Recommended
PPTX
Session 10 DROWNING and managements.pptx
PPTX
ASPHYXIA (Drowning).pptx ALL THE DETAILED PRESENTATION RELATED TO DROWNING
PPTX
DROWNING_Forensic_Medicine 2026 FINAL.pptx
PPTX
DROWNING_Forensic_Medicine_2026 FINAL.pptx
PPTX
Violent Asphyxial Deaths - Drowning.pptx
PPTX
Lecture 5 Asphyxia- drowning (1)NOTES .pptx
PPTX
pathophysiology of drowning.pptx Dr. Haricharan MD RIMS Imphal . ...
PPTX
Drowning_Forensic_Medicine_With_Diagrams.pptx
PPTX
Drowning_Forensic_Medicine_With_Diagrams.pptx
PDF
Dr. Sangeeta Asphyxia-2.for agad students pdf
PPTX
PPTX
drowning - Forensic Subject PPT by mbbs final year student
PPTX
Drowning and drowning mechanism and patho physiology
PPTX
Drowning 29-07-2024.pptxdrowning micro teaching according to forensic medici...
PPTX
PPTX
Forensic Investigation of Drowning.pptx.
PPTX
Drowning Chapter from Forensic Medicine.pptx
PPTX
Drowning and near drowning
PDF
according to NCISM drowning useful for UG/PG Student.
PPTX
Death by drowning (1).pptx
PPTX
drowning - micro teaching.pptxdrowning micro teaching according to forensic ...
PDF
Drowning case for forensic medicine scenario .pdf
PPTX
Drowning A detailed Case Study from postmortem examination
PPTX
PPTX
Differential diagnosis between Drowning Vs Retention of cadaver in water
PPTX
PPTX
Drowning. (fresh water / seawater )pptx
PPT
MECHANICAL ASPHYXIA FORENSIC MEDICINE .ppt
PPTX
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles - The Americas 1-25-2026
PPT
West Hatch High School - GCSE History Option
More Related Content
PPTX
Session 10 DROWNING and managements.pptx
PPTX
ASPHYXIA (Drowning).pptx ALL THE DETAILED PRESENTATION RELATED TO DROWNING
PPTX
DROWNING_Forensic_Medicine 2026 FINAL.pptx
PPTX
DROWNING_Forensic_Medicine_2026 FINAL.pptx
PPTX
Violent Asphyxial Deaths - Drowning.pptx
PPTX
Lecture 5 Asphyxia- drowning (1)NOTES .pptx
PPTX
pathophysiology of drowning.pptx Dr. Haricharan MD RIMS Imphal . ...
PPTX
Drowning_Forensic_Medicine_With_Diagrams.pptx
Similar to Drowning_Lecture_Presentation_with_Diagram.pptx
PPTX
Drowning_Forensic_Medicine_With_Diagrams.pptx
PDF
Dr. Sangeeta Asphyxia-2.for agad students pdf
PPTX
PPTX
drowning - Forensic Subject PPT by mbbs final year student
PPTX
Drowning and drowning mechanism and patho physiology
PPTX
Drowning 29-07-2024.pptxdrowning micro teaching according to forensic medici...
PPTX
PPTX
Forensic Investigation of Drowning.pptx.
PPTX
Drowning Chapter from Forensic Medicine.pptx
PPTX
Drowning and near drowning
PDF
according to NCISM drowning useful for UG/PG Student.
PPTX
Death by drowning (1).pptx
PPTX
drowning - micro teaching.pptxdrowning micro teaching according to forensic ...
PDF
Drowning case for forensic medicine scenario .pdf
PPTX
Drowning A detailed Case Study from postmortem examination
PPTX
PPTX
Differential diagnosis between Drowning Vs Retention of cadaver in water
PPTX
PPTX
Drowning. (fresh water / seawater )pptx
PPT
MECHANICAL ASPHYXIA FORENSIC MEDICINE .ppt
Recently uploaded
PPTX
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles - The Americas 1-25-2026
PPT
West Hatch High School - GCSE History Option
PPTX
Definition of communication skills and it's process.
PDF
Beak Modifications by Dr. Ramzan Virani pptx.pdf
PDF
U.S. Departments of Education and Treasury fact sheet
PPTX
Poster Based Ethical Reflection - Dharma and Values Poster.pptx
PPTX
"Aristotle : Father Of Western Philosophy"
PPTX
TLE 8 W1 Q4 D2.pptx COMMON FLOOR PLAN SYMBOLS PLUMBING SYMBOLS
PPTX
Day 2 ppt english.powerpoint presentation ppt
PDF
Darwinism: Theory of Natural Selection and Origin of Species
PPTX
West Hatch High School -- GCSE Geography
PDF
Fast Followers Project, Embedding Net Zero into Wakefield Metropolitan Distri...
PPTX
COMMUNICATION ITS PROCESS ELEMENTS & BARRIER .pptx
PDF
Lamarckism: Theory of Evolution, Principles, Examples, Objections and Neo-Lam...
PPTX
PREVENTIVE PEDIATRICS.pptx
PPTX
Powerpoint for testing in embed test with Sway
PPTX
MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION Part-1.Shilpa hotakar.pptx
PDF
West Hatch High School - GCSE French Specification
PPTX
Reimagining Academic Library Services through Artificial Intelligence: A Case...
PPTX
Mohan - "A man of silence and authority"
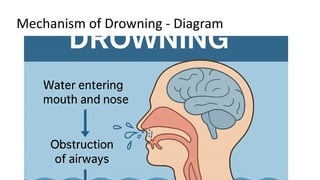
Drowning_Lecture_Presentation_with_Diagram.pptx 1. 2. Classification of Drowning
• 1. Typical (Wet)
• 2. Dry Drowning
• 3. Immersion Syndrome
• 4. Near Drowning
• 5. Secondary Drowning
• 6. Delayed Drowning
3. 4. External Findings
• 1. Washerwoman's Skin
• 2. White Froth
• 3. Cutis Anserina
• 4. Cadaveric Spasm
• 5. External Injuries
5. Internal Findings
• 1. Emphysema Aquosum
• 2. Paltauf's Spots
• 3. Water in stomach
• 4. Water in sinuses/middle ear
• 5. Heart chamber differences
6. Special Tests
• 1. Gettler Test: Chloride difference
• 2. Diatom Test: Algae in organs
• 3. Hydrostatic Test: Neonatal lungs
7. 8. 9. 10.