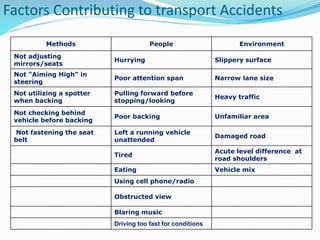
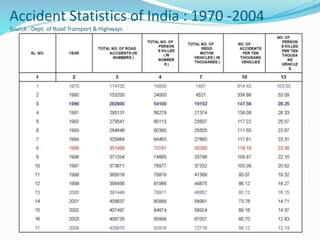
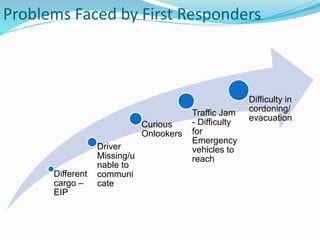
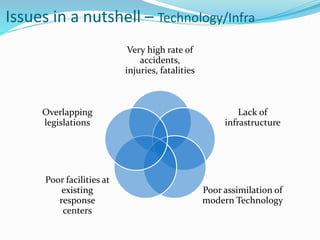
Emerging Technologies in Chemical Transportation & Emergency Response discusses technologies that can improve the transportation of hazardous chemicals and emergency response. It notes that chemical transportation accidents can cause fires, explosions and toxic releases. It then provides examples of technology solutions like GPS tracking, GIS mapping of routes and response centers, advanced emergency response vehicles and equipment, and training programs to reduce accidents and improve coordination during emergencies. Administrative solutions are also proposed, such as harmonizing rules and collecting accident data to enhance safety.