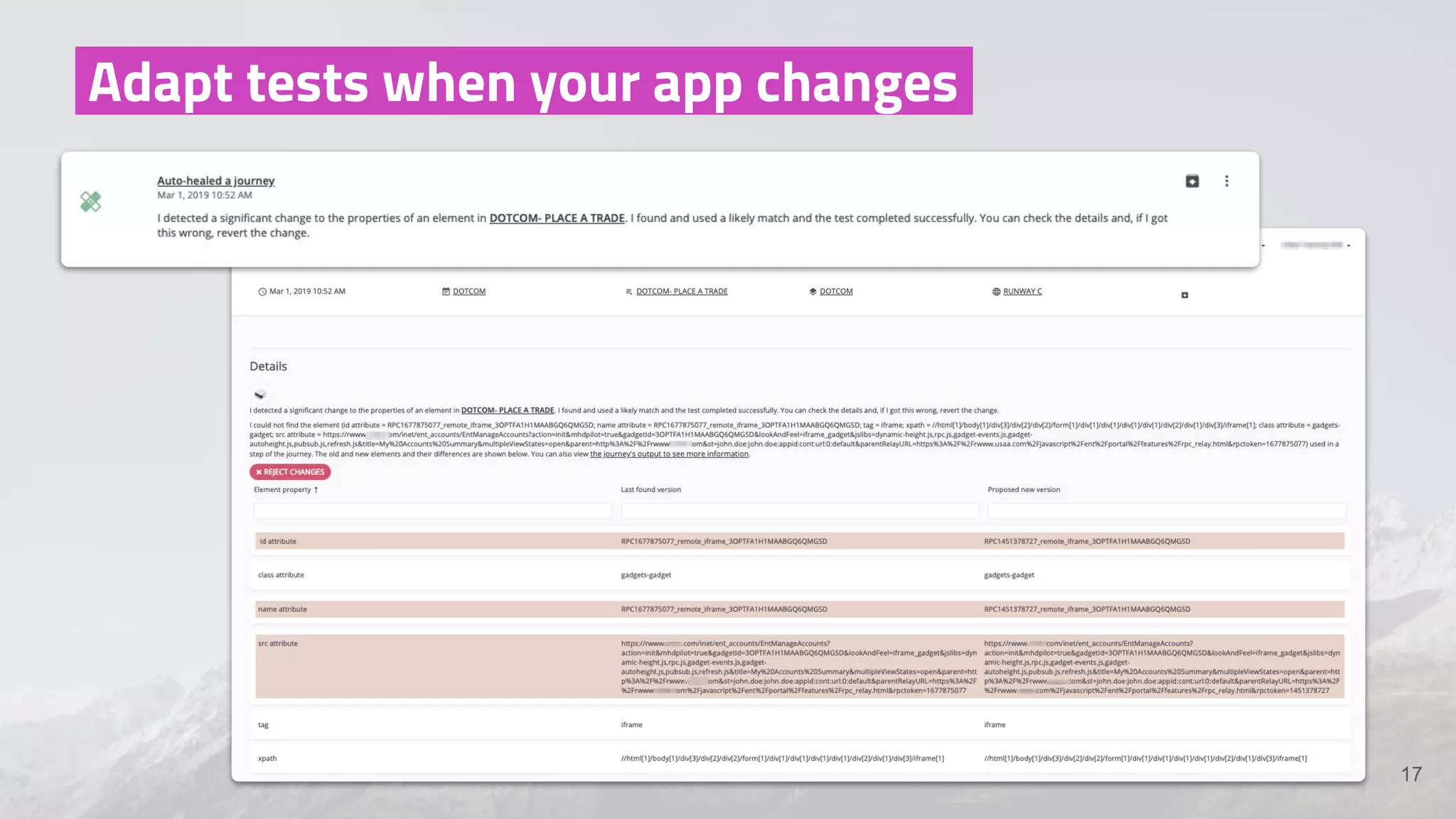
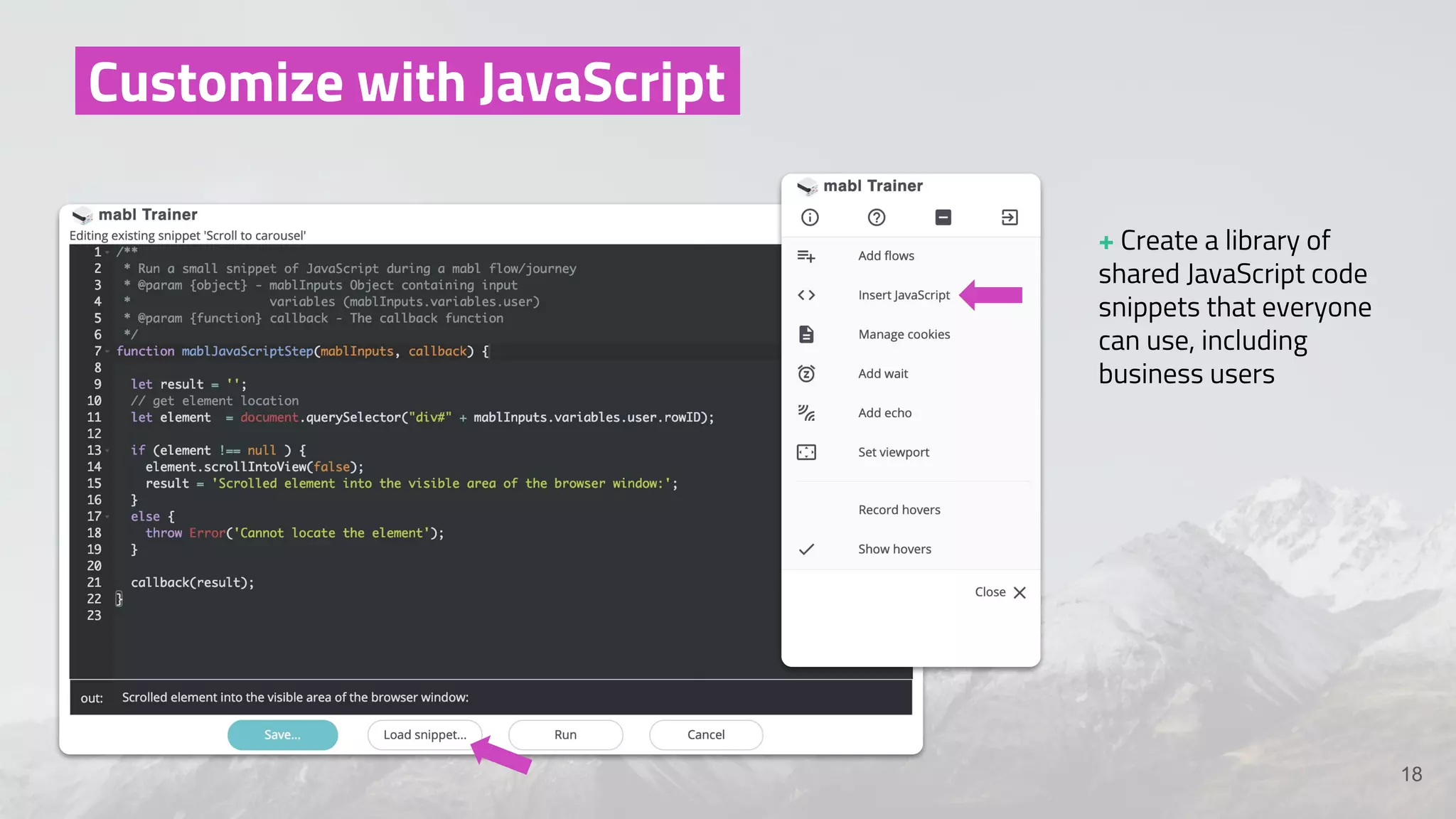
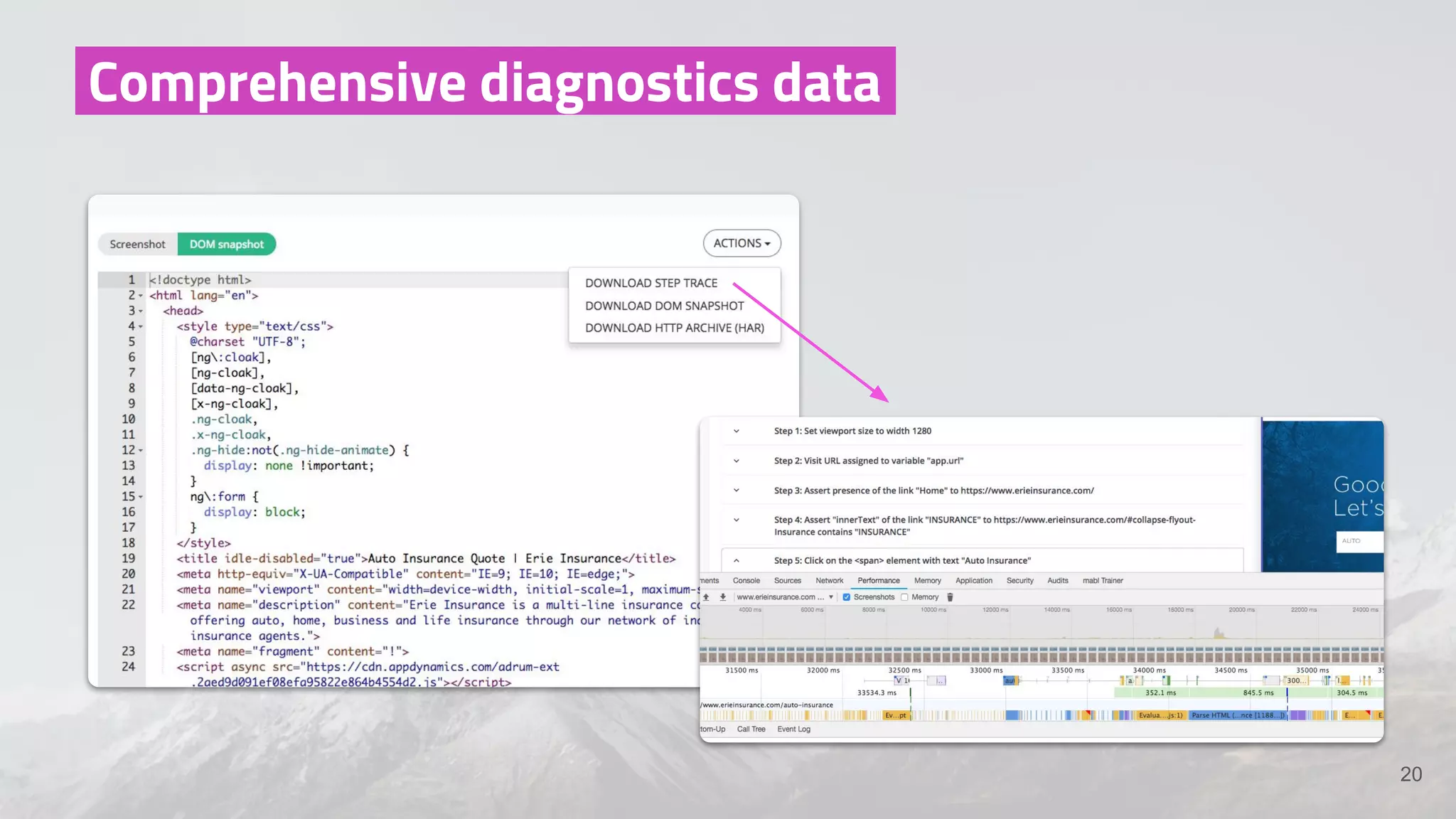
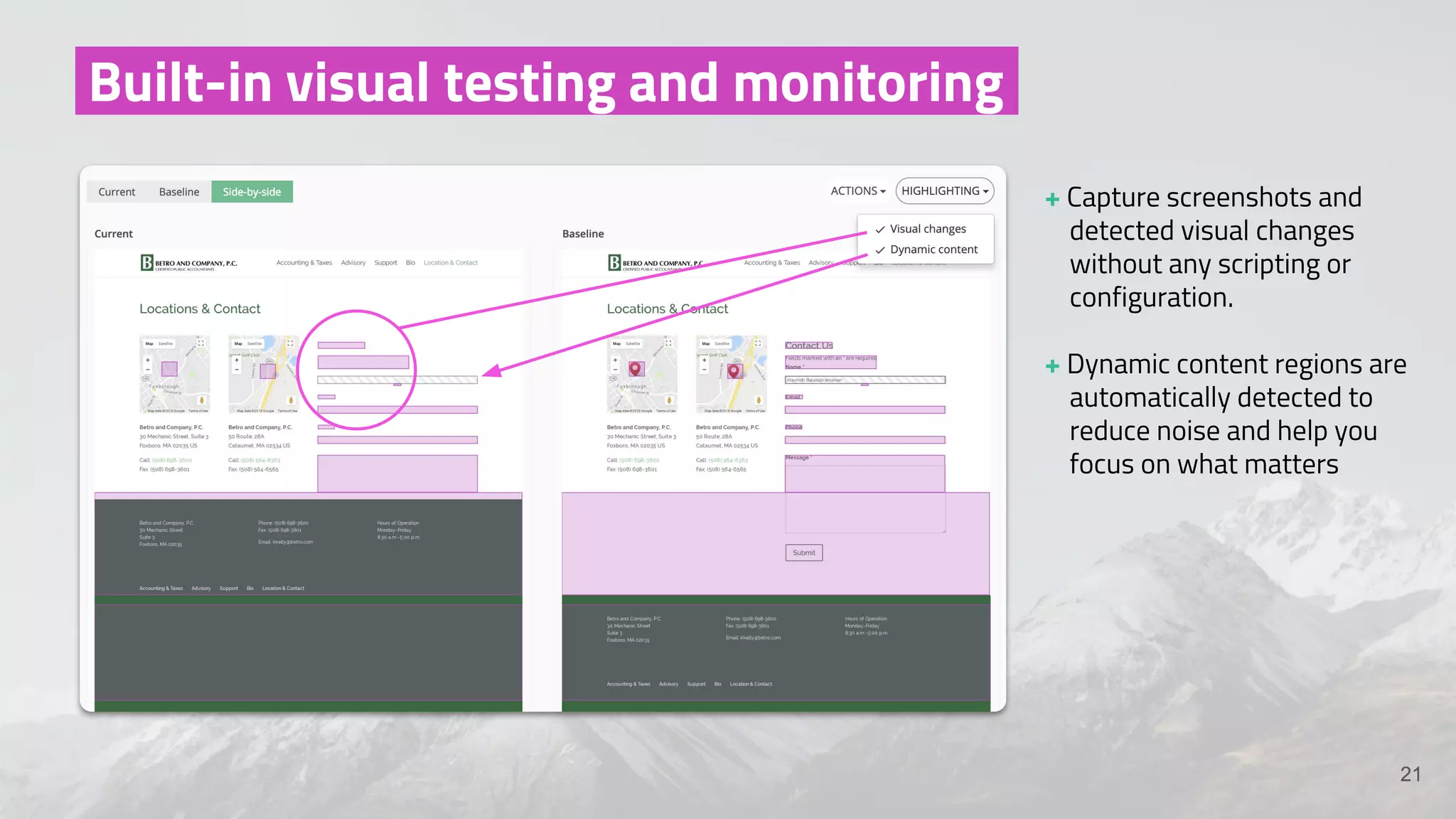
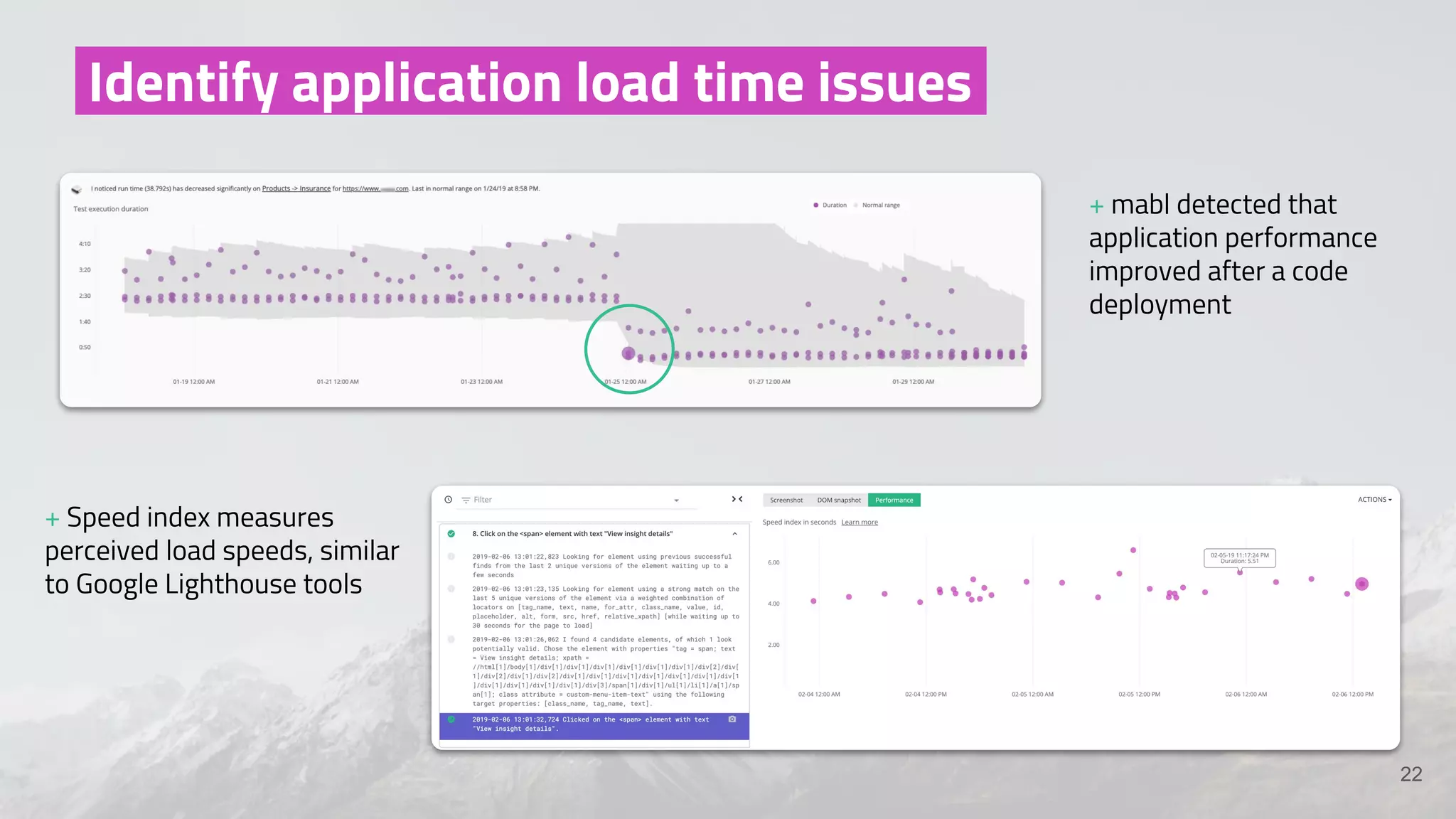
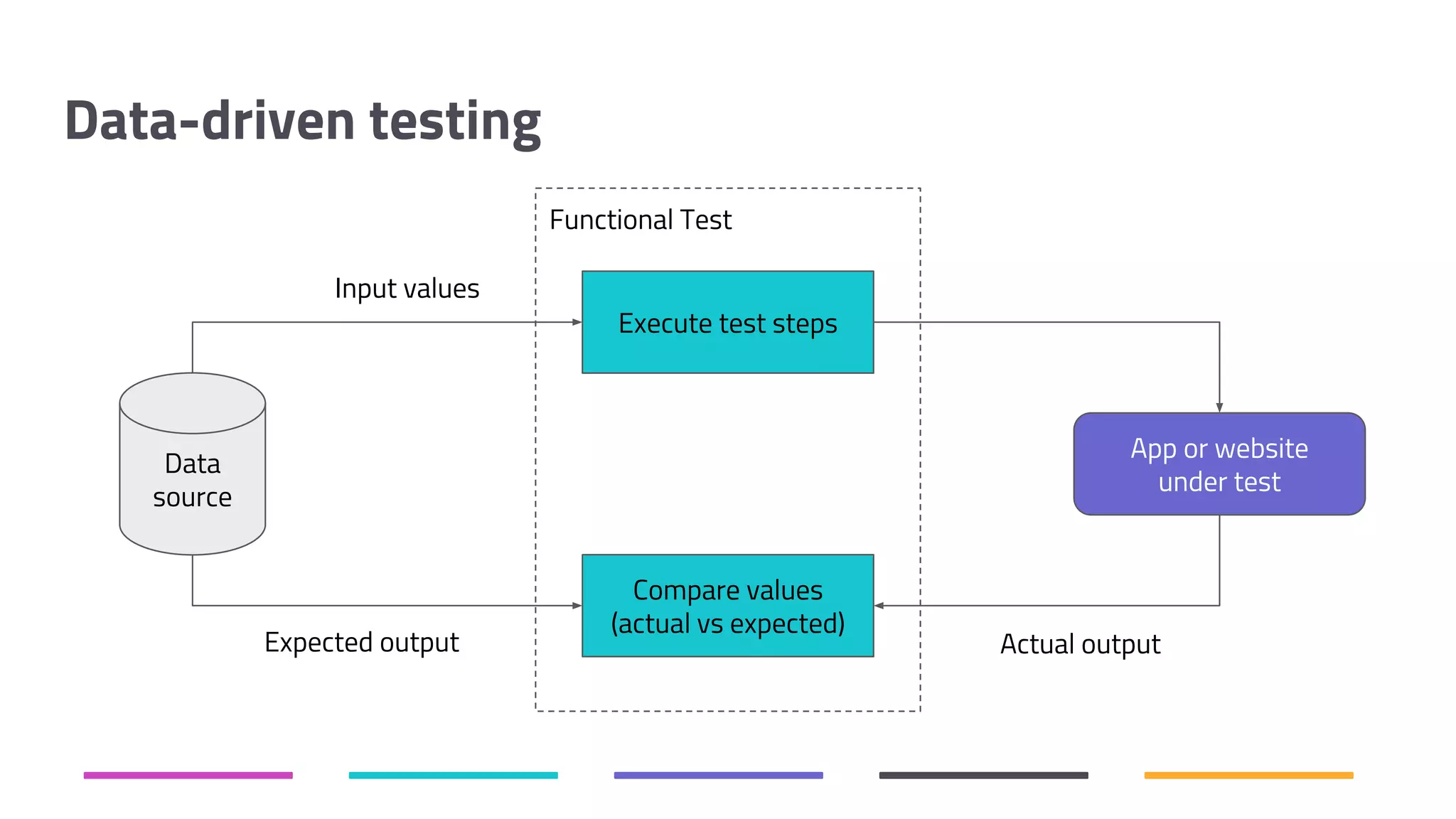
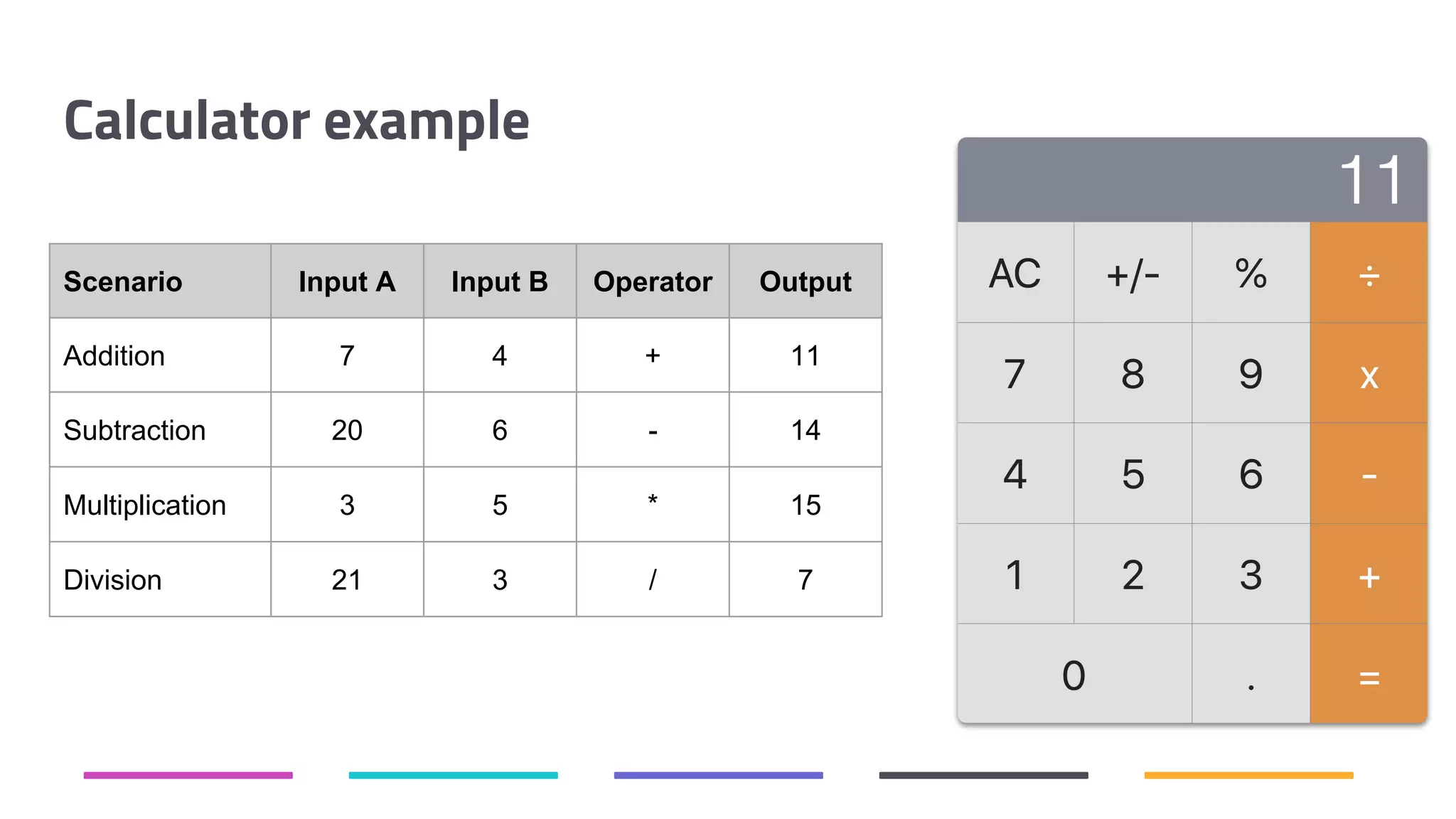
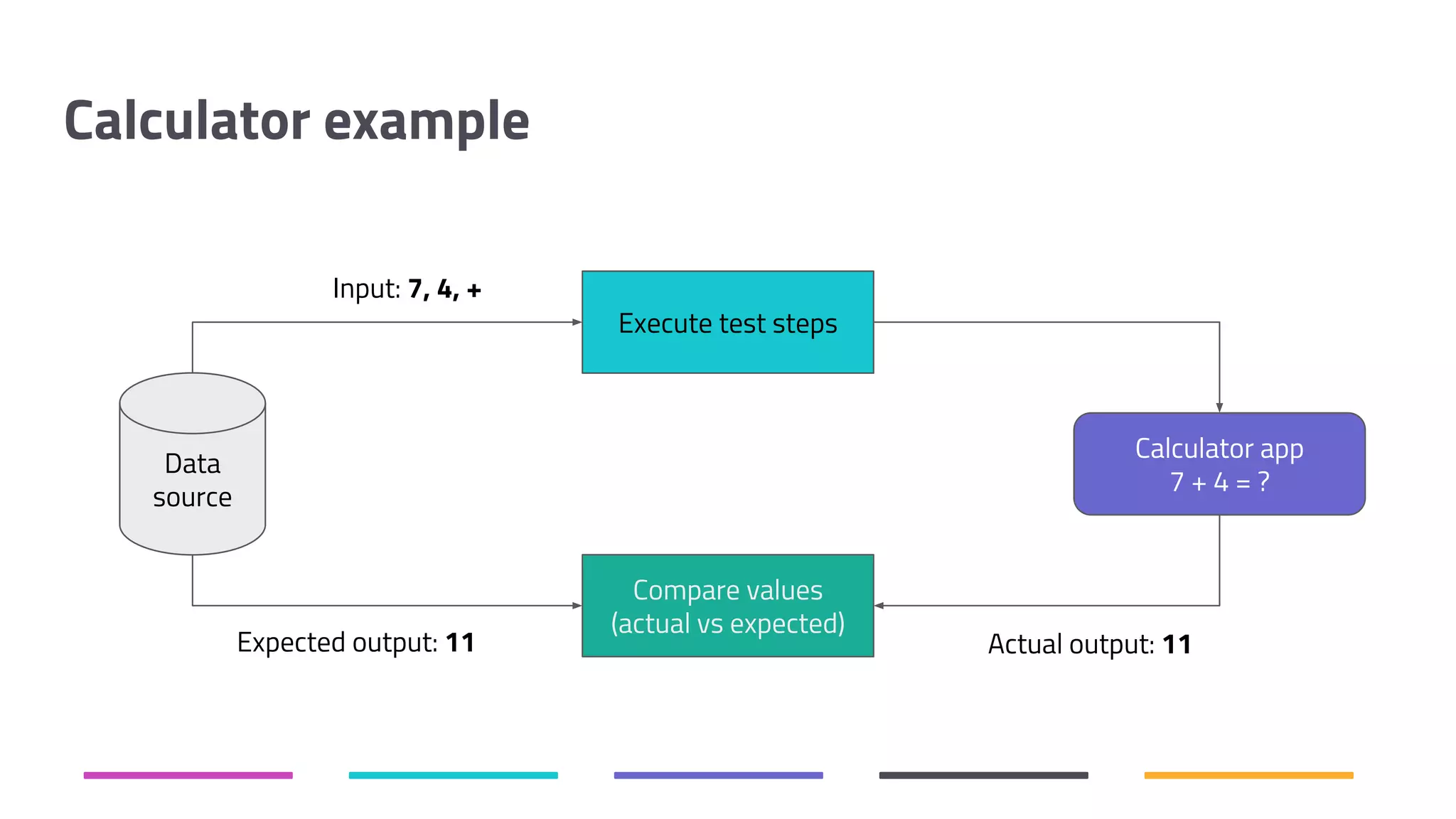
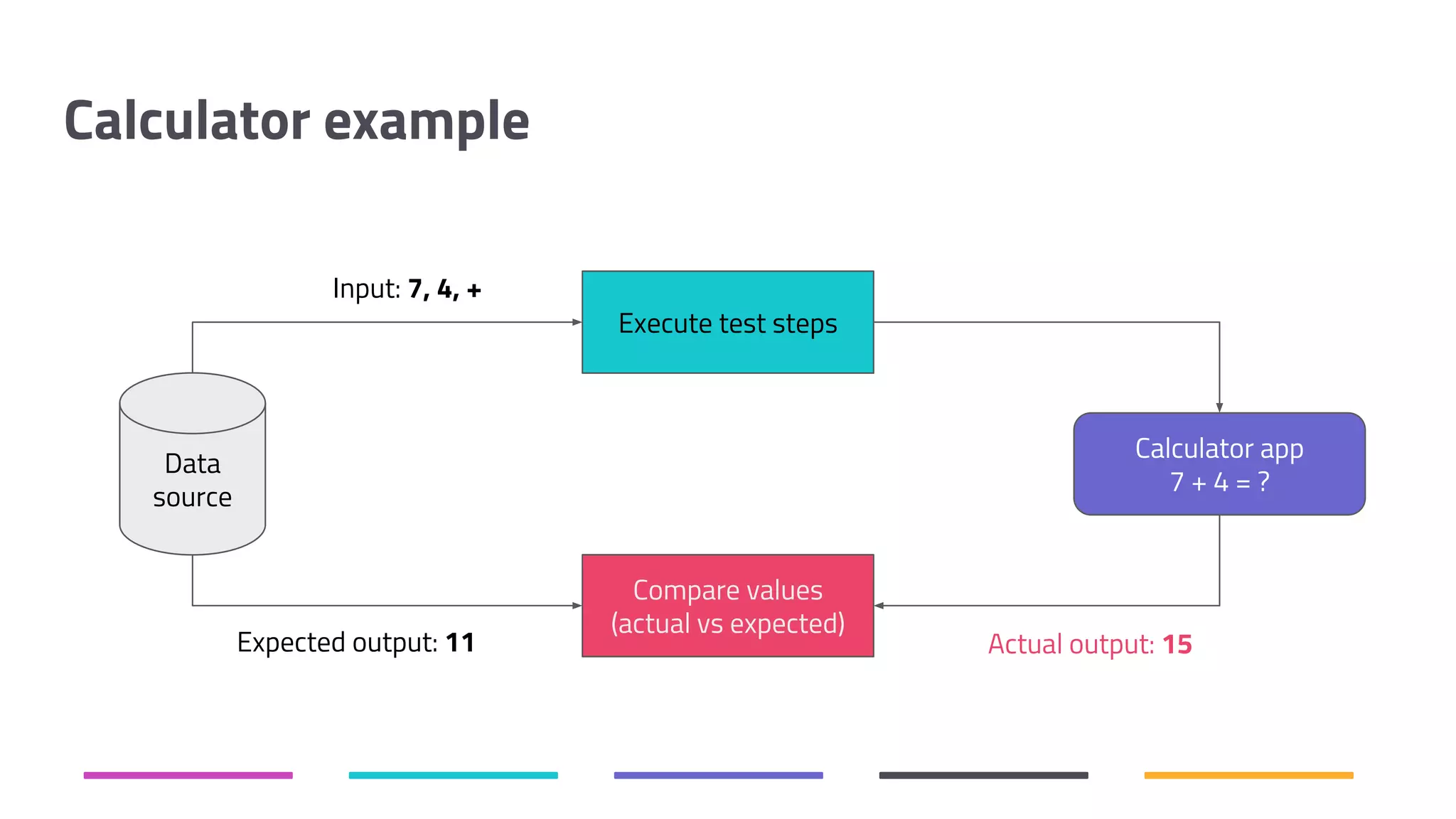
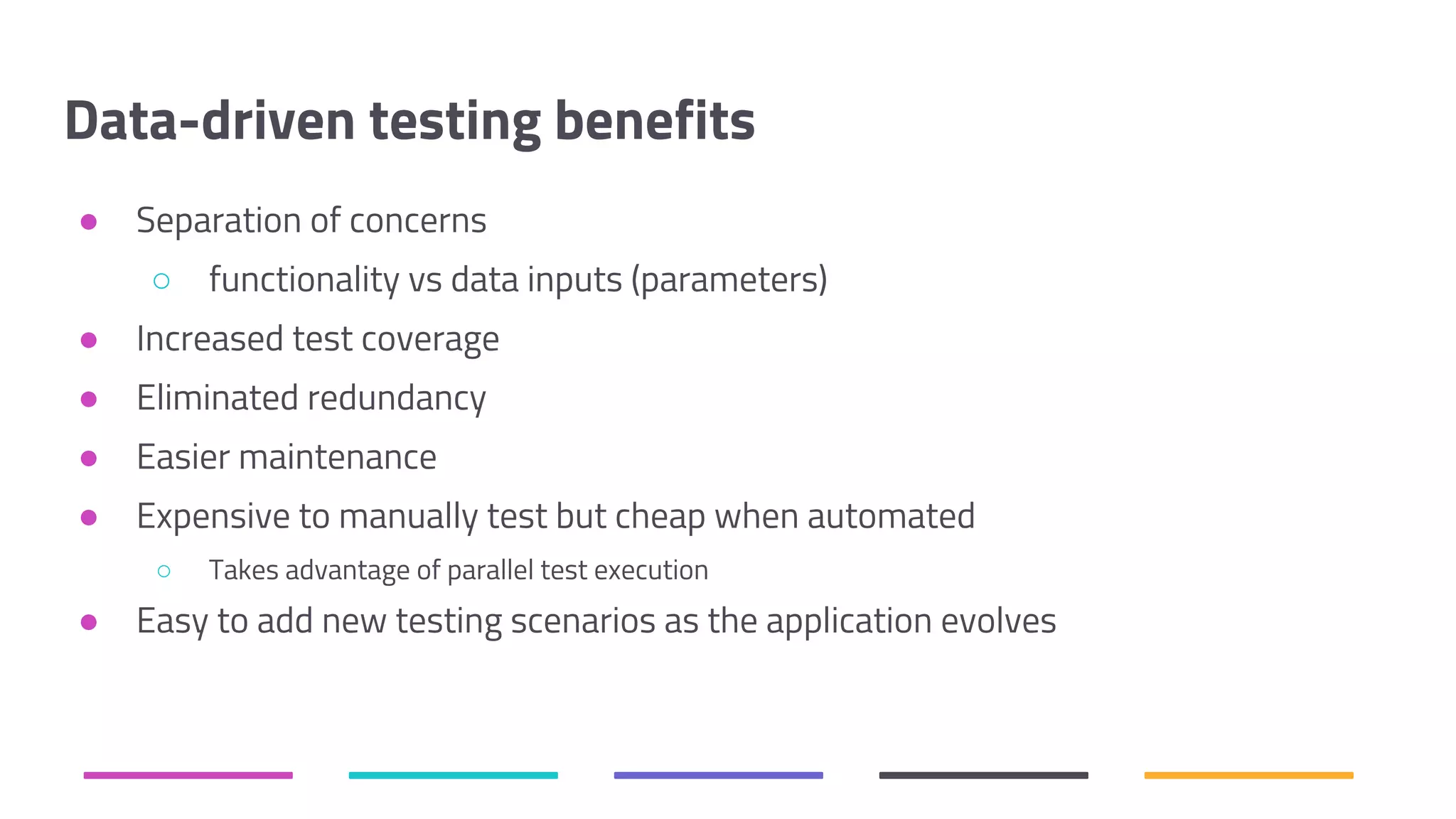
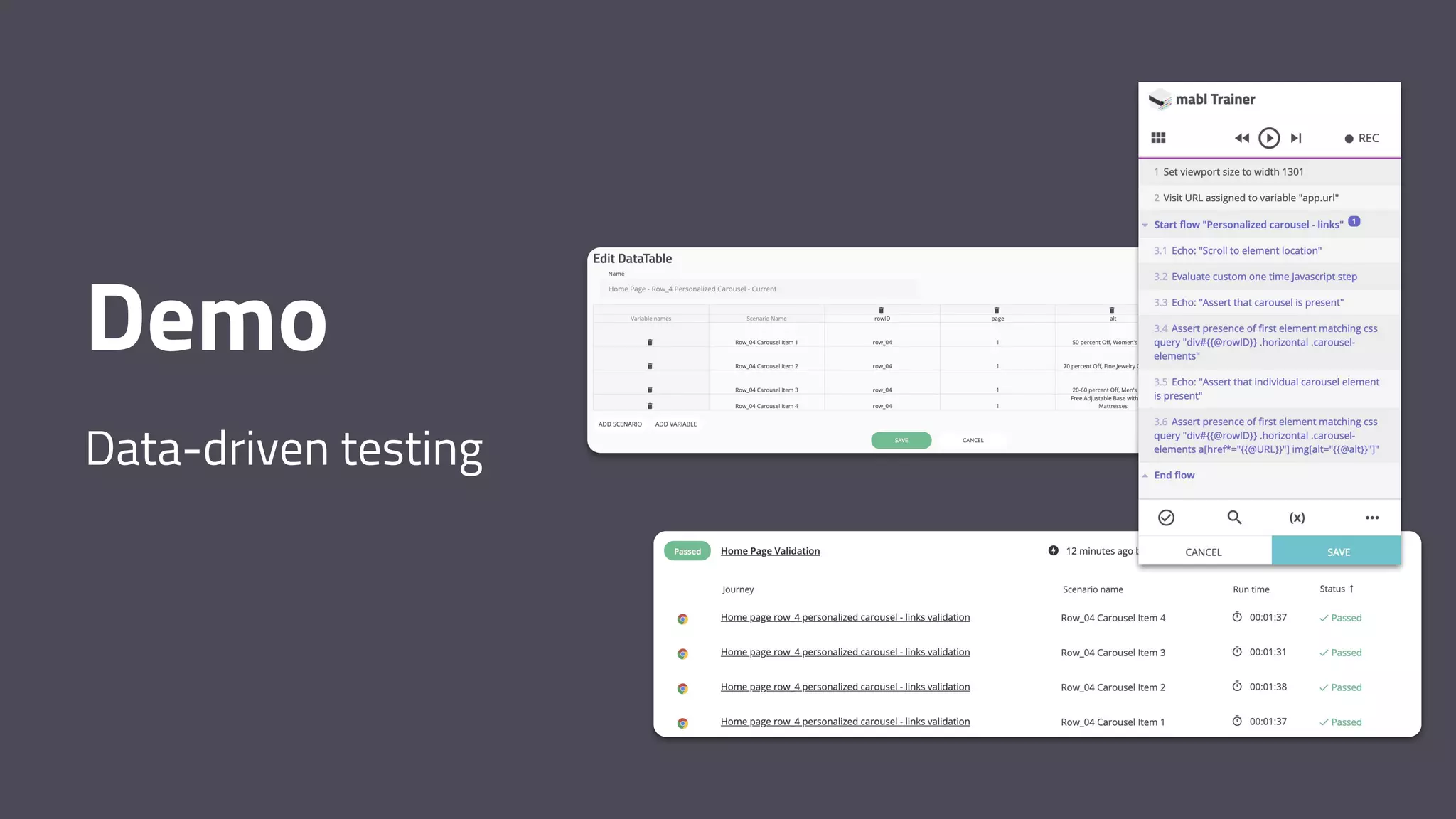
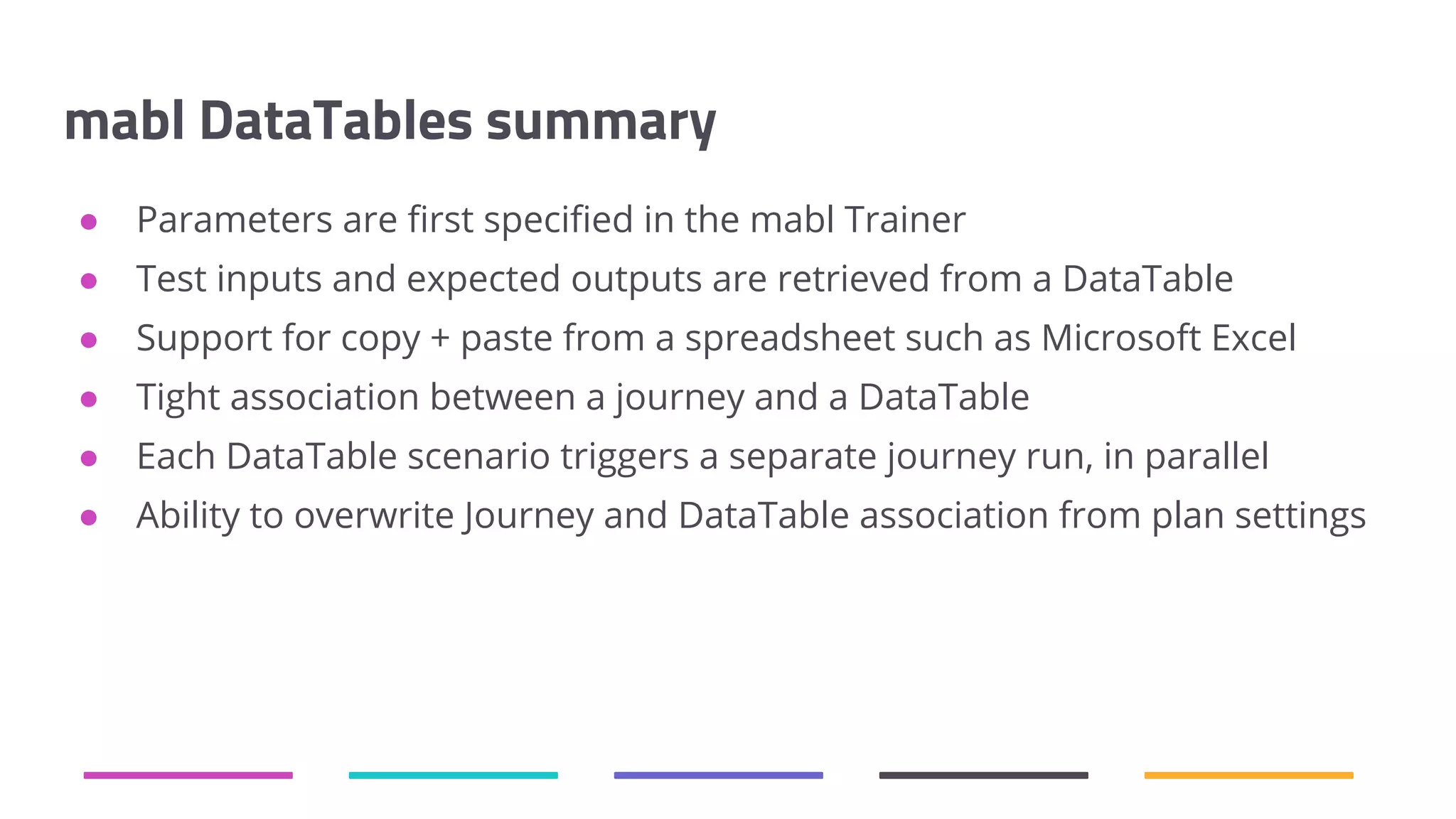
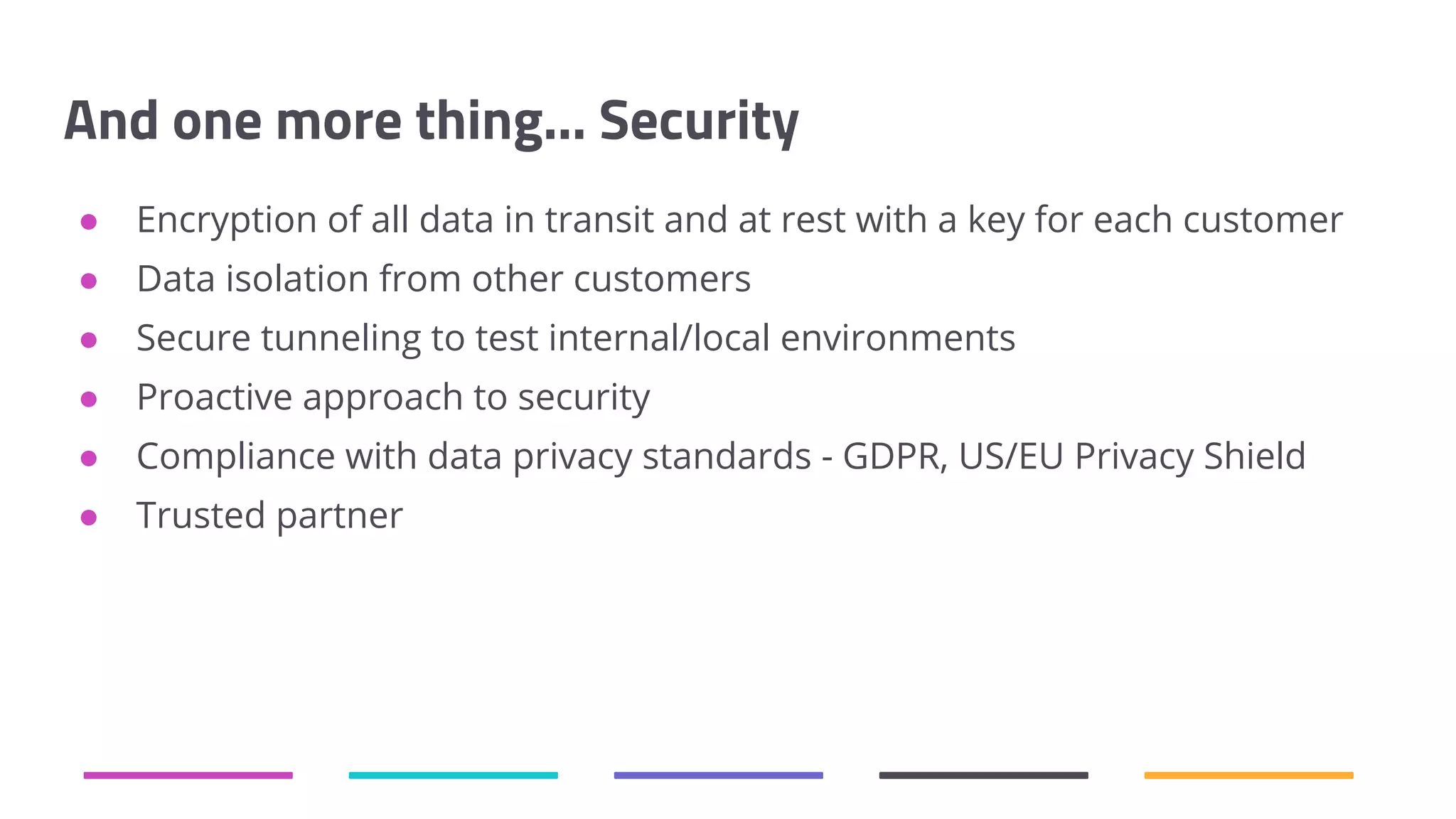
The document discusses the shift from traditional quality assurance to quality intelligence in the context of end-to-end test automation. It emphasizes the need for modular, data-driven testing within a continuous integration and deployment framework to enhance efficiency and reduce long lead times associated with legacy testing tools. Additionally, it highlights the importance of collaborative workflows and comprehensive diagnostics in the development process to ensure faster delivery of quality software.