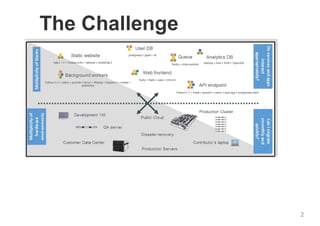
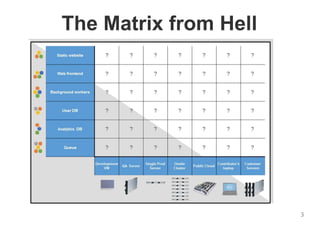
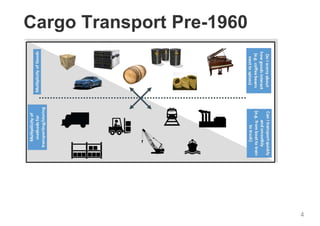
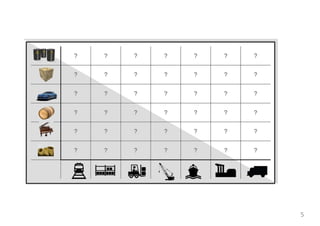
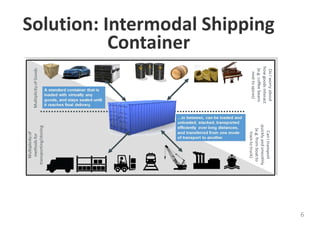
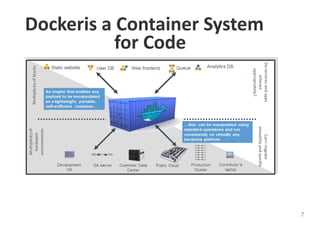
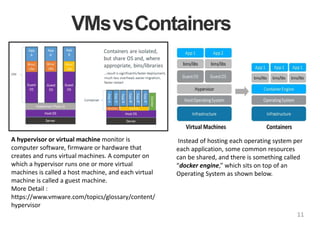
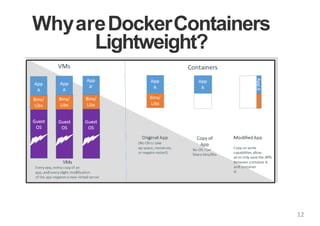
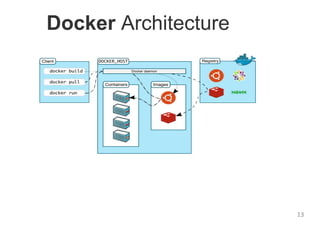
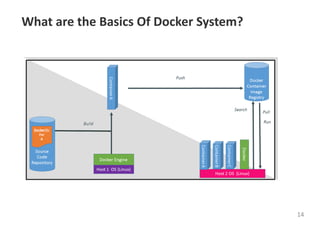
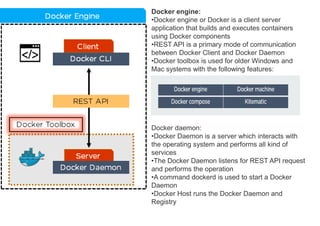
The document provides an introduction to Docker, explaining its functions as a container system for code that allows applications to be portable and run in isolated environments. It emphasizes the advantages for both developers and administrators, including improved deployment efficiency, consistency, and resource management. Additionally, it outlines the architecture of Docker and its integration with various systems and tools.