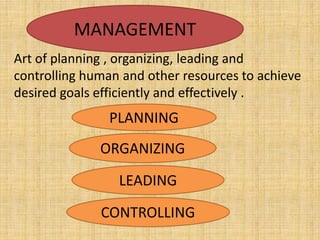
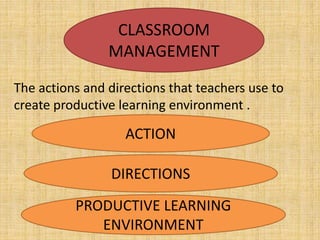
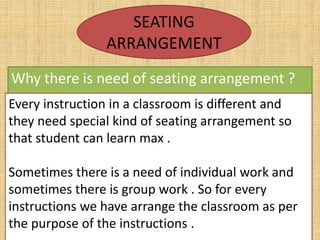
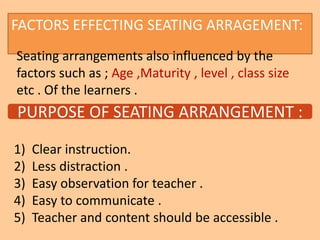
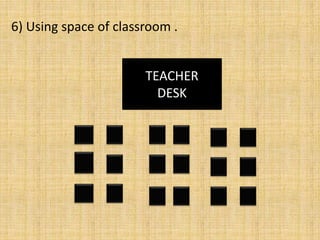
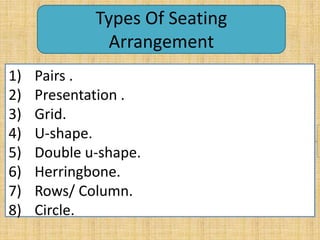
This document discusses classroom management for health extension workers and students. It covers concepts of classroom management including basic steps like task analysis and formulation of objectives. It emphasizes the importance of a positive classroom environment through factors like seating arrangement, classroom climate, and decoration. Different types of seating arrangements are outlined for different classroom purposes and sizes, including pairs, presentation, grid, U-shape, and circle formats. Classroom climate is defined as the intellectual, social, emotional and physical environments that determine how students learn.