This document is a student lab manual for configuring Huawei routers. It provides instructions for 6 experiments: 1) Introduction to Huawei routers, which demonstrates configuring IP addresses on router interfaces and PCs to enable communication; 2) PAP authentication protocol, which configures PAP authentication between two routers; 3) Frame Relay Protocol; 4) CHAP authentication protocol; 5) X.25; and 6) Frame Relay Sub-interfaces. The introduction experiment provides a baseline for the other experiments by demonstrating basic router and IP address configuration. The PAP, CHAP, and other experiments build on this by adding different WAN protocols and authentication methods.




![7
(5) Abbreviation list (command can be abbreviated when typing if it does not
conflict with another command):
Normal Command Abbreviated
Command
Normal Command Abbreviated
Command
display disp Ethernet e
Interface Int
Serial s
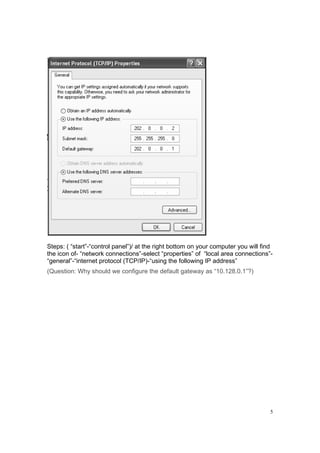
(6) When you finish the configuration, you can check the configuration by:
[RTA] display current-configuration
You can check the configuration of ports by:
[RTA] display interface
There are many more commands you can use which are not listed in this
manual.
(7) Type the first two/three letters of a command, the rest will be automatically
completed by pressing “Tab” button on the keyboard.
If you need help, then just type “?”, you may get the information you need.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-7-320.jpg)

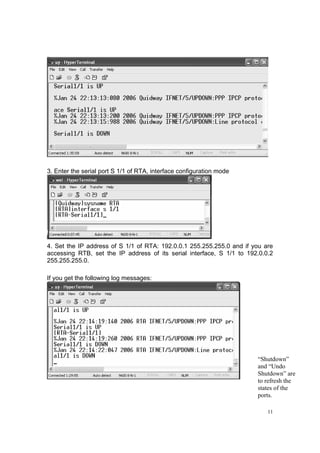
![14
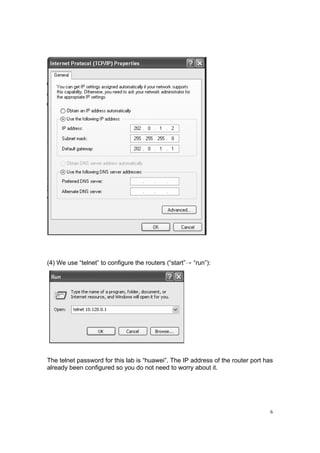
ping 192.0.0.2
From PCs 2, 4, 6 or 8:
ping 10.128.1.1, 192.0.0.2 and 192.0.0.1.
(Question: Why do we ping the IP addresses in this order from both PCs?)
3.1.6 Conclusion
When you check the configuration of RTA and RTB by:
[RTA]display interfaces
You will find that PPP encapsulation has automatically been selected for the
serial interfaces. That means the default protocol of the serial interface on a
Huawei router is PPP.
From this experiment we learn how to set the IP address of serial ports and
Ethernet ports, how to set the IP address of PCs, and how to check the
communication between the PCs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-14-320.jpg)
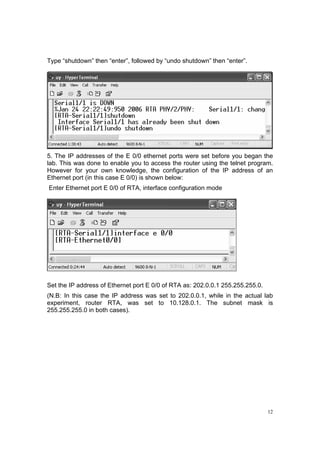
![15
The steps are summarized:
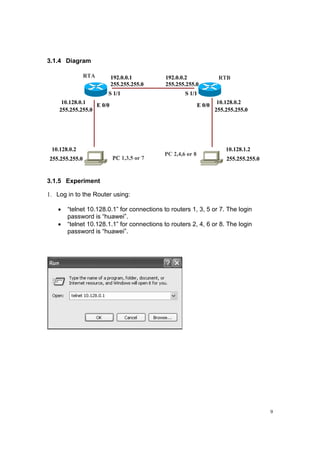
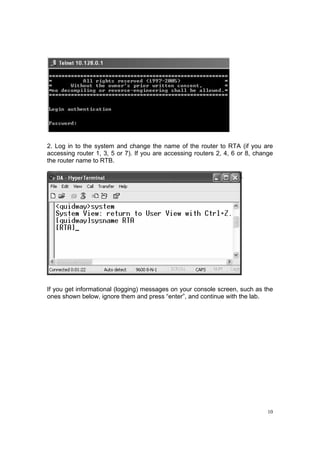
(1) Log in to the routers.
(2) Set the IP address of serial port and Ethernet port of RTA and RTB.
(2) Set the IP address of the PCs.
(3) Check the result of this experiment whether PCA and PCB can communicate.
3.1.7 Commands
RTA:
[RTA] interface S 1/1
[RTA-s 1/1] IP address 192.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
[RTA] display current-configuration
[RTB]:
[RTB] interface S 1/1
[RTB-s 1/1] IP address 192.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
[RTB] display current-configuration
3.2 PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
3.2.1 Objective
Learn to configure PPP PAP authentication protocol.
Realize the communication between two routes with PAP authentication protocol.
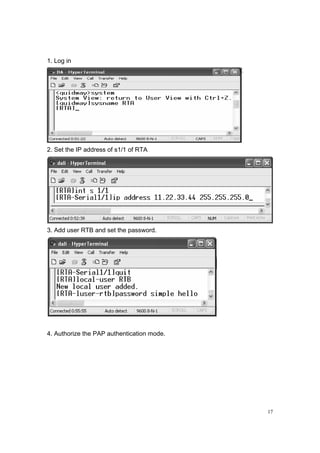
3.2.2 Introduction
PAP is a 2-handshake authentication and the password is transmitted in plain
text.
In the first lab of this chapter, we know that if we do not configure any protocol,
PPP will be automatically encapsulated.
This lab wants to configure PAP protocol to realize the communication between
two Huawei routers. Serial ports s 1/1 are selected to configure PAP protocol.
This lab wants to realize the communication between two s 1/1 with PAP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-15-320.jpg)
![19
3.2.6 Conclusion
This lab wants to realize the communication between two PCs with PAP
authentication.
There are two parts of PAP, authenticating party and authenticated party.
In authenticating party we should:
(1) Configure user list with the password and
(2) Configure PAP authentication.
In authenticated party we should
(1) Configure PAP send user.
3.2.7 Commands
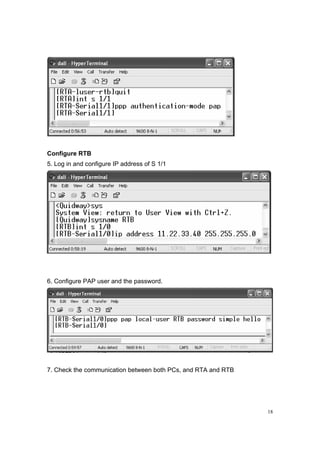
RTA
[RTA] local-user RTB
[RTA-luser-RTB] password simple hello
[RTA-luser-RTB] quit
[RTA] int s 1/1
[RTA-s 1/1] IP address 11.22.33.44 255.255.255.0
[RTA-s 1/1] PPP authentication-mode pap
RTB
[RTB] int s 1/1
[RTB-s1/1] IP address 11.22.33.40 255.255.255.0
[RTB-s1/1] PPP pap local-user RTB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-19-320.jpg)
![20
[RTB-luser-RTA] password simple hello
3.3 FRP (Frame Relay Protocol)
3.3.1 Objective
Learn to configure FRP.
Realize the communication of two routers with FRP protocol.
3.3.2 Introduction
The frame relay protocol is a kind of fast packet switching technology based on
X.25 protocol. FRP only implements the function of the core of the link layer;
therefore it is simpler and more efficient to forward or switch data units in the
data link layer.
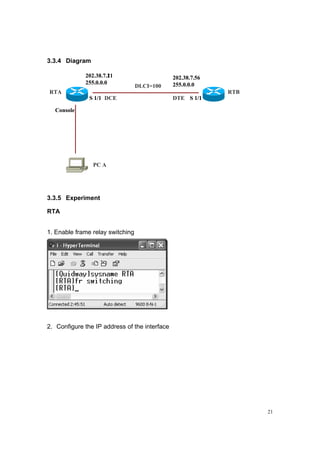
This experiment has the following steps:
1. Encapsulate interface.
2. Configure the terminal type of frame relay interface.
3. Allocate DLCI on DCE.
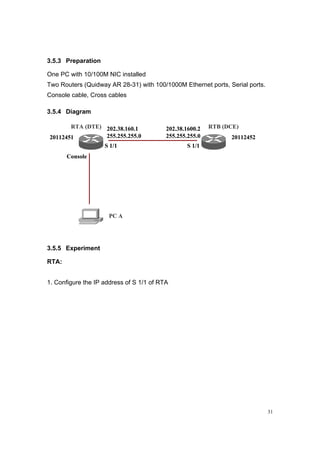
3.3.3 Preparation
One PC with 10/100M NIC installed
Two Routers (Quidway AR 28-31) with 100/1000M Ethernet ports, Serial ports.
Console cable, Cross cables](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-20-320.jpg)
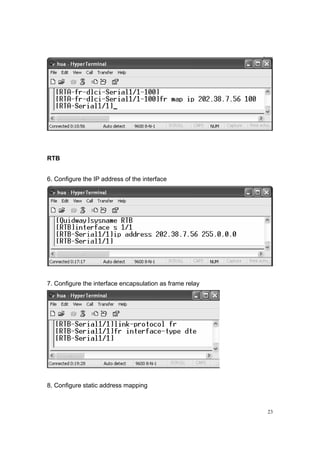
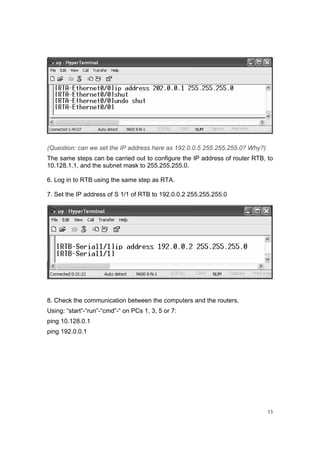
![24
9. Check the communication between both PCs, and RTA and RTB
(Question: Change the DLCI for R1 S 2/1 as 200:
[RTA -S 1/1] fr dlci 200
Ping the address 202.38.7.21, succeed or not?
Then change the command as:
[R1-S 2/1] fr inarp
Ping the address 202.38.7.21, succeed or not?)
3.3.6 Conclusion
FRP is an important lab. In this lab, the following job should be completed to
realize the communication between two Huawei routers:
(1) Encapsulate the frame relay protocol
Link-protocol frame-relay
(2) Configure the terminal type of the frame relay interface
Fr interface {dce / dte}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-24-320.jpg)
![25
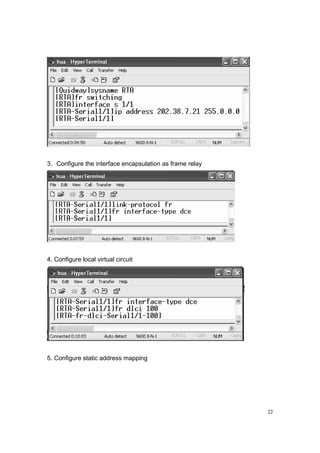
3.3.7 Commands:
RTA
[RTA] fr switching
[RTA] interface S 1/1
[RTA-S 1/1] IP address 202.38.7.21 255.0.0.0
[RTA-S 1/1] link-protocol fr
[RTA-S 1/1] fr interface-type dce
[RTA-S 1/1] fr dlci 100
[RTA-fr-dlci-S 1/1-100] fr map ip 202.38.7.56 dlci 100
RTB
[RTB] interface S 1/1
[RTB-S 1/1] IP address 202.38.7.56 255.0.0.0
[RTB-S 1/1] link-protocol fr
[RTB-S 1/1] fr interface-type dte
[RTB-S 1/1] fr map IP 202.38.7.21 dlci 100
3.4 CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication
Protocol)
3.4.1 Objective
Learn to configure CHAP protocol.
Realize the communication between two Huawei routers using CHAP
authentication protocol.
3.4.2 Introduction
CHAP is a 3-handshake protocol. The authentication is originated by the
authenticating part.
Like PAP authentication protocol, there are two parts in CHAP, authenticating
party and authenticated party.
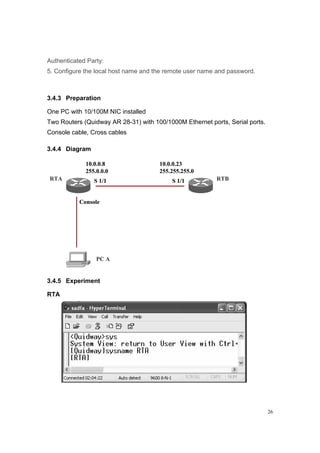
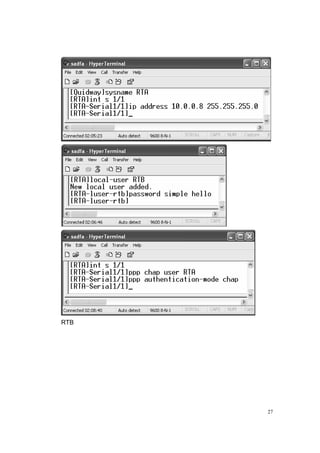
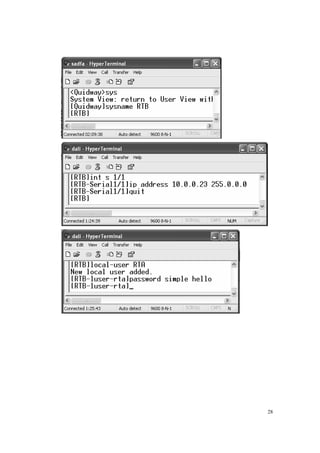
1. Set the IP address of the selected serial port interface of the Router
Authentication Party:
2. Configure authentication method.
3. Configure local host name.
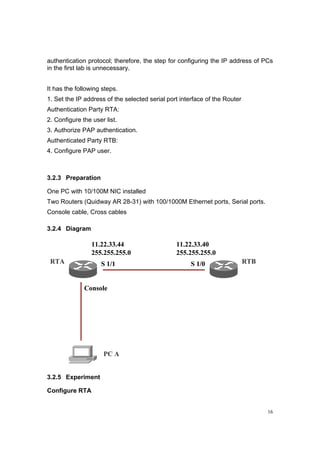
4. Add the remote user name and password to the local user list.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-25-320.jpg)
![29
Check the communication between both PC, and RTA and RTB.
3.4.6 Conclusion
In CHAP authentication protocol, we have the following things to do:
(1) Authenticating party configuration:
Configure authentication method
ppp authentication-mode chap
Configure local host name
ppp CHAP user username
Add the remote user name and password to the local user list.
local-user username password simple password
(2) Authenticated party configuration:
Configure the local host name and the remote user name and the
password.
ppp CHAP user username
local-user username password simple password
3.4.7 Commands
RTA
[RTA] local-user RTB
[RTA-luser-RTB] password simple hello
[RTA] int s 1/1
[RTA-s 1/1] PPP chap user RTA
[RTA-s 1/1]PPP authentication-mode chap](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-29-320.jpg)
![30
RTB
[RTB] local-user RTA
[RTA-luser-RTB] password simple hello
[RTA] int s 1/1
[RTA-s1/1] PPP chap user RTB
3.5 X.25
3.5.1 Objective
Learn to configure X.25 protocol.
Realize the communication of two computer use X.25 protocol.
3.5.2 Introduction
The X.25 recommendation is the interface specification between the DTE and the
DCE. Its main function is to describe how to set up virtual circuit, transmission
packets, set up links, transmit data, release links and to clear the virtual circuits
between the DTE and the DCE, and in the meantime, it will implement the error
control, flow control, statistics, etc. And also it provides users with some optional
services and configuration functions. (Note: The DTE and DCE here are different
form the DTE and DCE of the physical interface. Here DTE means the user
equipment such as routers, etc; DCE means equipments such as packet switch,
etc. Route can also sever as the DCE.)
In the first experiment of this chapter, we know that if we do not configure any
protocol, PPP will be automatically encapsulated. That means this experiment
should configure X.25 by hand.
It has the following steps.
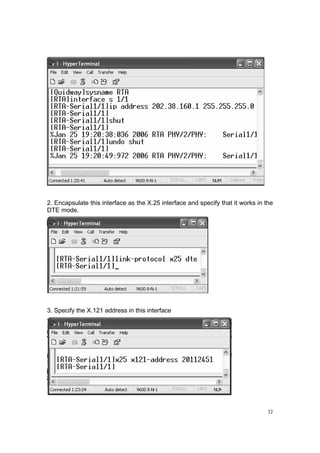
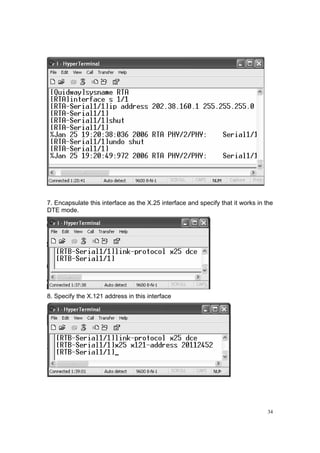
1. Set the IP address of the selected interface of the Router
2. Configure the interface to encapsulate it as the X. 25.
3. Specify its work model: DTE or DCE.
4. Specify the address mapping.
5. Set the flow control parameter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-30-320.jpg)

![36
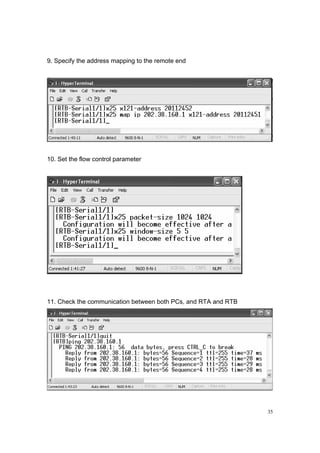
(Question: Please change the command of step 9 as:
[RTB- S 1/1] X25 map IP 202.38.160.5 X121-address 20112451
Try to ping the address 202.38.160.2, succeed or fail? Why?)
Then input:
[RTB- S 1/1] undo X25 map IP 202.38.160.1 X121-address 20112451, ping
again, succeed or fail? Why?)
3.5.6 Conclusion
In this lab, the following steps should be completed:
(1) Configure the work mode of X.25
link-protocol X. 25 [dte/dce]
(2) Congigure the X. 121 address
X25 X121-address X. 121-address
(3) Create the map between network address and X. 121 address
X25 map protocol protocol-address x121-address X.121-address [?]
3.5.7 Commands
[RTA] interface s 1/1
[RTA- S 1/1] IP address 202.38.160.1 255.255.255.0
[RTA- S 1/1] link-protocol X25 DTE
[RTA- S 1/1] X25 X121-address 20112451
[RTA- S 2/0] X25 map IP 202.38.160.2 X121-address 20112452
[RTB] interface s 1/1
[RTB- S 1/1] IP address 202.38.160.2 255.255.255.0
[RTA- S 1/1] link-protocol X25 DCE
[RTA- S 1/1] X25 X121-address 20112452
[RTA- S 1/1] X25 map IP 202.38.160.1 X121-address 20112451](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-36-320.jpg)

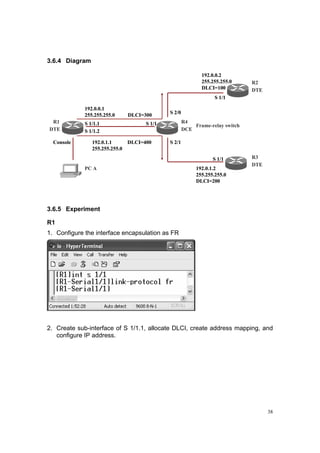
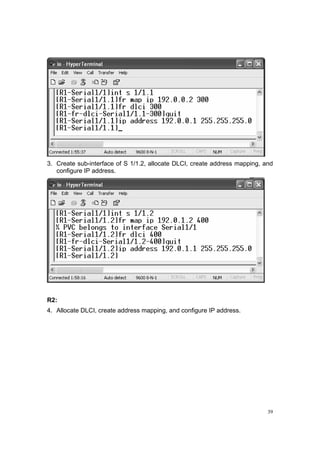
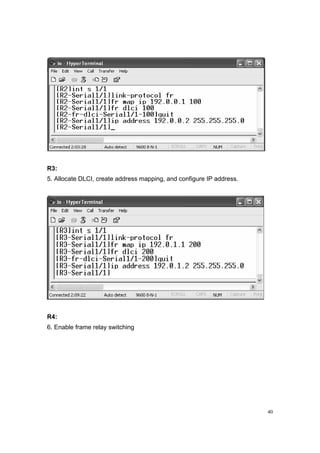
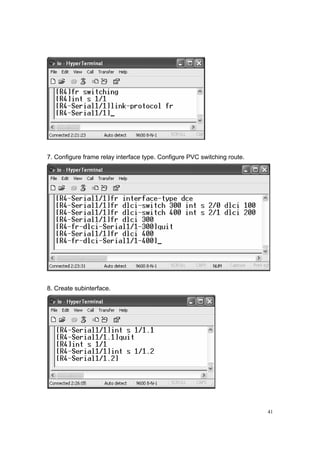
![42
9. Configure FRP on S 2/0.
10. Configure FRP on S 2/1.
11. Check the communication among the routers:
Ping from [R1] S 1/1.1 to 192.0.0.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-42-320.jpg)
![43
Ping from [R1] S 1/1.1 to 192.0.1.2
Ping from [R3] S 1/1 to 192.0.1.1
Ping from [R3] S 1/1 to 192.0.0.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-43-320.jpg)
![44
3.6.6 Conclusion
In FRS lab, we should follow three steps:
(1) Configure the frame relay switch (R4), including;
Set IP address, enable frame relay switching, configure frame relay
interface type, and configure PVC route.
(Question: Why should not we set the IP address here?)
(2) Configure R1, including:
Create subinterface, set up address mapping, allocate DLCI
(3) Configure R2 and R3, including:
Sep IP address, enable frame relay switching, create address mapping,
allocate DLCI.
3.6.7 Command
R1:
[R1] int s 1/1
[R1-s 1/1] link-protocol fr
[R1-s 1/1] int s 1/1.1
[R1-s 1/1.1] fr map ip 192.0.0.2 300
[R1-s 1/1.1] fr dlci 300
[R1-s 1/1.1] ip address 192.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
[R1-s 1/1] int s 1/1.2
[R1-s 1/1.2] fr map ip 192.0.1.2 400
[R1-s 1/1.2] fr dlci 400
[R1-s 1/1.2] ip address 192.0.1.1 255.255.255.0
R2:
[R2] fr switching
[R2] link-protocol fr
[R2-s 1/1] fr interface-type dce
[R2-s 1/1] fr dlci-switch 300 interface s 2/0 dlci 100
[R2-s 1/1] fr dlci-switch 400 interface s 2/1 dlci 200
[R2-s 1/1] fr dlci 300](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-44-320.jpg)
![45
[R2-s 1/1] fr dlci 400
[R2-s 1/1] int s 1/1.1
[R2-s 1/1.1] int s 1/1.2
[R2] int s 2/0
[R2-s 2/0] link-protocol fr
[R2-s 2/0] fr interface-type dce
[R2-s 2/0] fr dlci-switch 100 interface s 1/1 dlci 300
[R2-s 2/0] fr dlci 100
[R2] int s 2/1
[R2-s 2/1] link-protocol fr
[R2-s 2/1] fr interface-type dce
[R2-s 2/1] fr dlci-switch 200 interface s 1/1 dlci 400
[R2-s 2/1] fr dlci 200
R3:
[R3] int s 1/1
[R3-s 1/1] link-protocol fr
[R3-s 1/1] fr map ip 192.0.0.1 100
[R3-s 1/1] fr dlci 100
[R3-s 1/1] ip add 192.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
R4:
[R3] int s 1/1
[R4-s 1/1] link-protocol fr
[R4-s 1/1] fr map ip 192.0.1.1 200
[R4-s 1/1] fr dlci 100
[R4-s 1/1] ip add 192.0.1.2 255.255.255.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eee3080-lab031-160109030612/85/Eee3080-lab031-45-320.jpg)