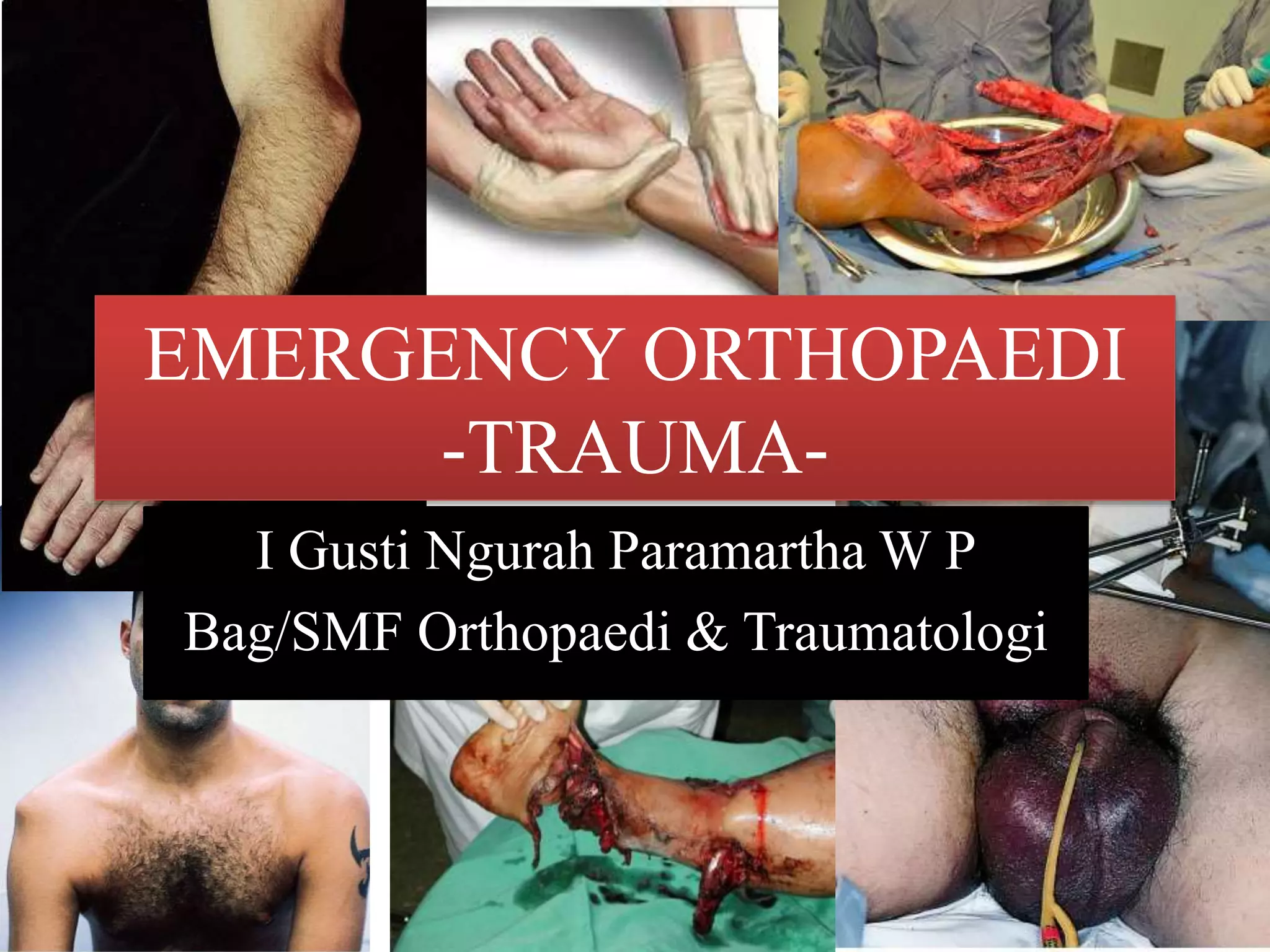
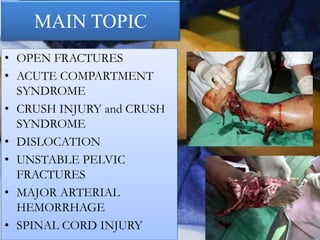
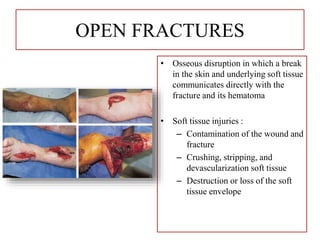
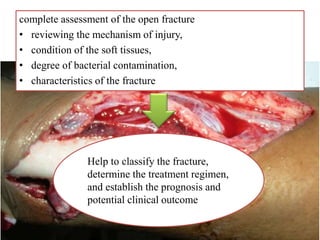
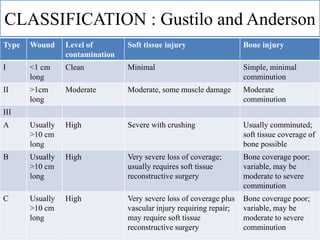
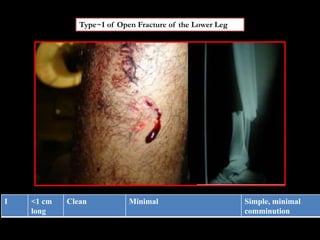
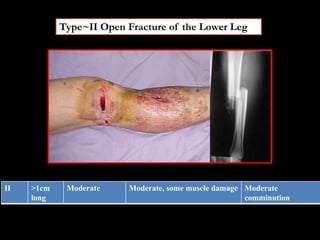
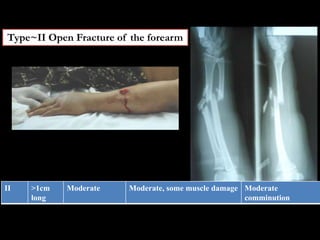
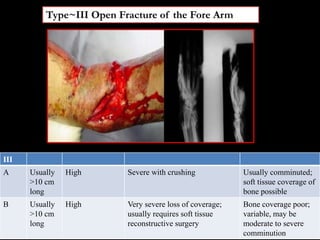
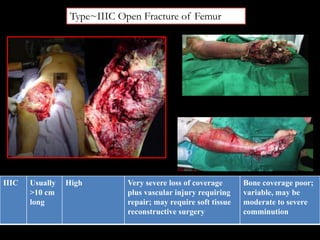
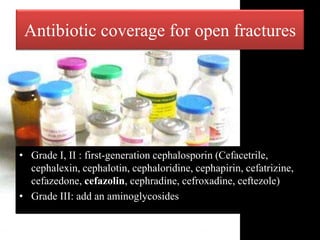
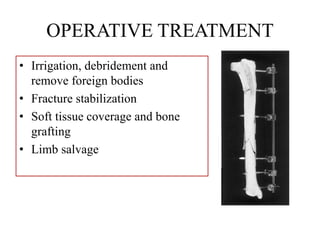
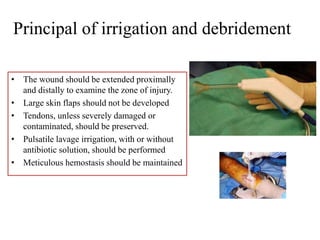
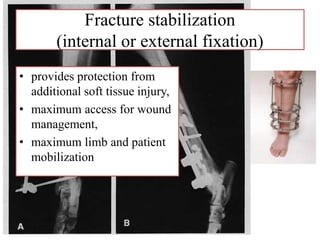
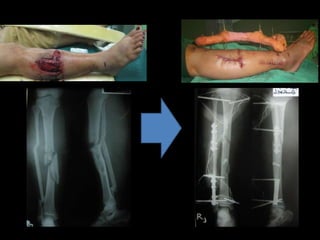
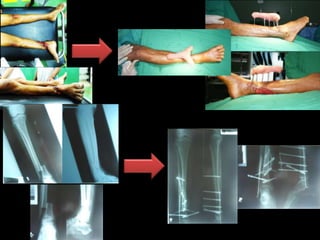
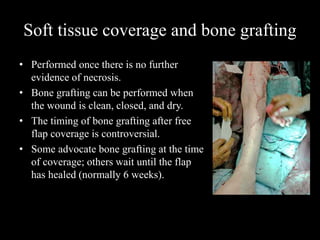
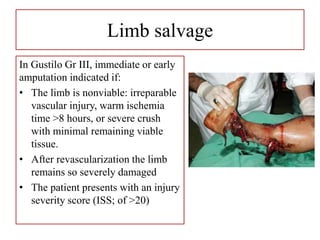
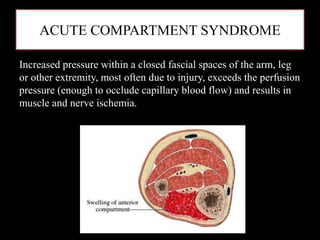
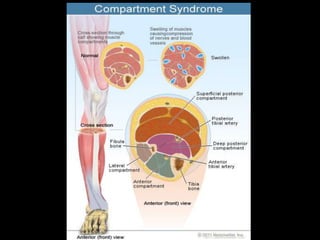
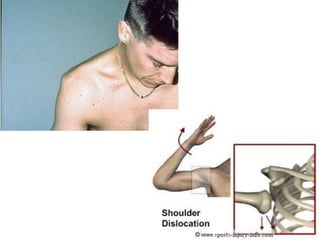
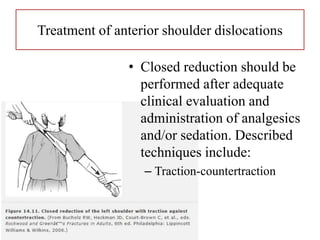
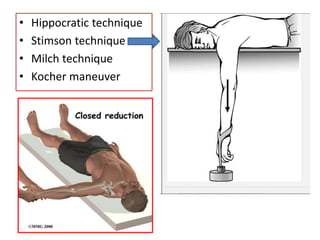
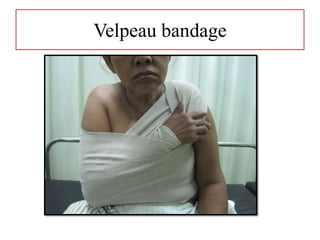
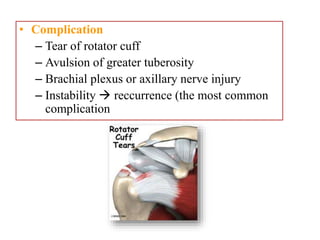
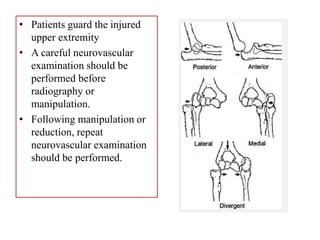
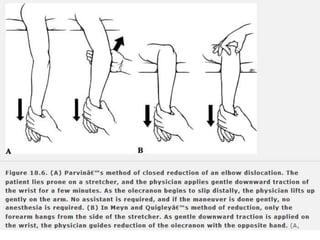
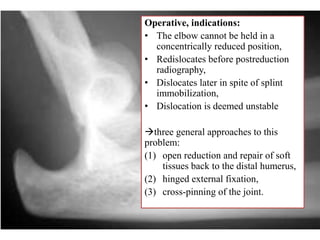
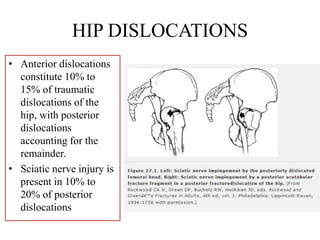
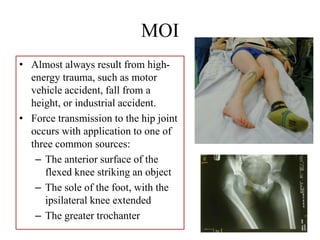
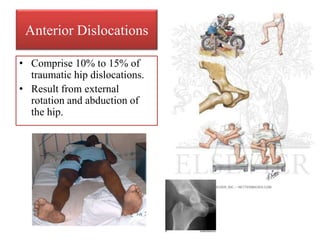
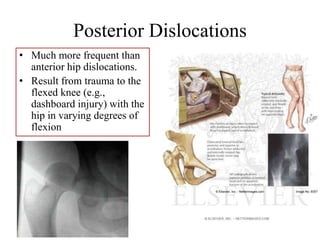
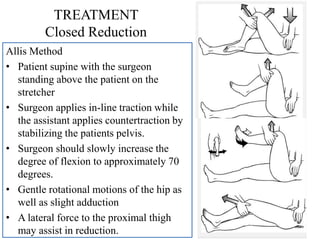
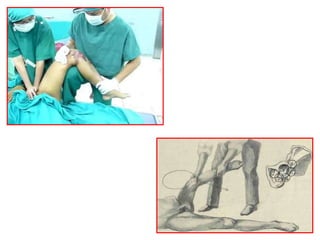
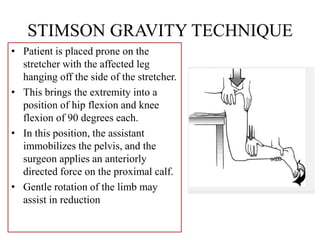
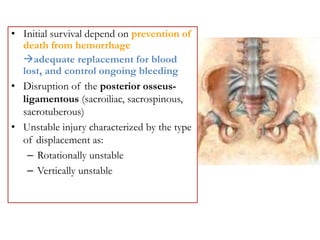
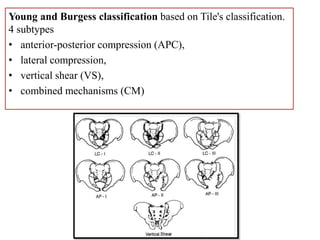
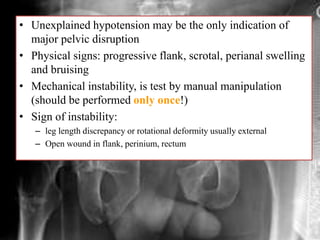
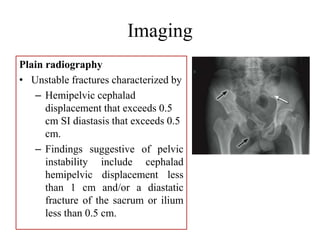
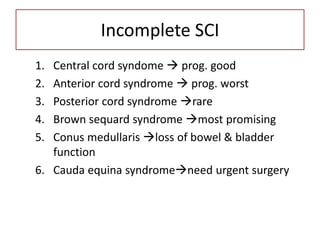
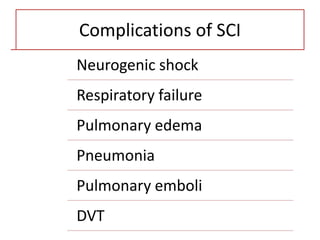
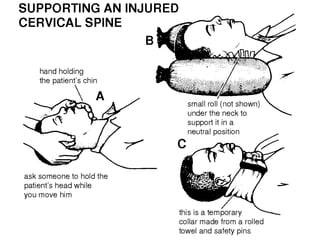
- Stabilizes the pelvis
Surgeon:
- Applies gentle traction and internal
rotation to the leg
- May also apply gentle adduction
- Reduction occurs through gravity
assisted positioning
�Open Reduction
Indications:
- Failed closed reduction
- Associated fractures
- Interposition of soft tissues
- Delayed presentation
- Hip dislocations in children
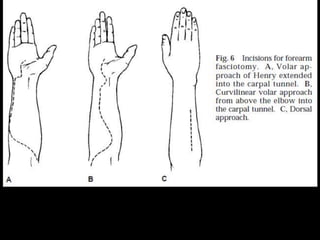
Approaches:
- Anterolateral (Watson-Jones)
- Posterior (Kocher-Langenbeck)
- Lateral (Hardinge)
Goals:
- Anatomic reduction
- Stability
- Preservation of blood supply
- Early mobilization
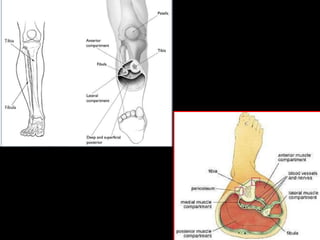
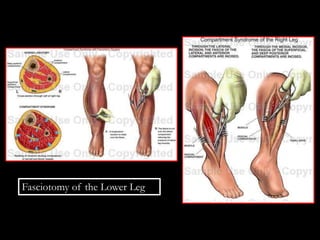
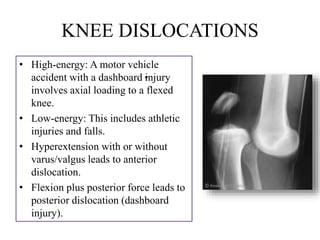
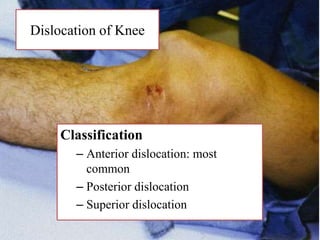
�KNEE DISLOCATION