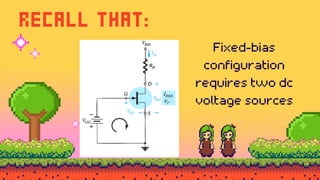
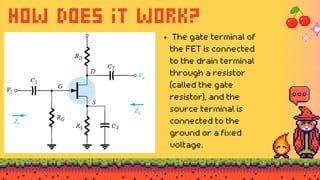
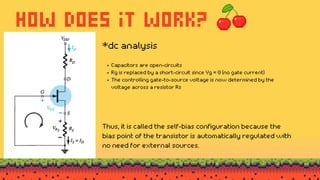
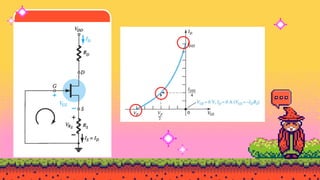
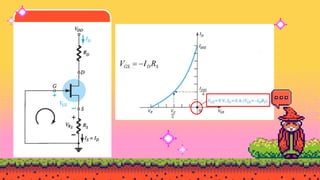
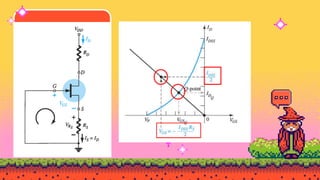
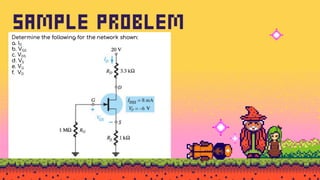
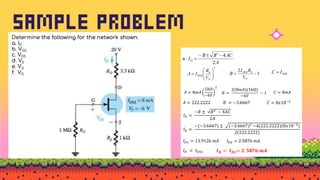
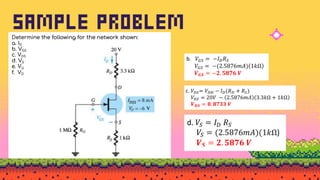
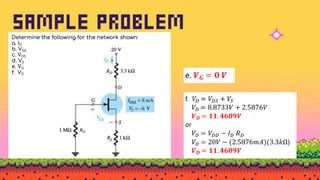
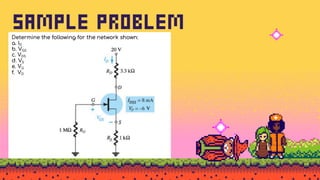
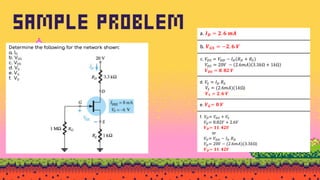
The document explains FET biasing, focusing on self-bias configuration which requires only one voltage source, as opposed to fixed-bias configuration that requires two. It describes how this configuration automates the regulation of the transistor's bias point using gate resistors and DC analysis. Mathematical and graphical approaches to determine the quiescent point (Q-point) are also outlined, along with references for further reading.