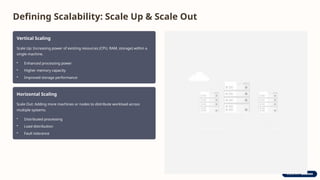
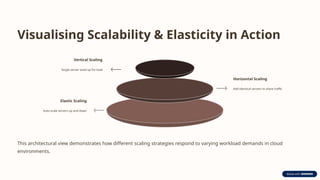
This architectural model enables cloud systems to adapt to fluctuating demand by automatically and rapidly adjusting their resource capacity. Dynamic scalability allows the system to grow or shrink in real-time, while elastic resource capacity ensures that resources are acquired and released on-demand.