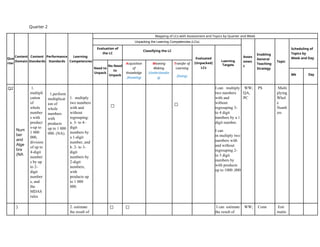
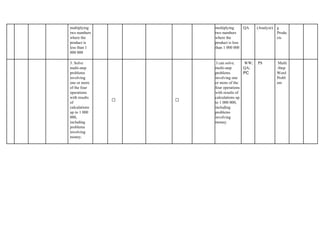
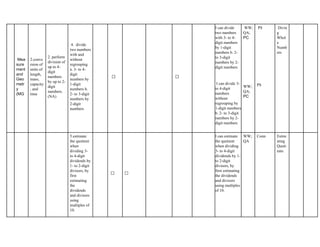
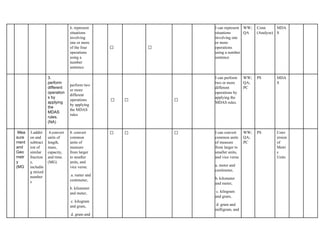
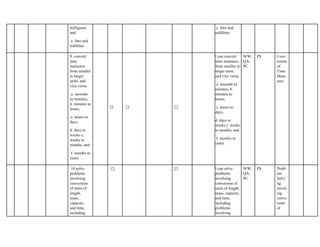
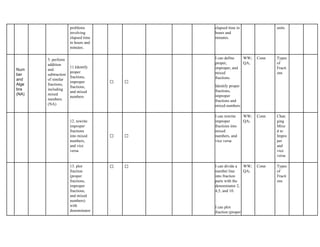
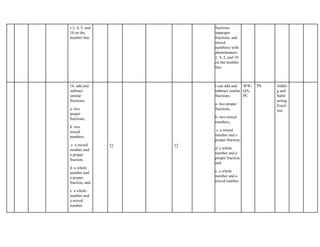
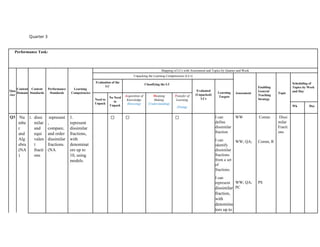
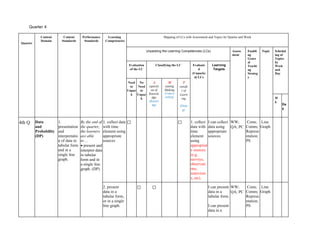
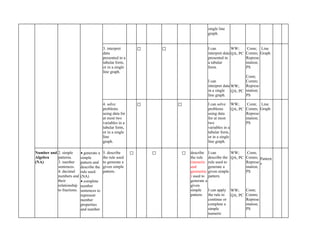
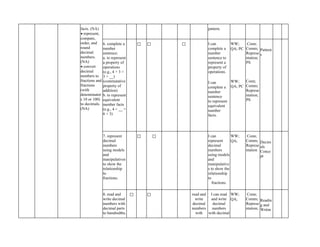
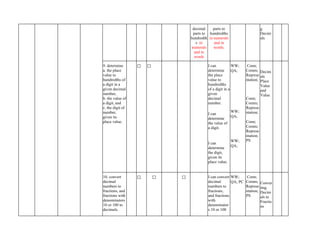
The document outlines the mathematics curriculum for grade 4 in the Philippines, aiming to develop students into proficient problem solvers through a focus on number, algebra, geometry, and data handling. It emphasizes the importance of problem-solving skills as essential life skills for 21st-century learners, and details specific performance standards and learning competencies across various mathematical topics. The curriculum is structured to enhance students' critical thinking, application of concepts, and appreciation for mathematics through practical problem-solving experiences.