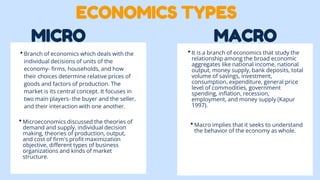
The document provides an overview of economics, defining it as the study of scarcity, resource utilization, and societal wealth, with Adam Smith's definition highlighting the focus on wealth production and distribution. It distinguishes between positive economics, which analyzes economic conditions objectively, and normative economics, which involves ethical judgments and policy implications. Additionally, it outlines the branches of microeconomics and macroeconomics, emphasizing their respective focuses on individual economic units and the economy as a whole.