Embed presentation


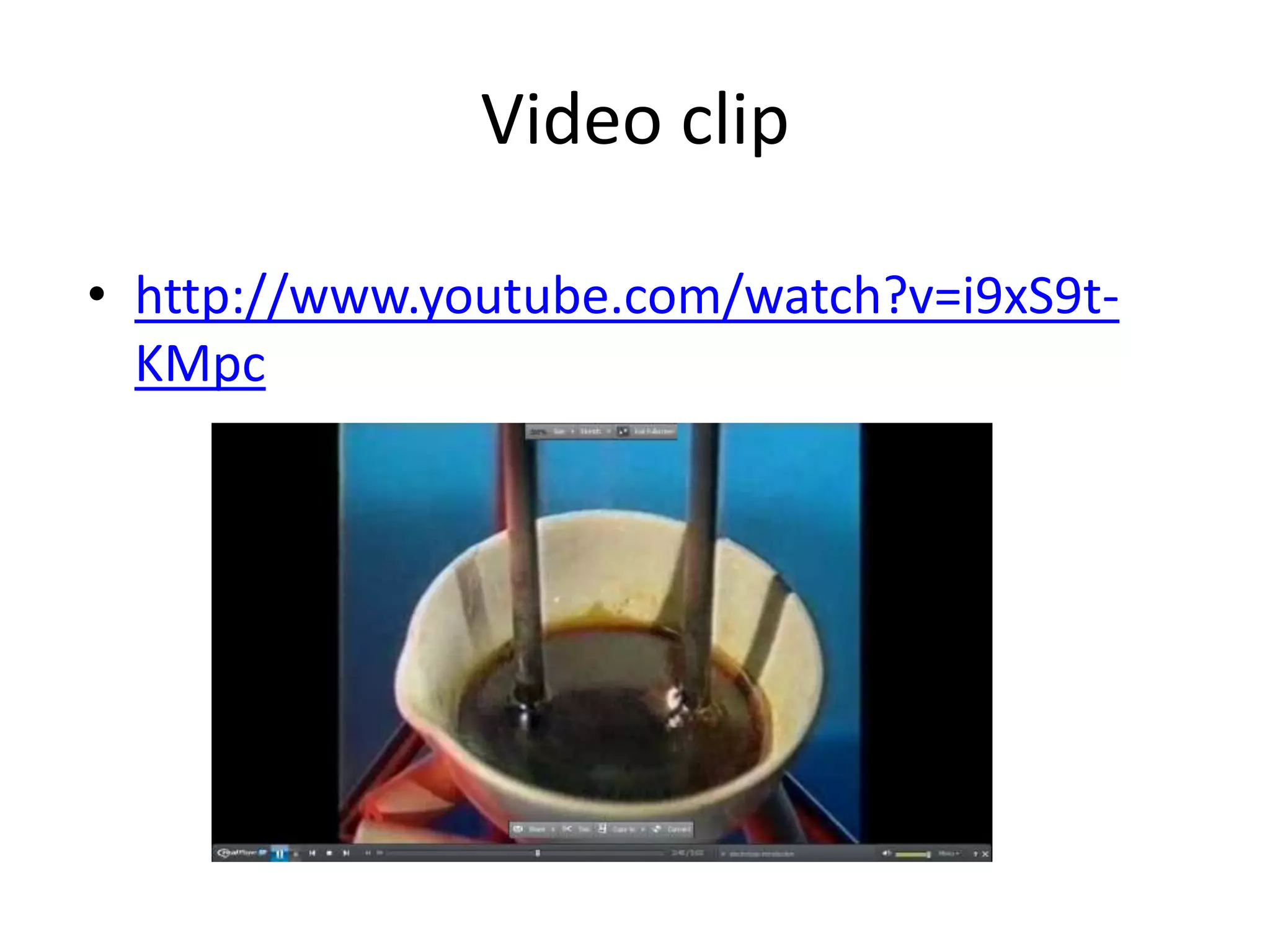
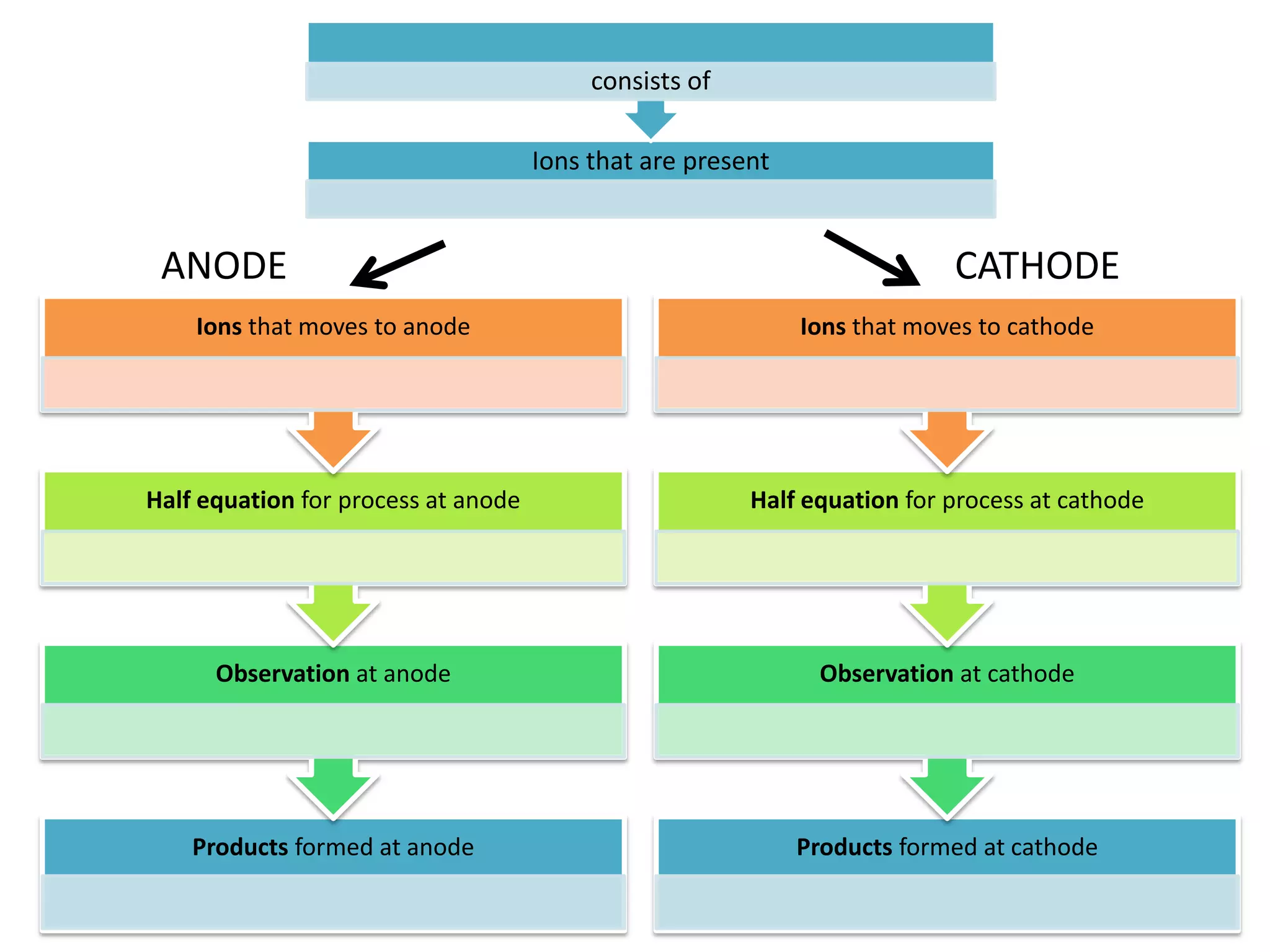
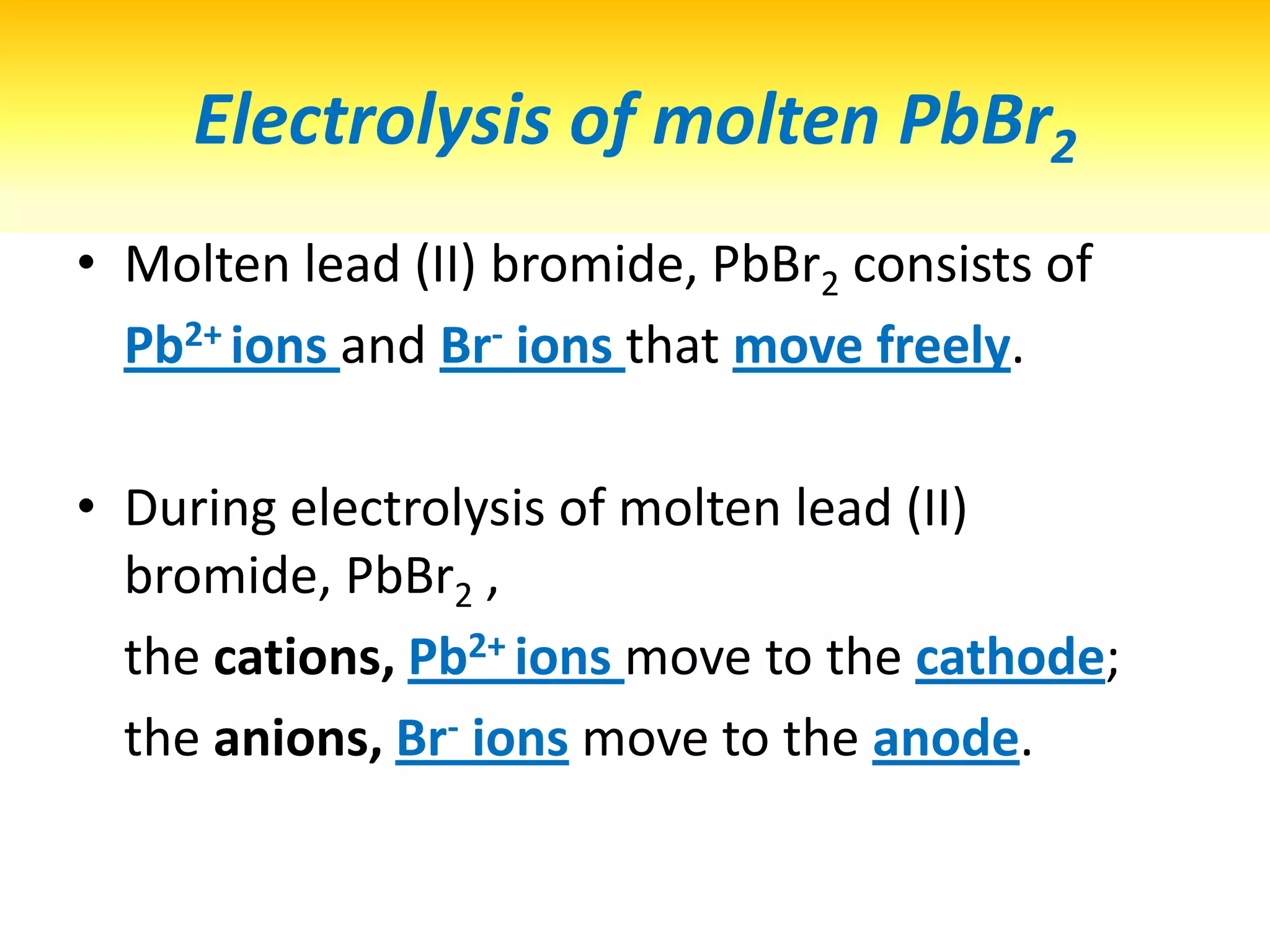


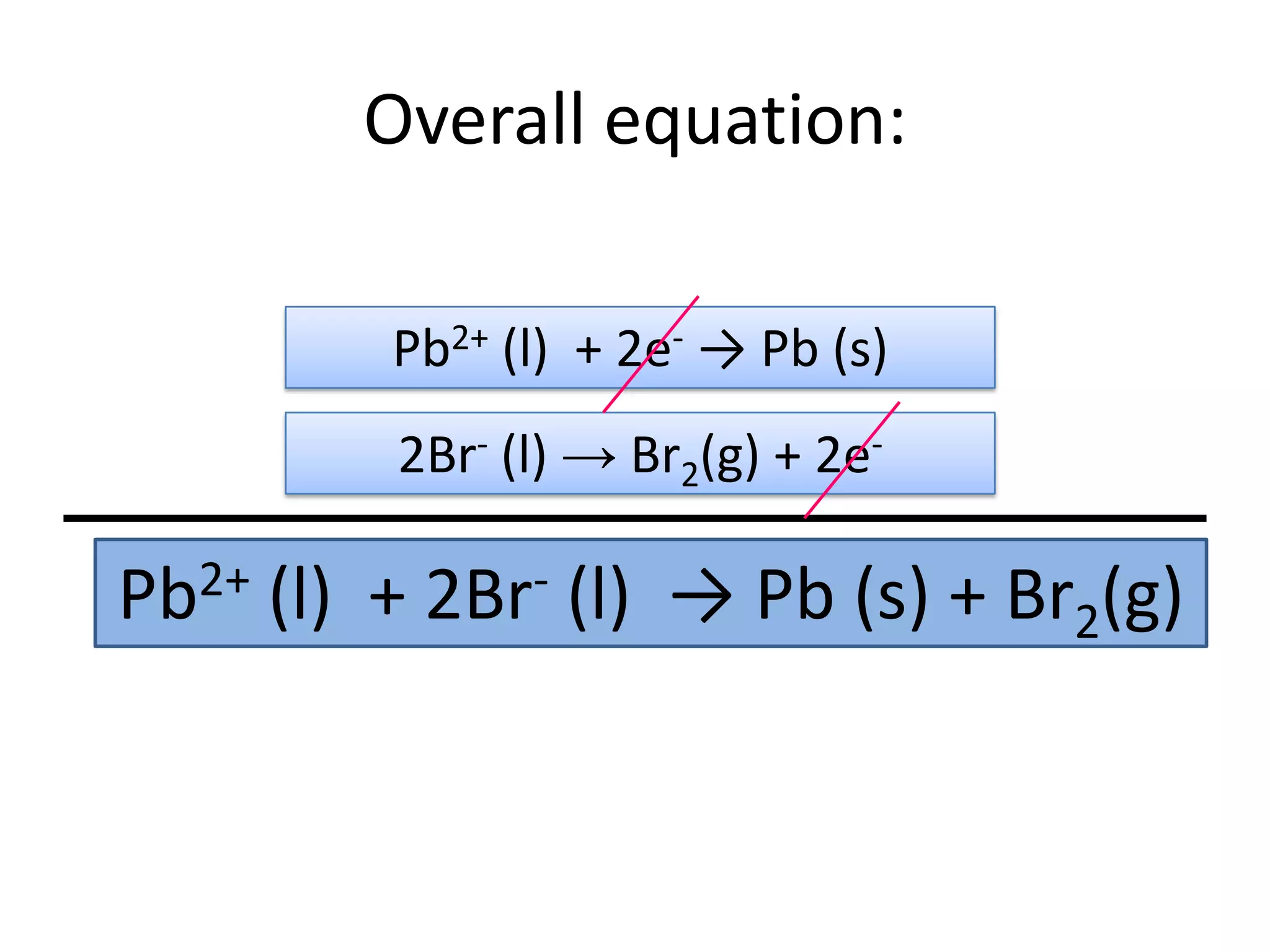

1) Electrolysis of molten compounds involves passing an electric current through a molten compound, causing its ions to migrate to the electrodes. 2) During electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide (PbBr2), the Pb2+ ions migrate to the cathode, where they gain electrons and deposit as metallic lead. Meanwhile, the Br- ions migrate to the anode, where they lose electrons and form a bromine gas product. 3) The overall reaction is the decomposition of PbBr2 into lead metal and bromine gas.









