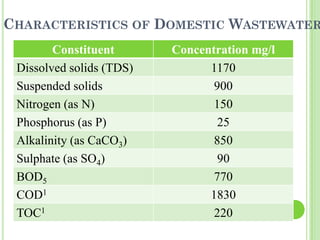
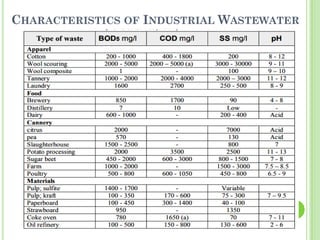
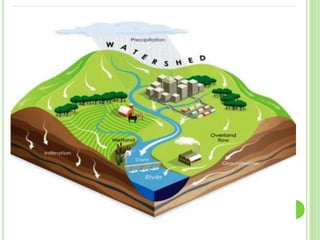
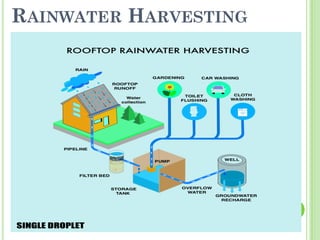
Wastewater is water that has been used and contains 0.1% impurities including organic matter, microorganisms, and inorganic compounds. There are two main types of wastewater: domestic wastewater which comes from households and contains constituents like dissolved solids, suspended solids, nitrogen, and phosphorus, and industrial wastewater which results from water used in industrial processes. Watershed management aims to develop land and water resources in a balanced ecological way through practices like rainwater harvesting, which is the collection, storage, and purification of rainwater running off surfaces for later use through systems that catch, convey, filter, and store the water.