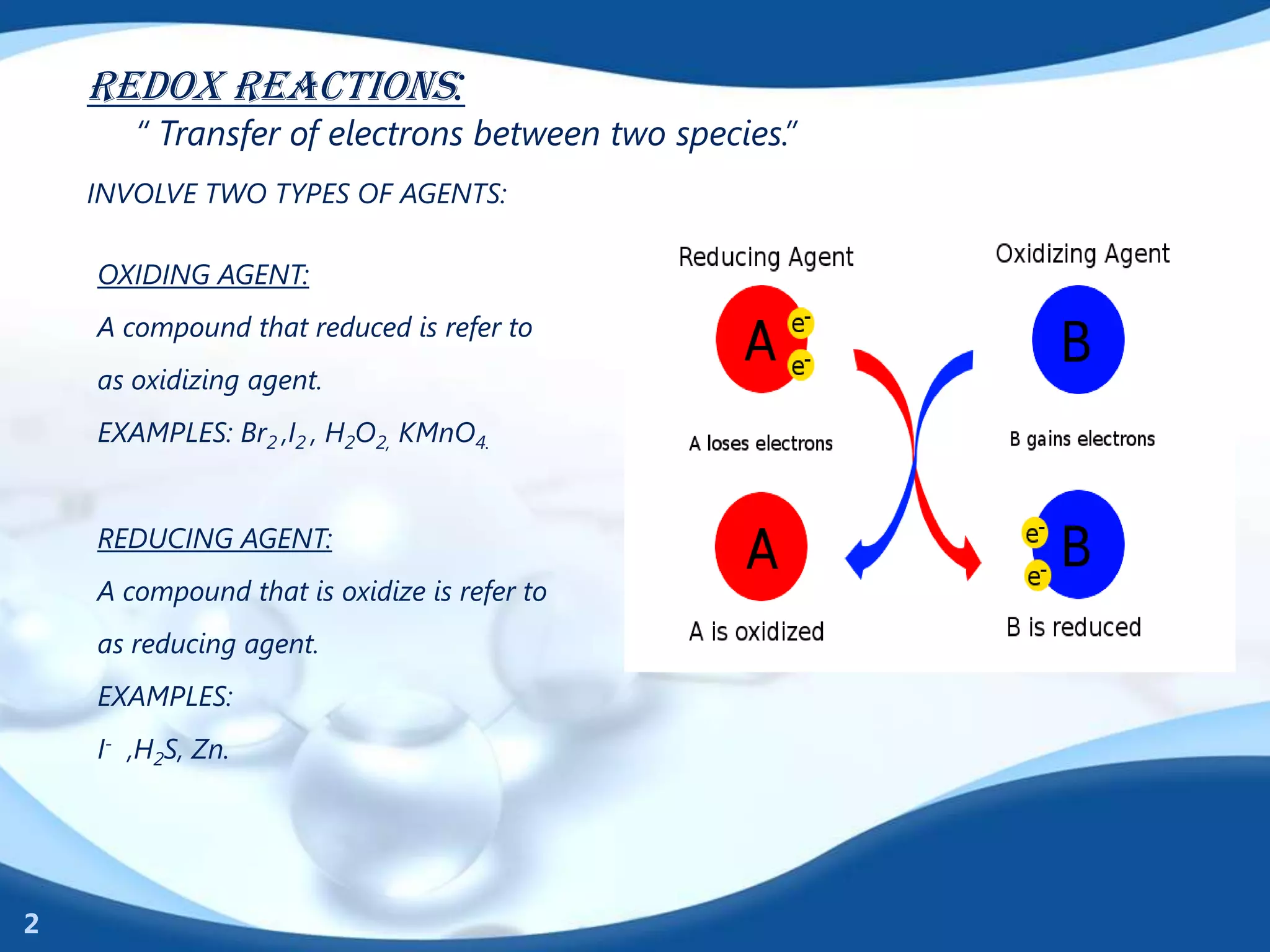
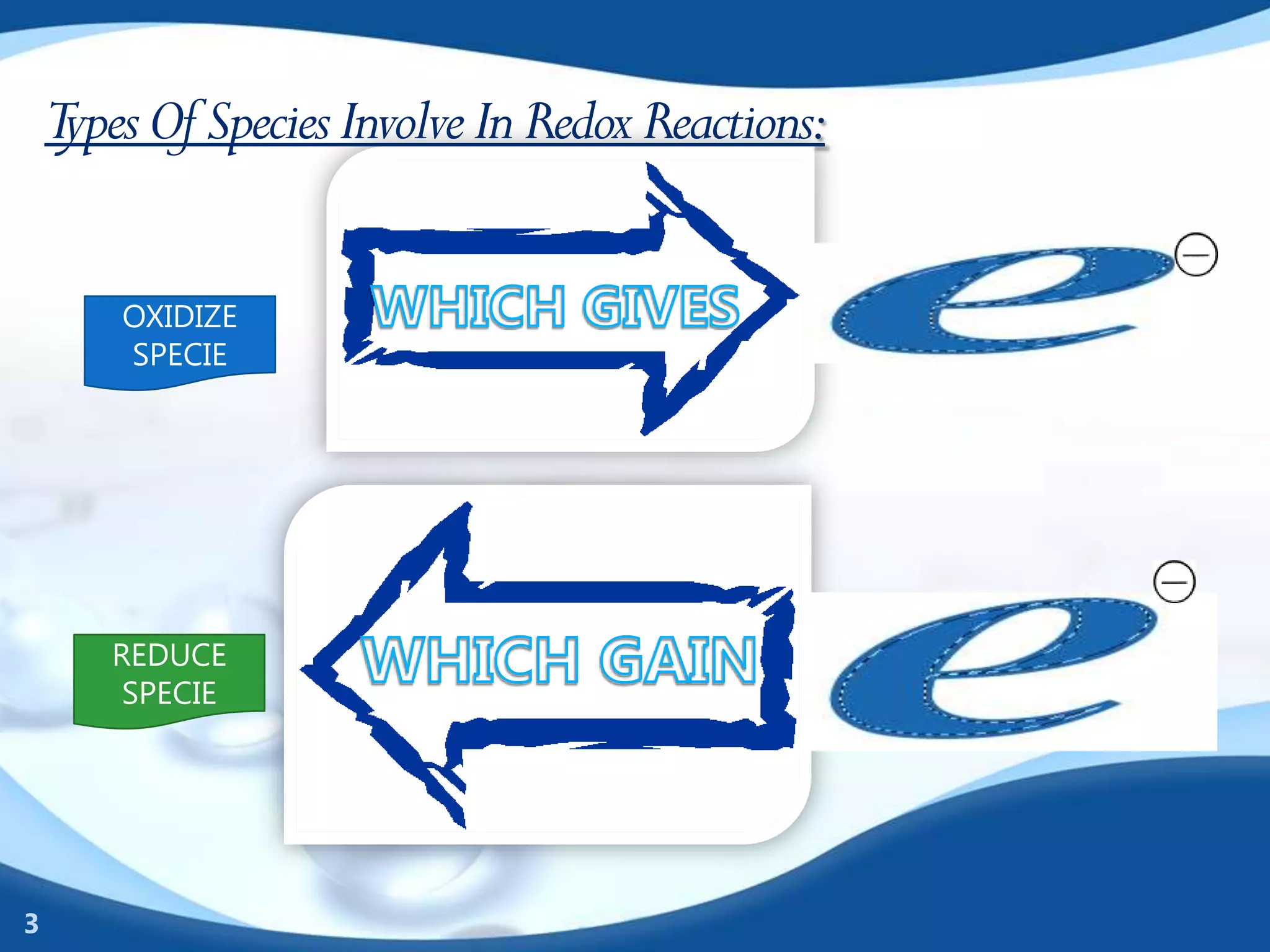
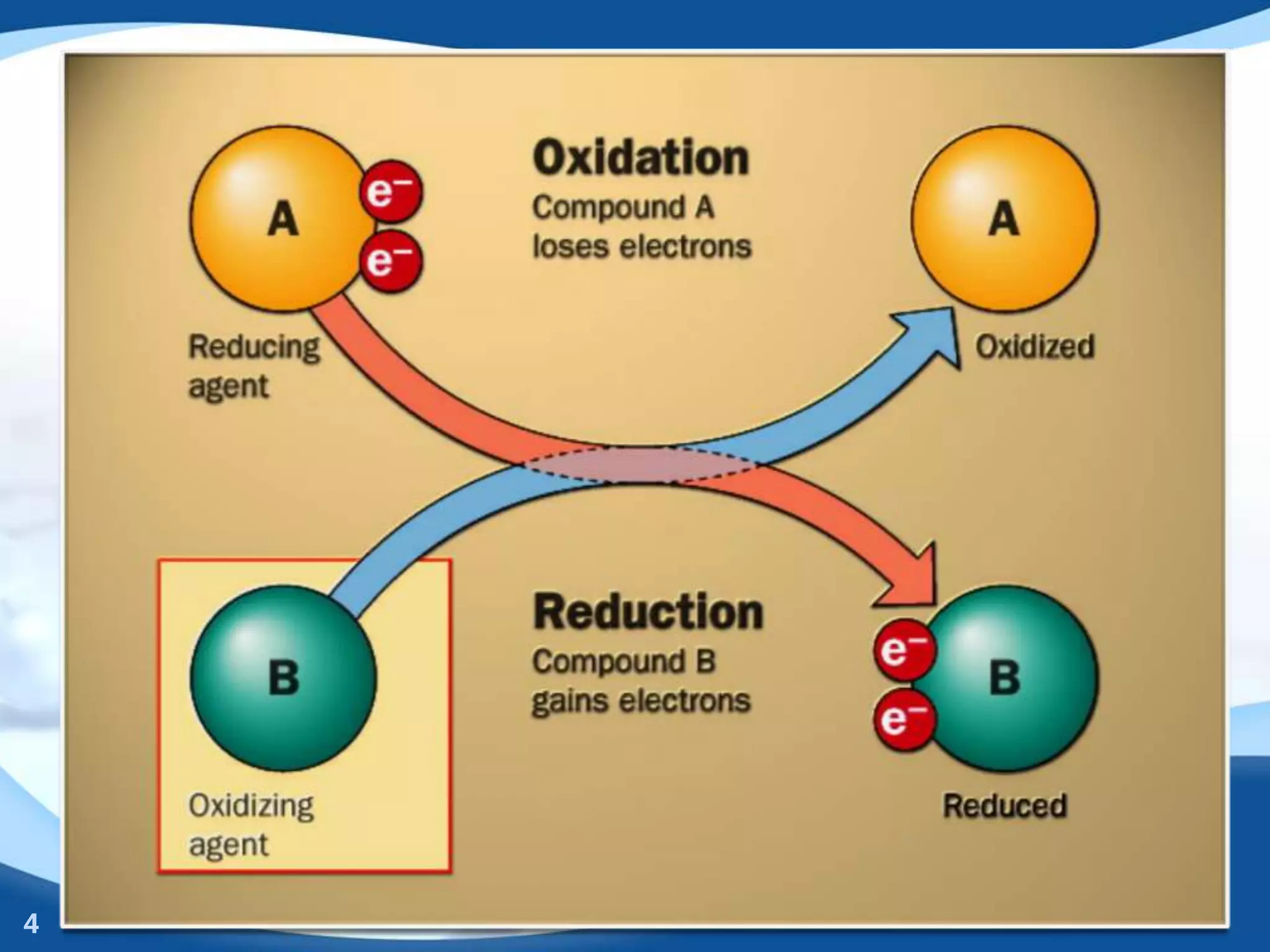
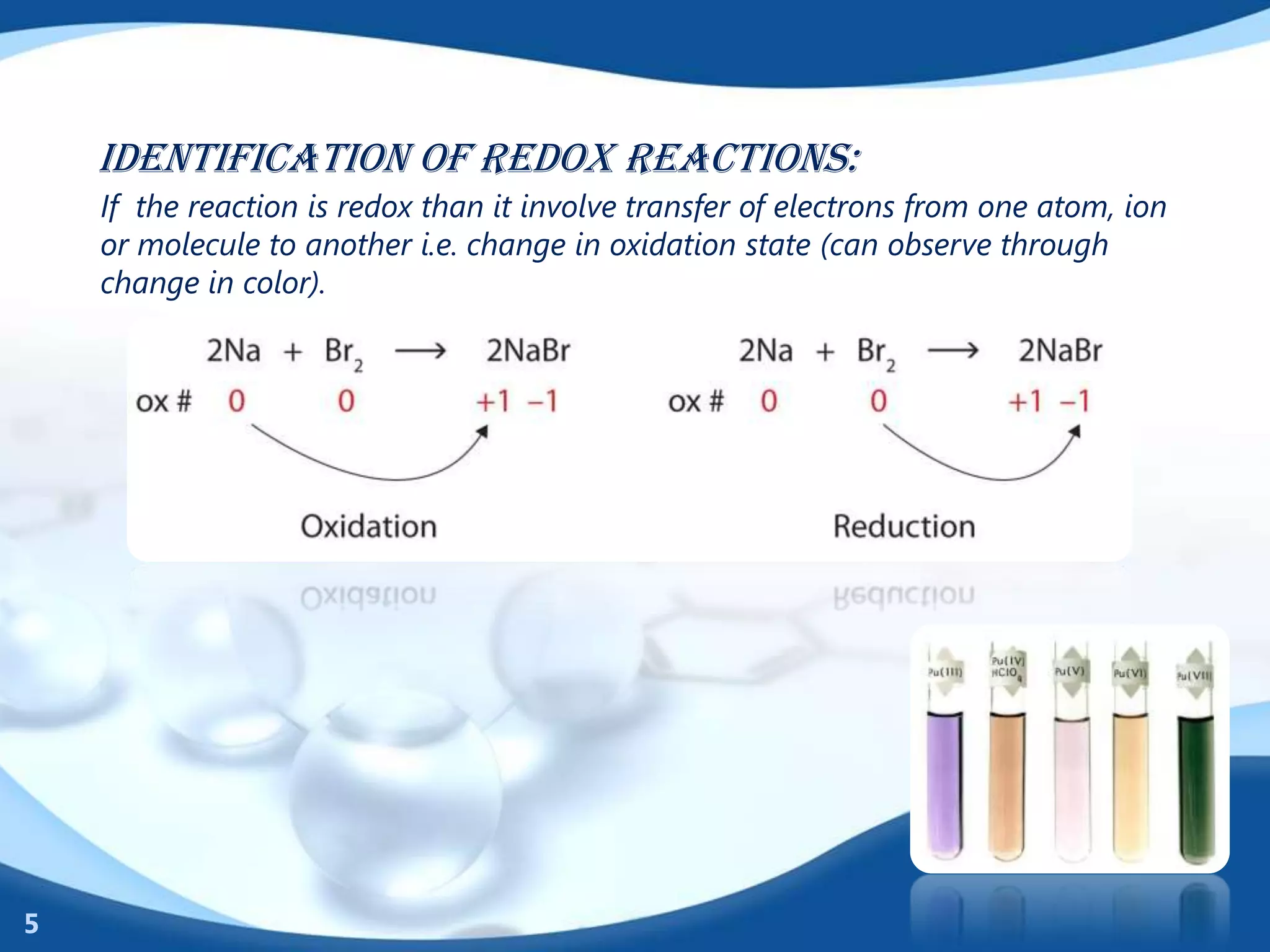
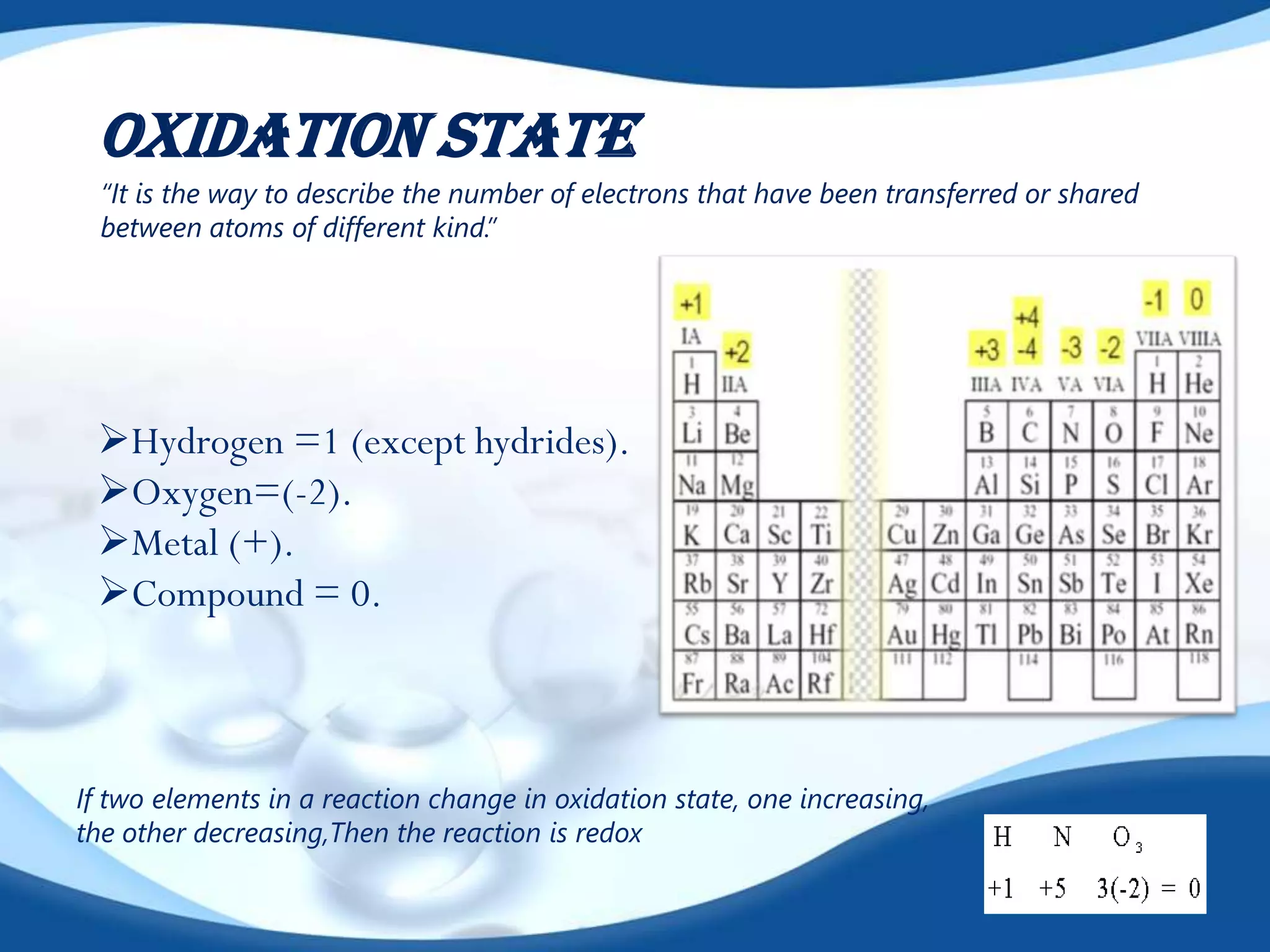
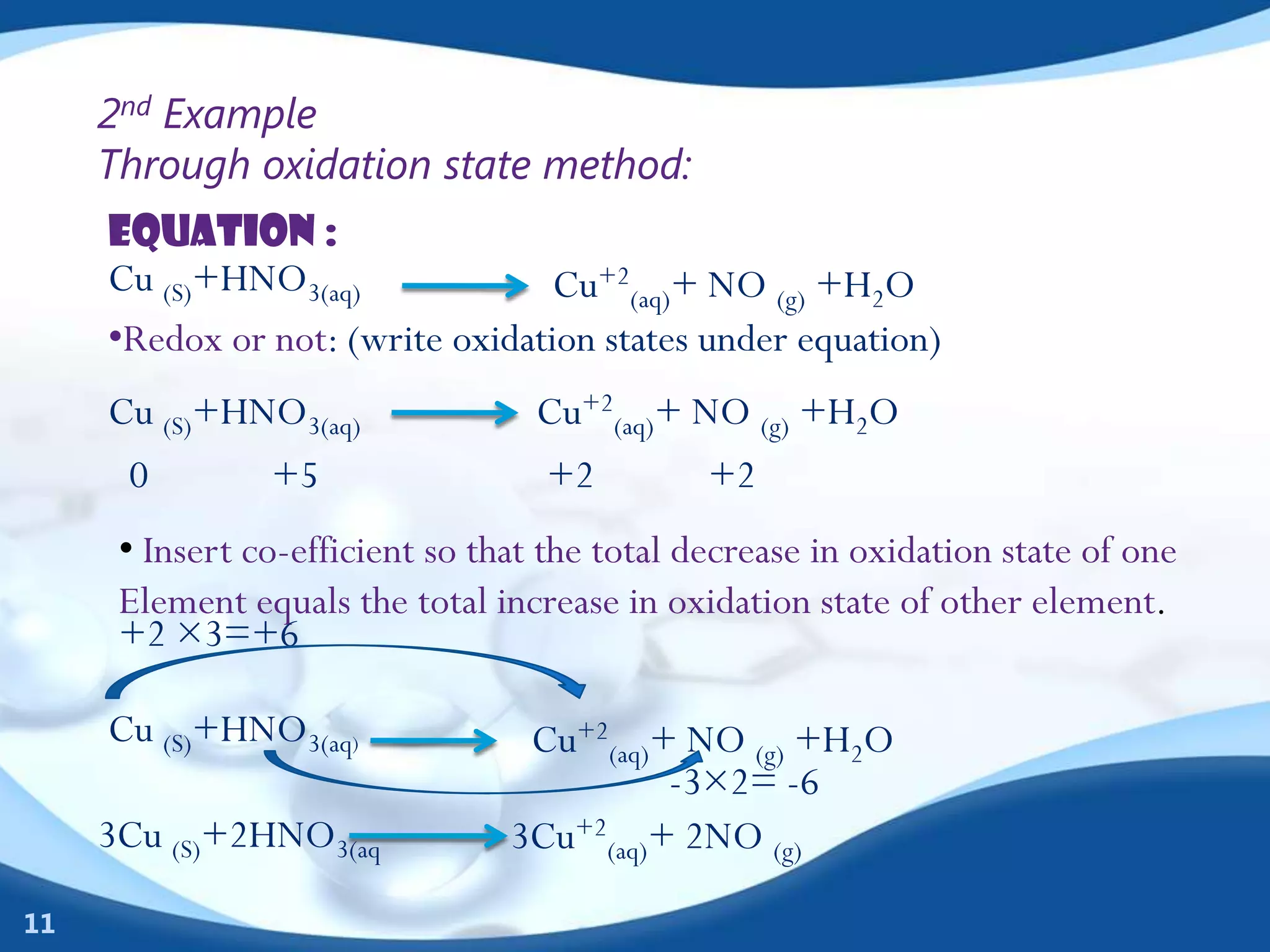
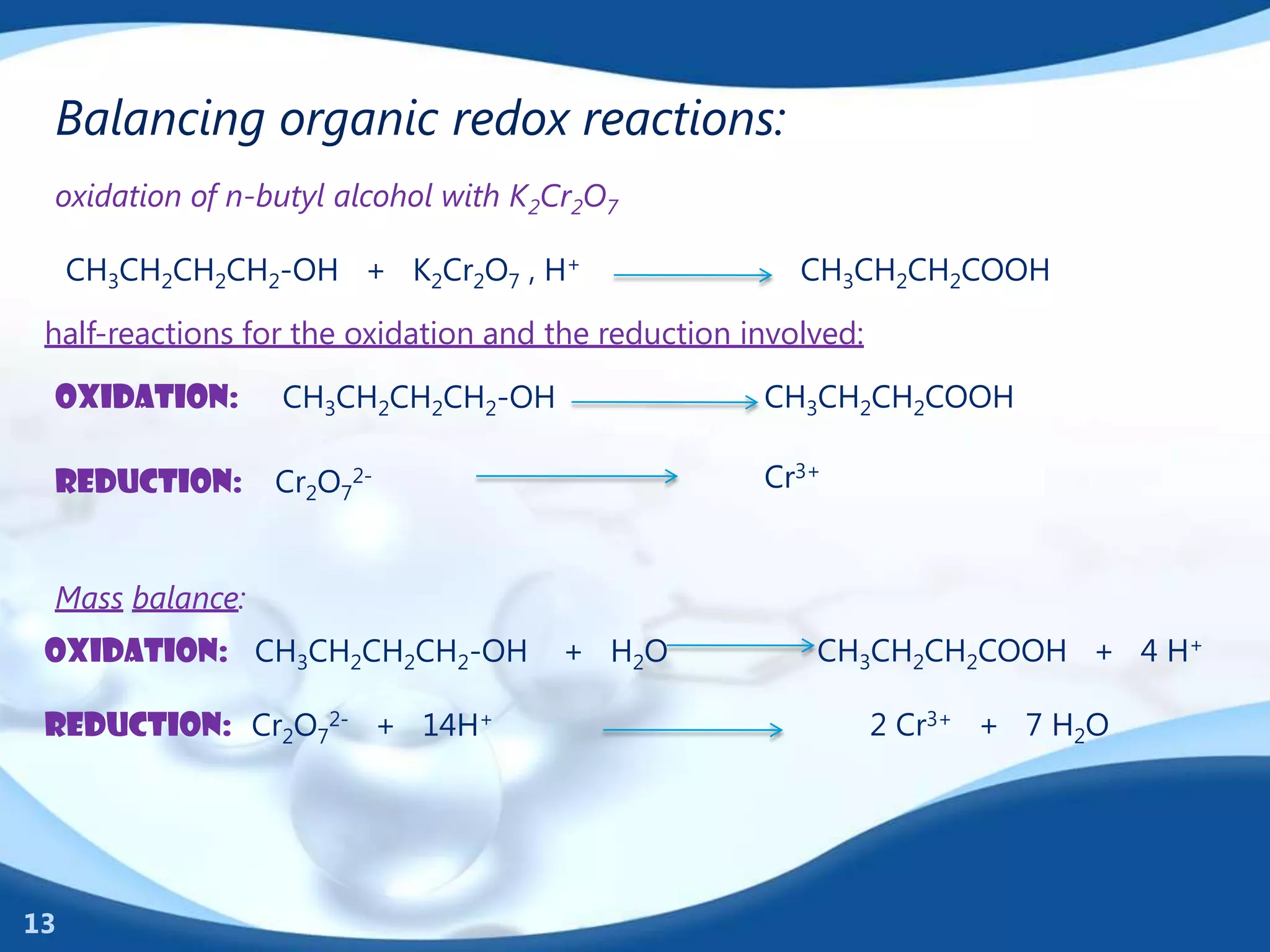
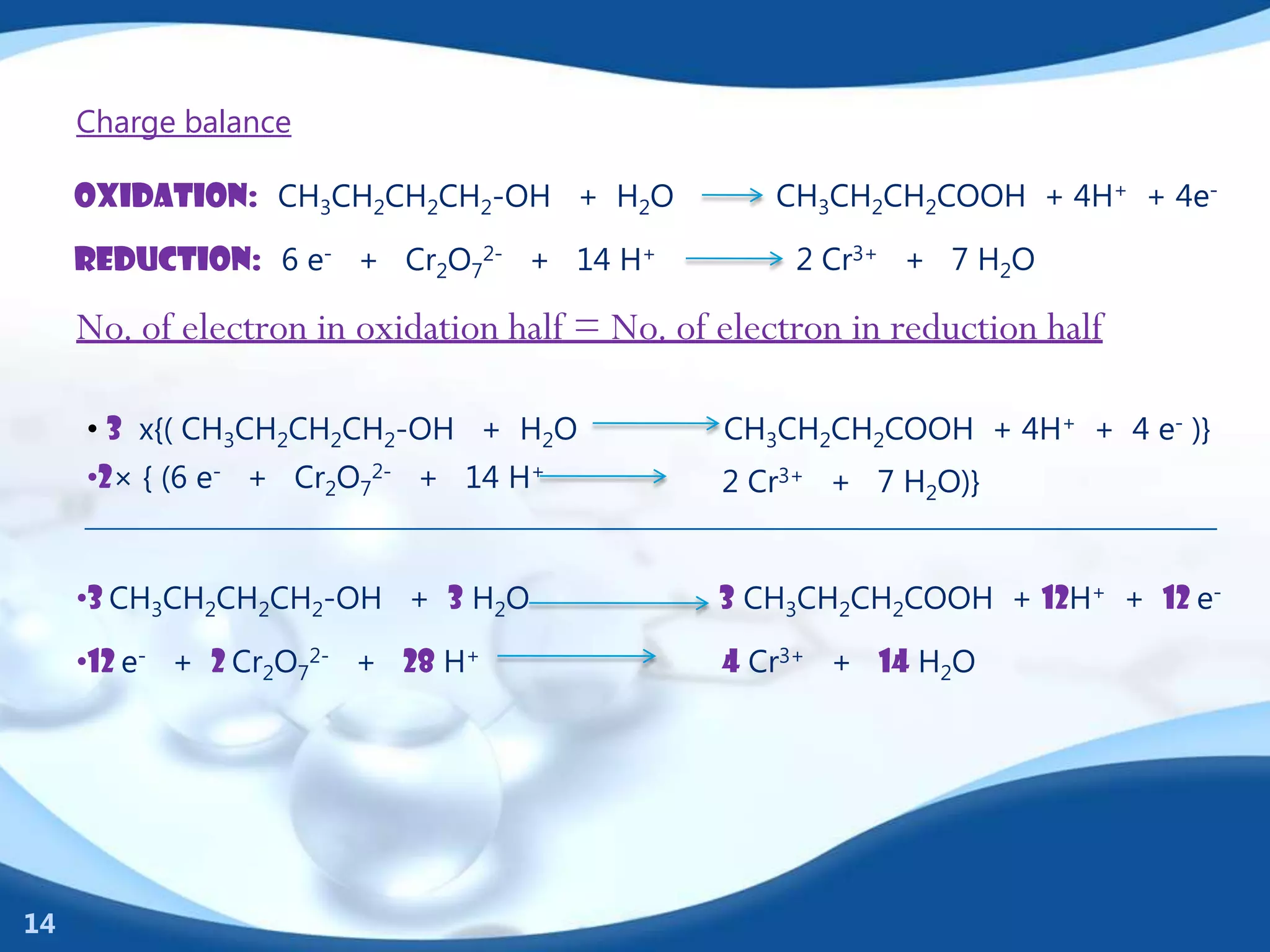
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. There are two types of agents involved - oxidizing agents that reduce other species by accepting electrons, and reducing agents that oxidize other species by donating electrons. Identification of redox reactions involves looking for a change in oxidation state between reactants and products. Balancing redox reactions uses the ion-electron method of writing and balancing half reactions for oxidation and reduction and combining them. Organic redox reactions use a similar process by writing oxidation and reduction half reactions and balancing mass, charge, and electrons.