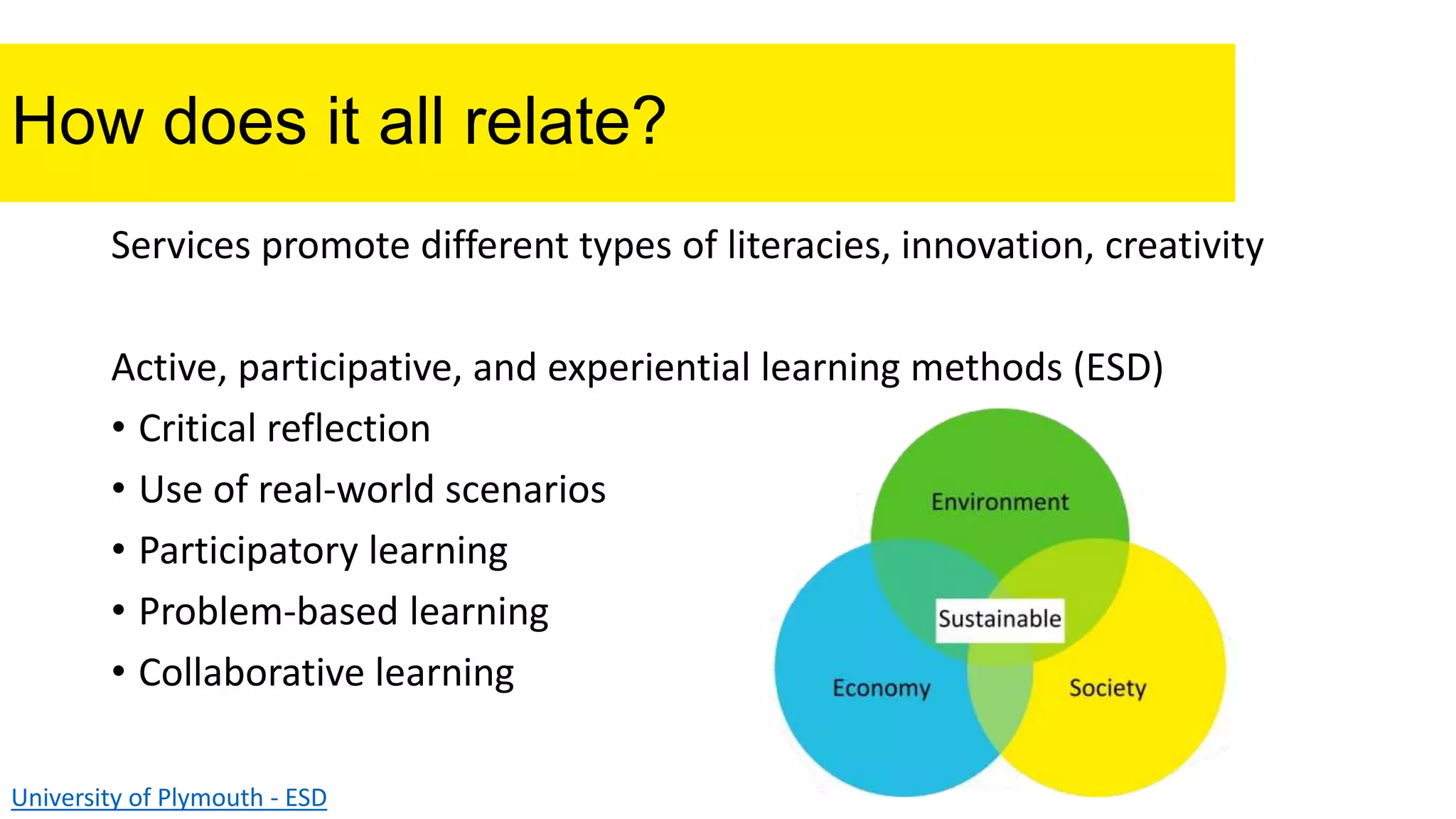
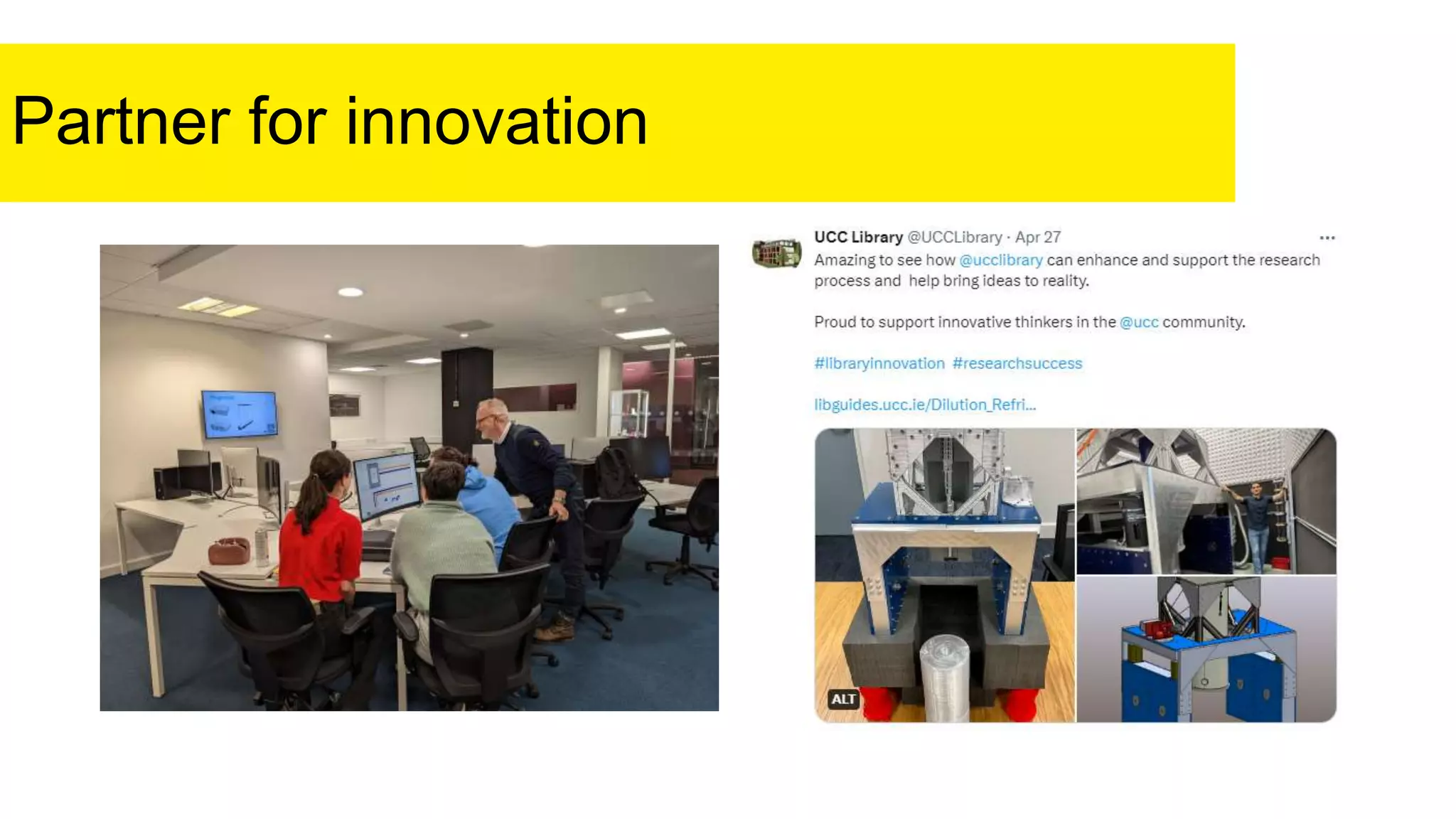
The document discusses the role of the UCC Library in contributing to the UN Sustainable Development Goals through education for sustainable development (ESD). It emphasizes the importance of acquiring knowledge and skills for a sustainable future, highlighting innovative and participatory learning methods. The conclusion thanks the reader and provides contact information for further inquiries.