After successful completion of this chapter, the students be able to:
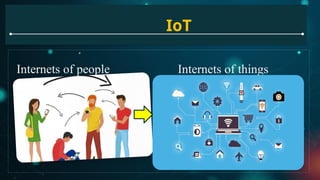
Explain IoT
Elaborate the advantages and disadvantages of IoT
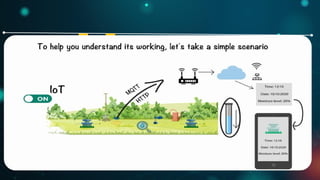
Explain how IoT works?
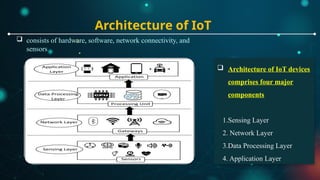
Explain the architecture of IoT
Describe IoT tools and platforms
Describe IoT application in different sector