This document discusses suicide bombers and methods for identifying potential terrorists. It provides:
1) Details of a famous suicide bombing in India where the bomber was able to smuggle explosives under her dress and detonate at an election rally while touching the victim's feet.
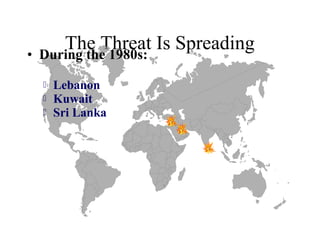
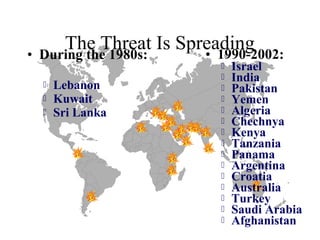
2) A list of countries that experienced increasing suicide bombings between the 1980s and 2002.
3) The key elements of a suicide bombing operation including secrecy, reconnaissance of targets, and rehearsals.
4) Suggestions for preventing attacks by disrupting planning during the surveillance phase and employing strong security measures.