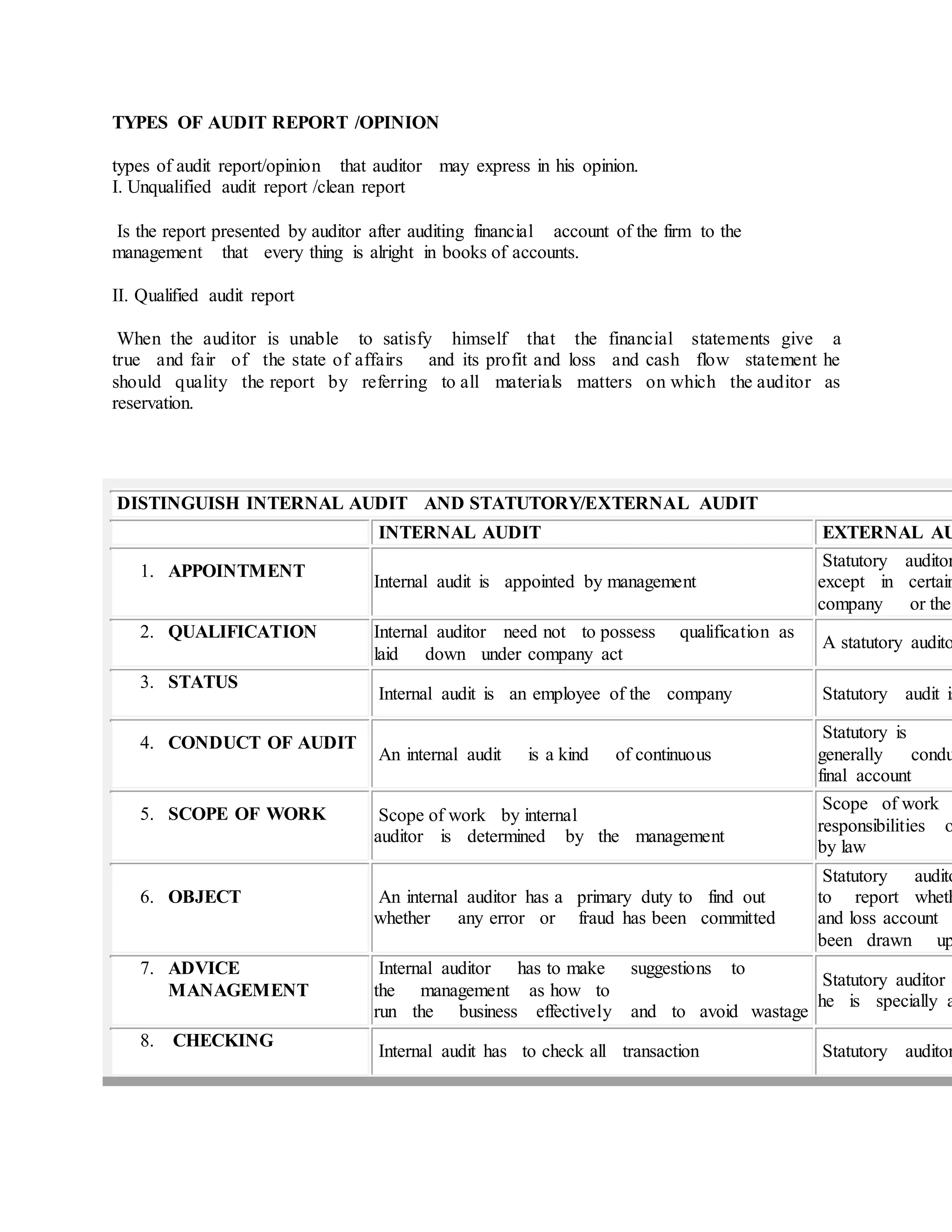
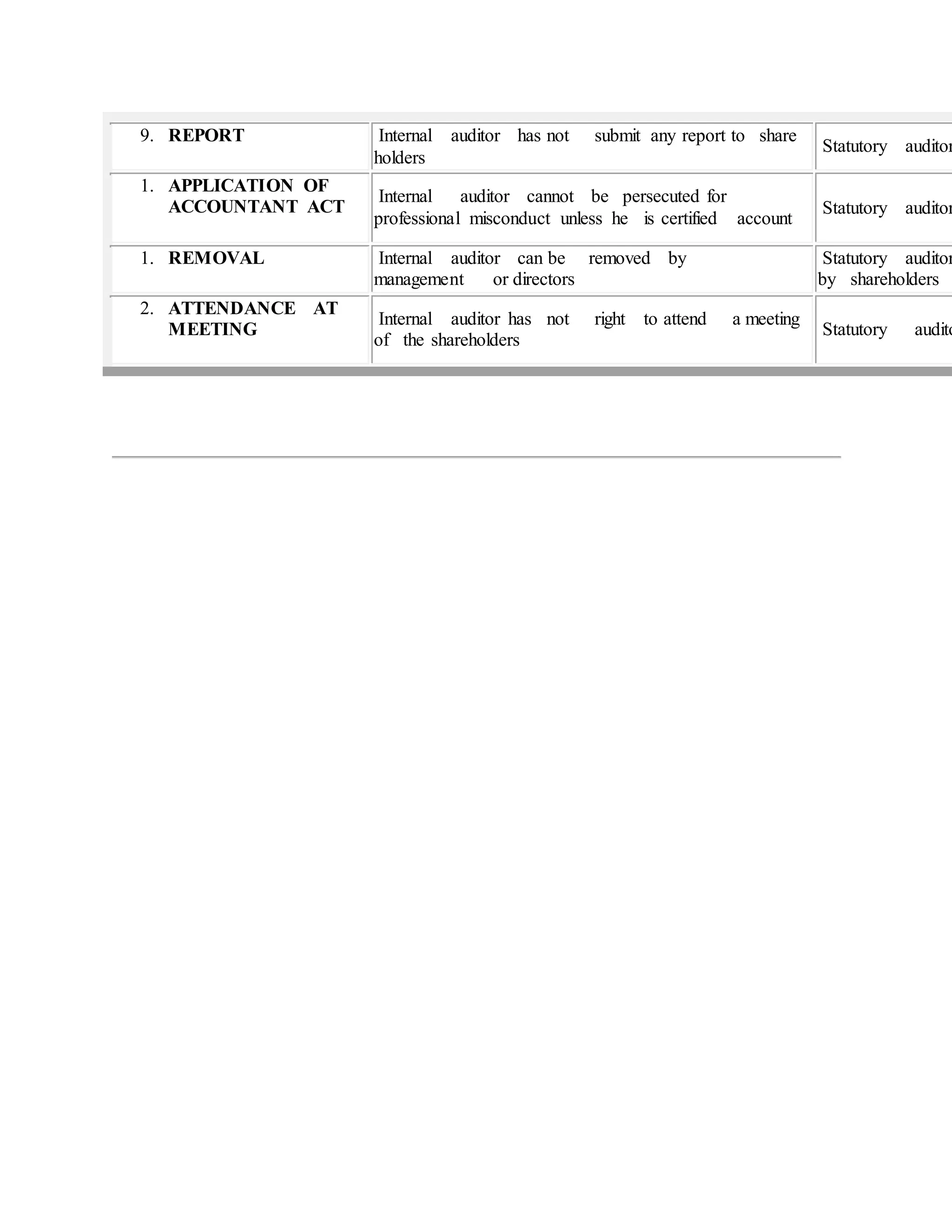
The document provides an extensive overview of auditing, detailing its definition, objectives, types of audits, and the qualifications and duties of auditors. It distinguishes between internal and external audits, outlining the roles and responsibilities of auditors, including the assessment of financial statements and the requirement for independence. Additionally, it highlights the internal control systems and processes necessary to ensure accuracy and accountability within an organization.