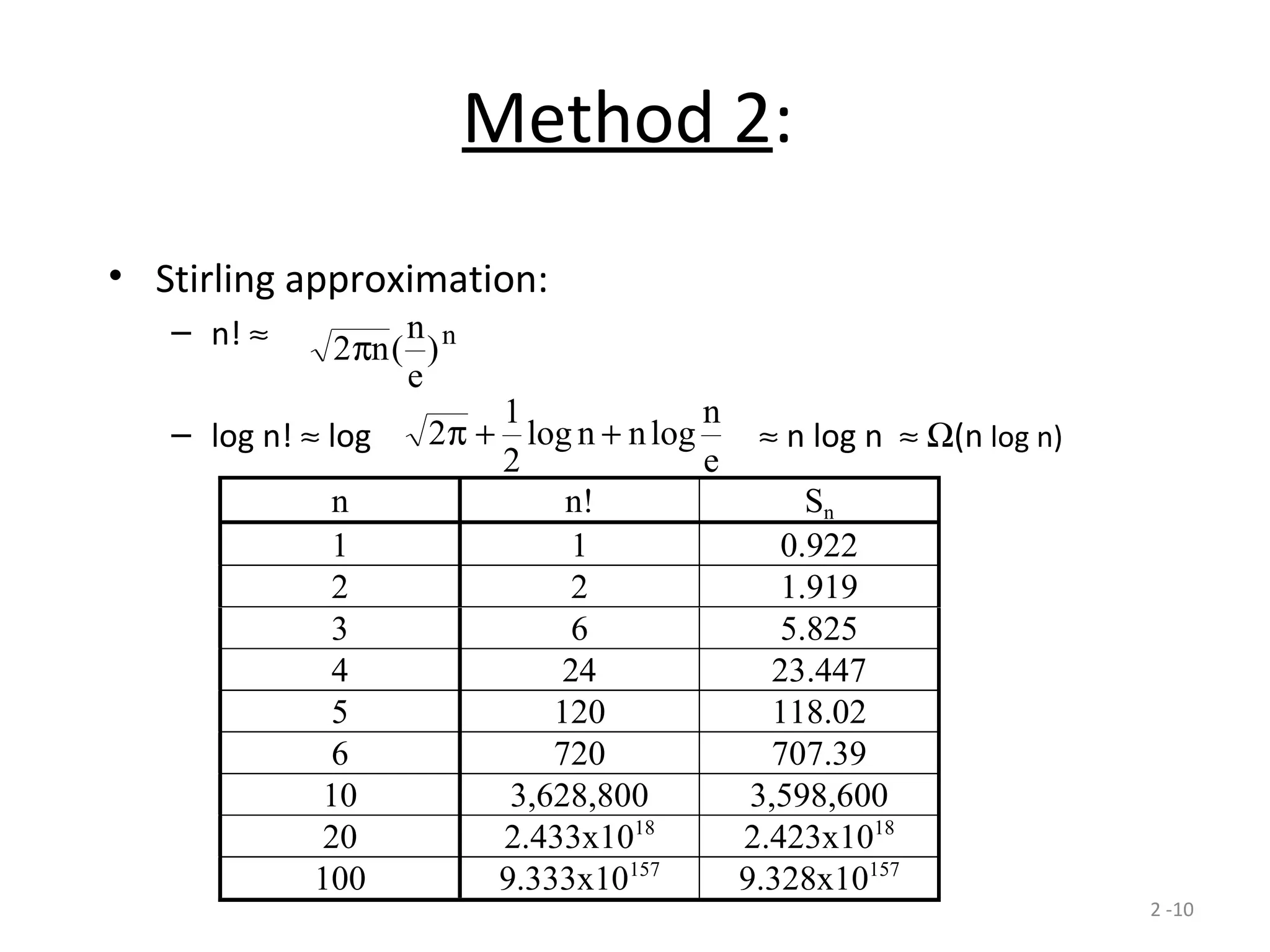
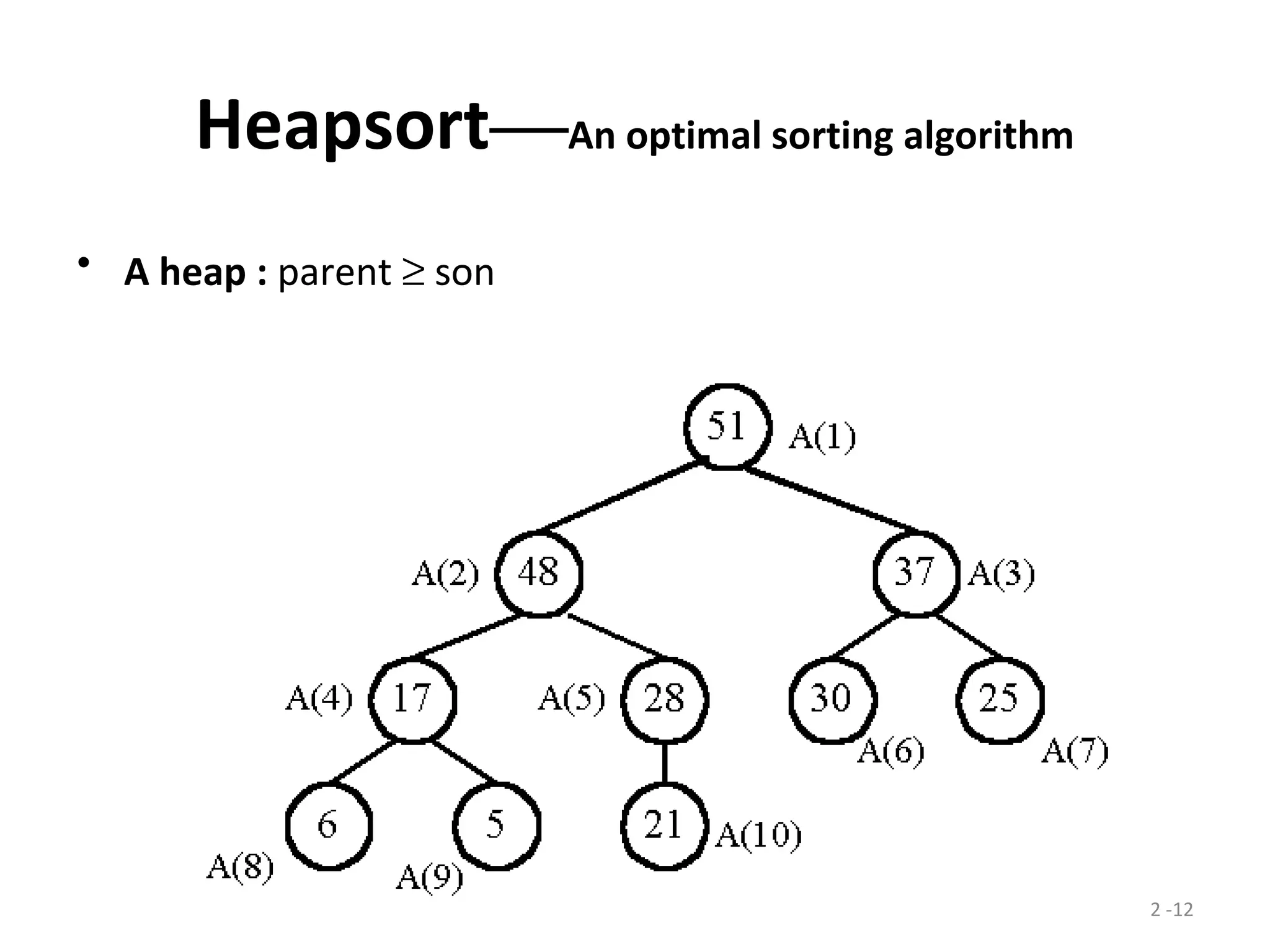
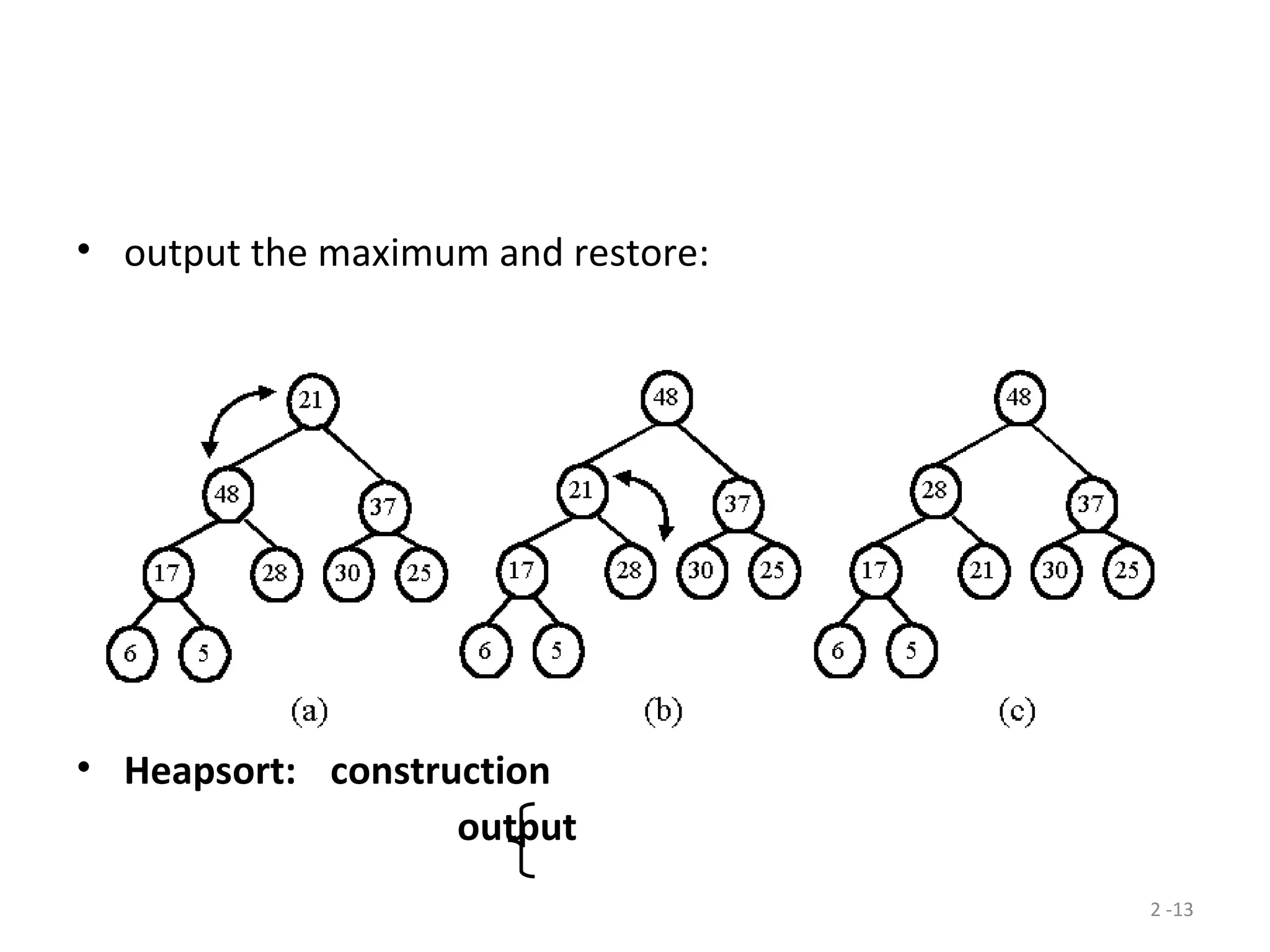
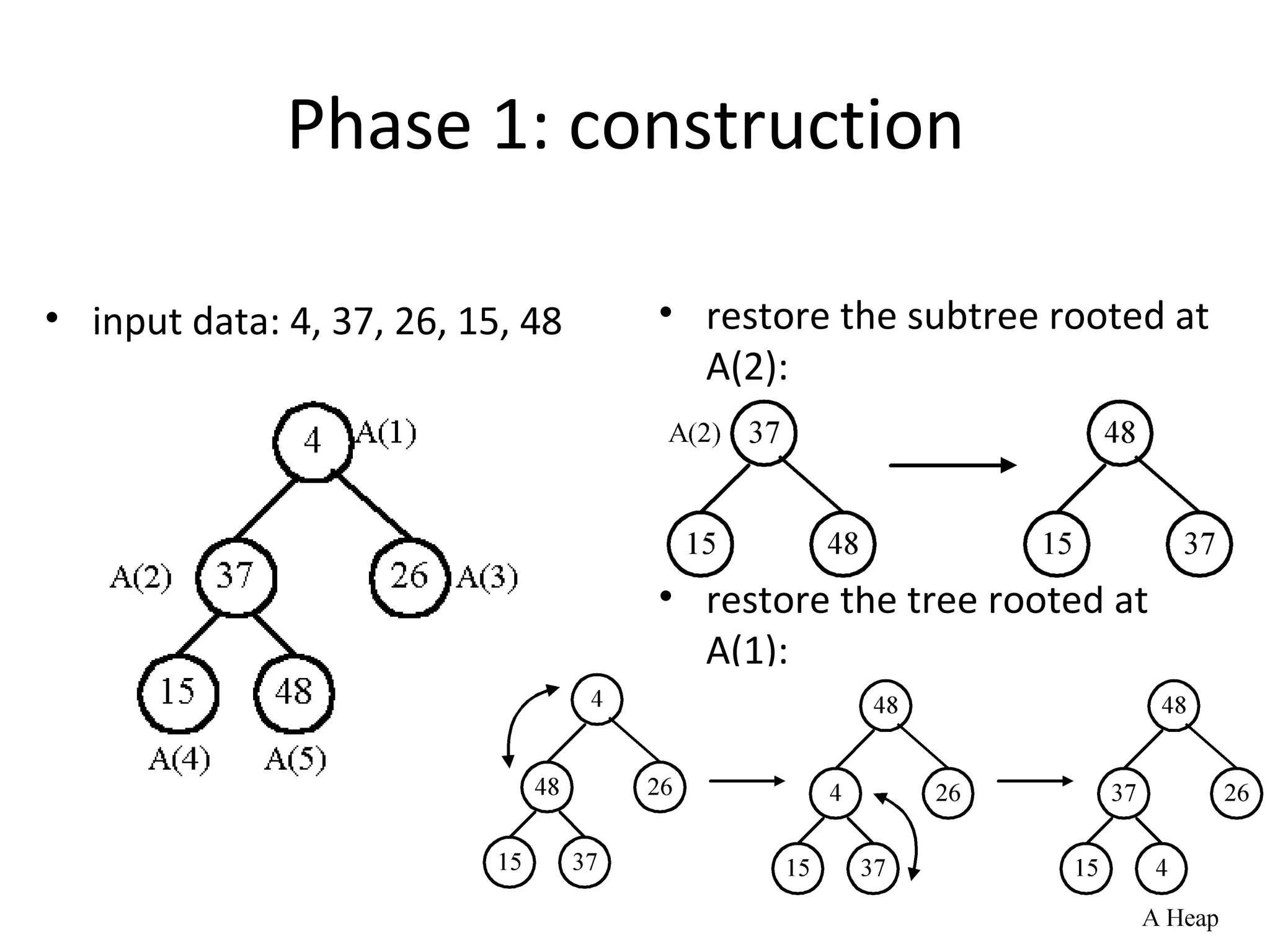
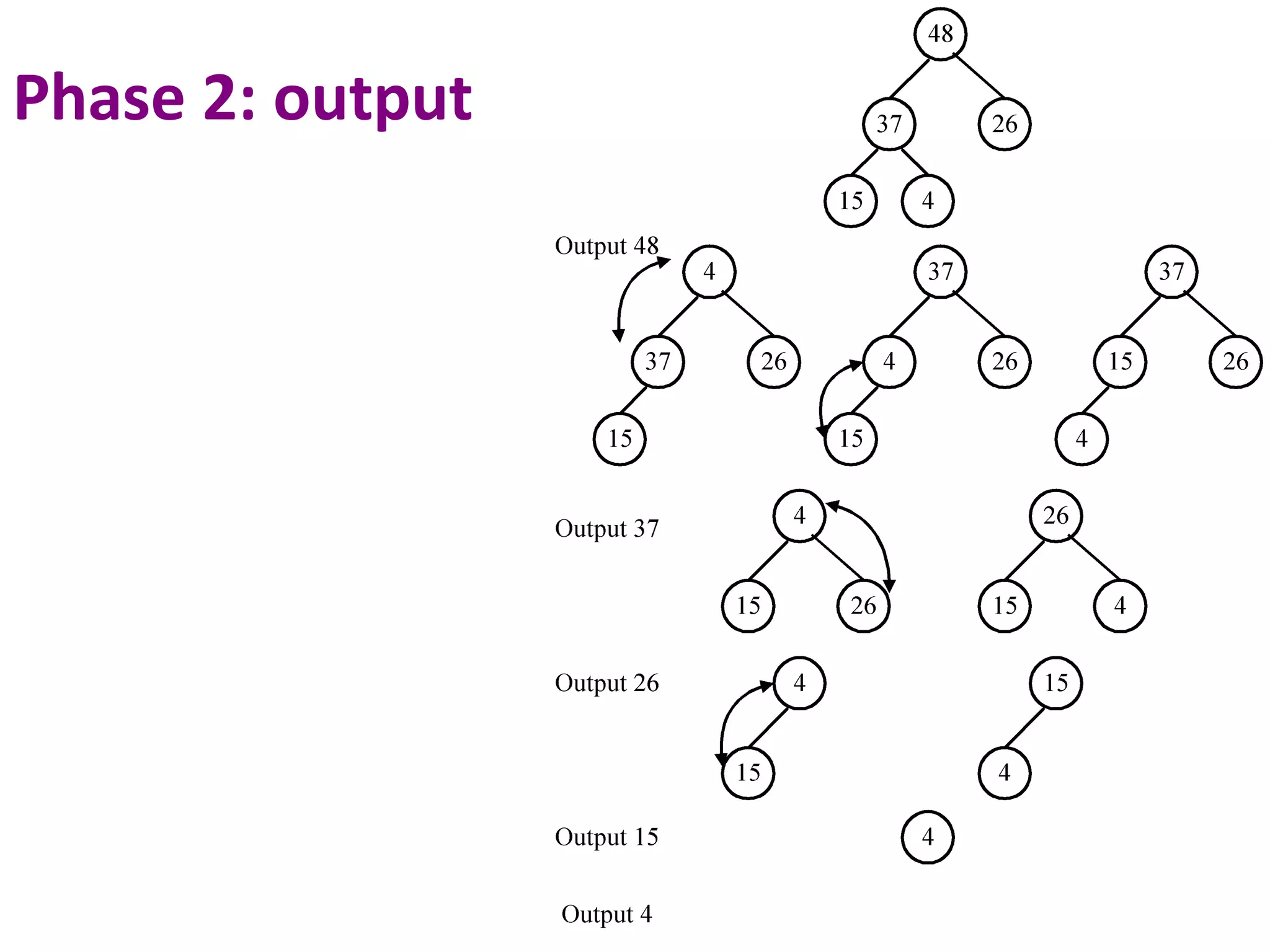
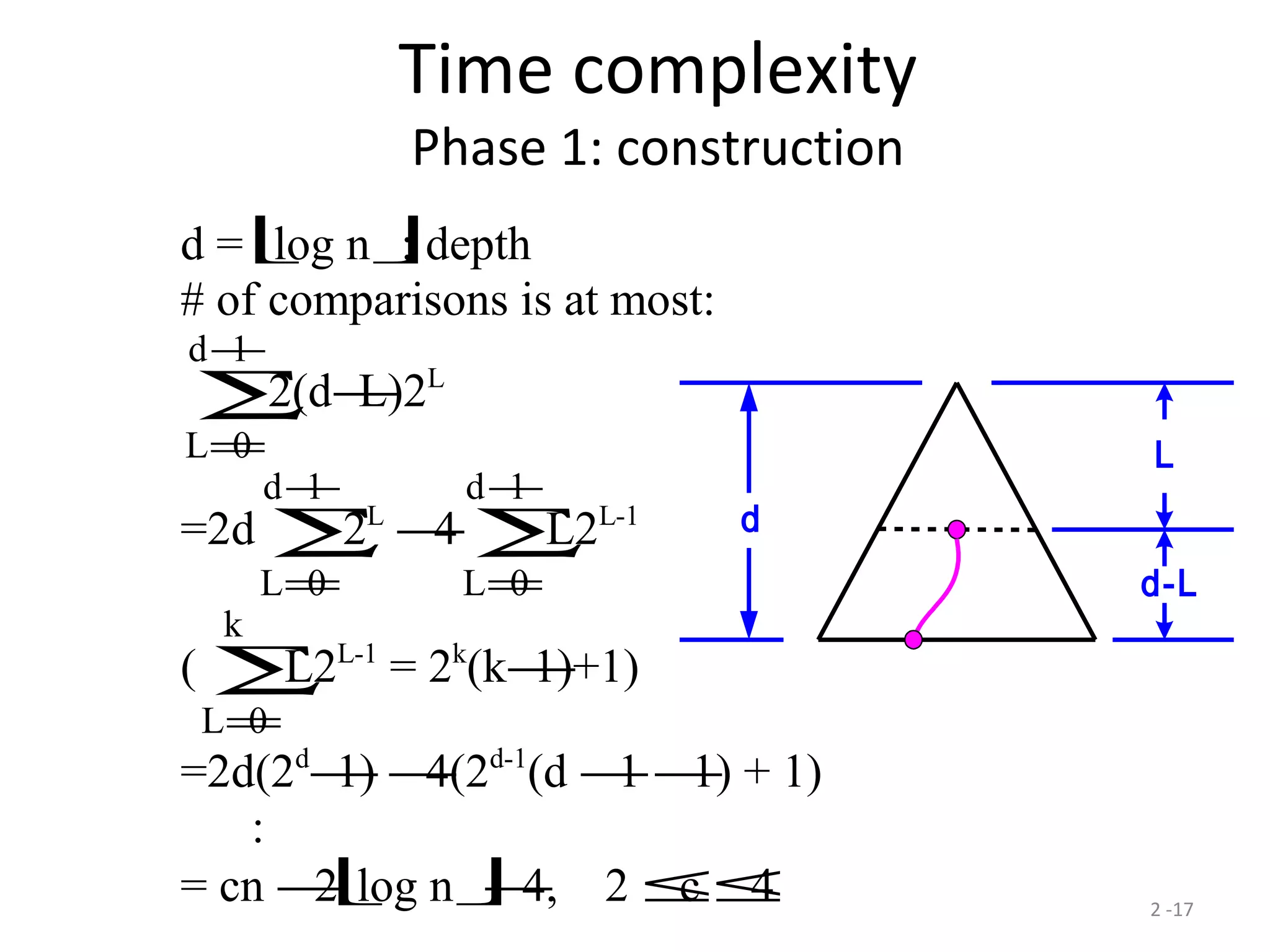
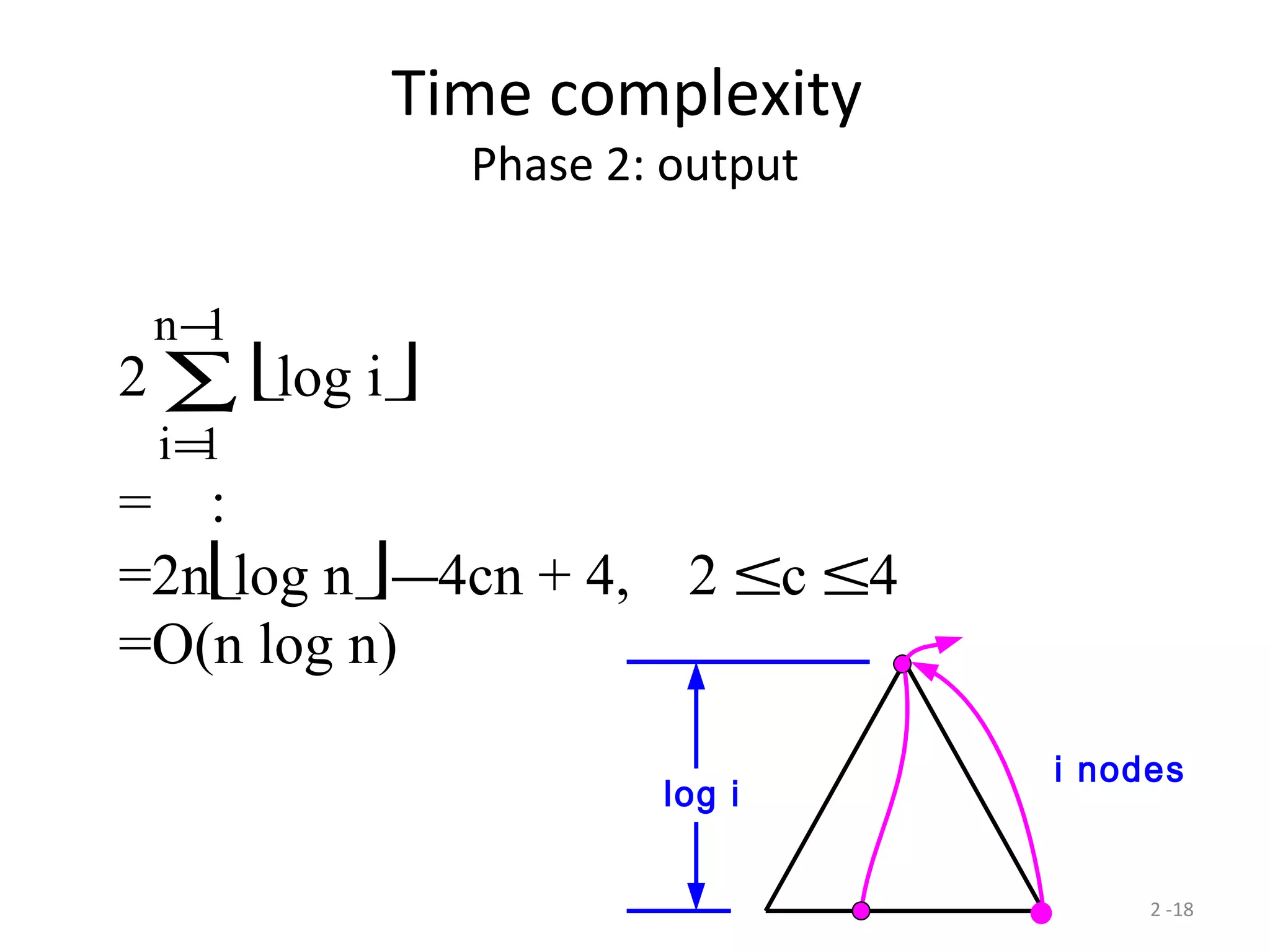
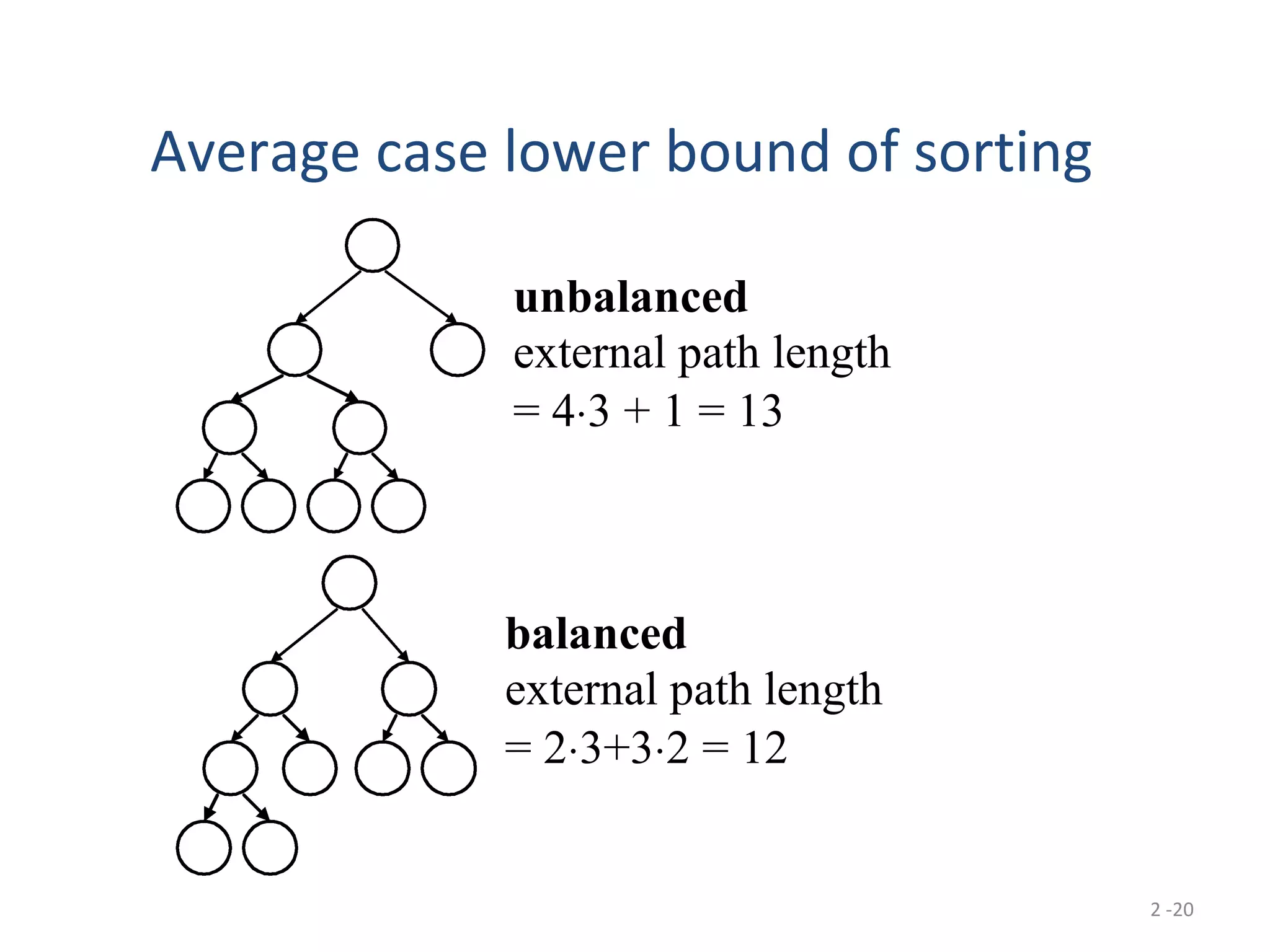
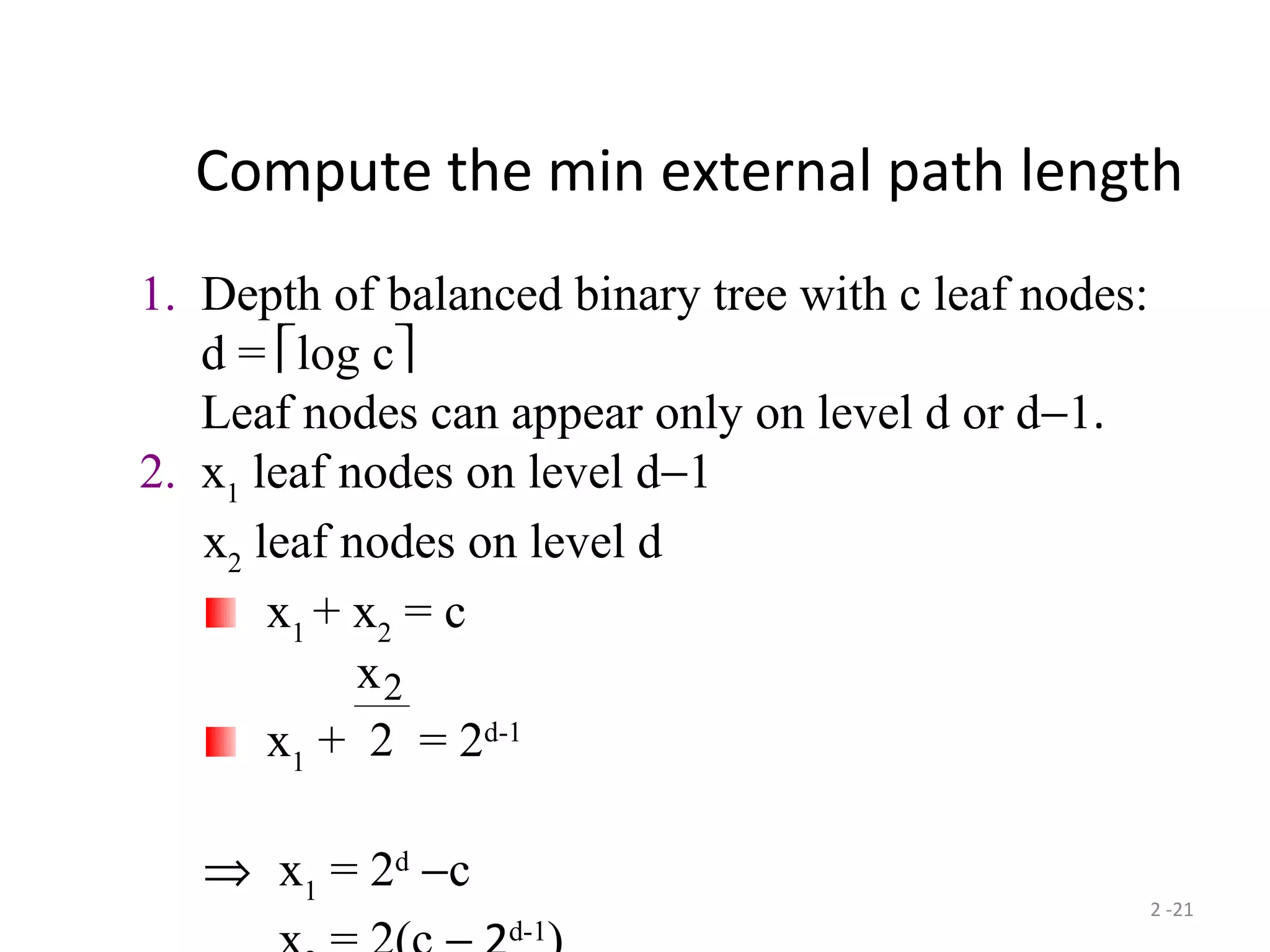
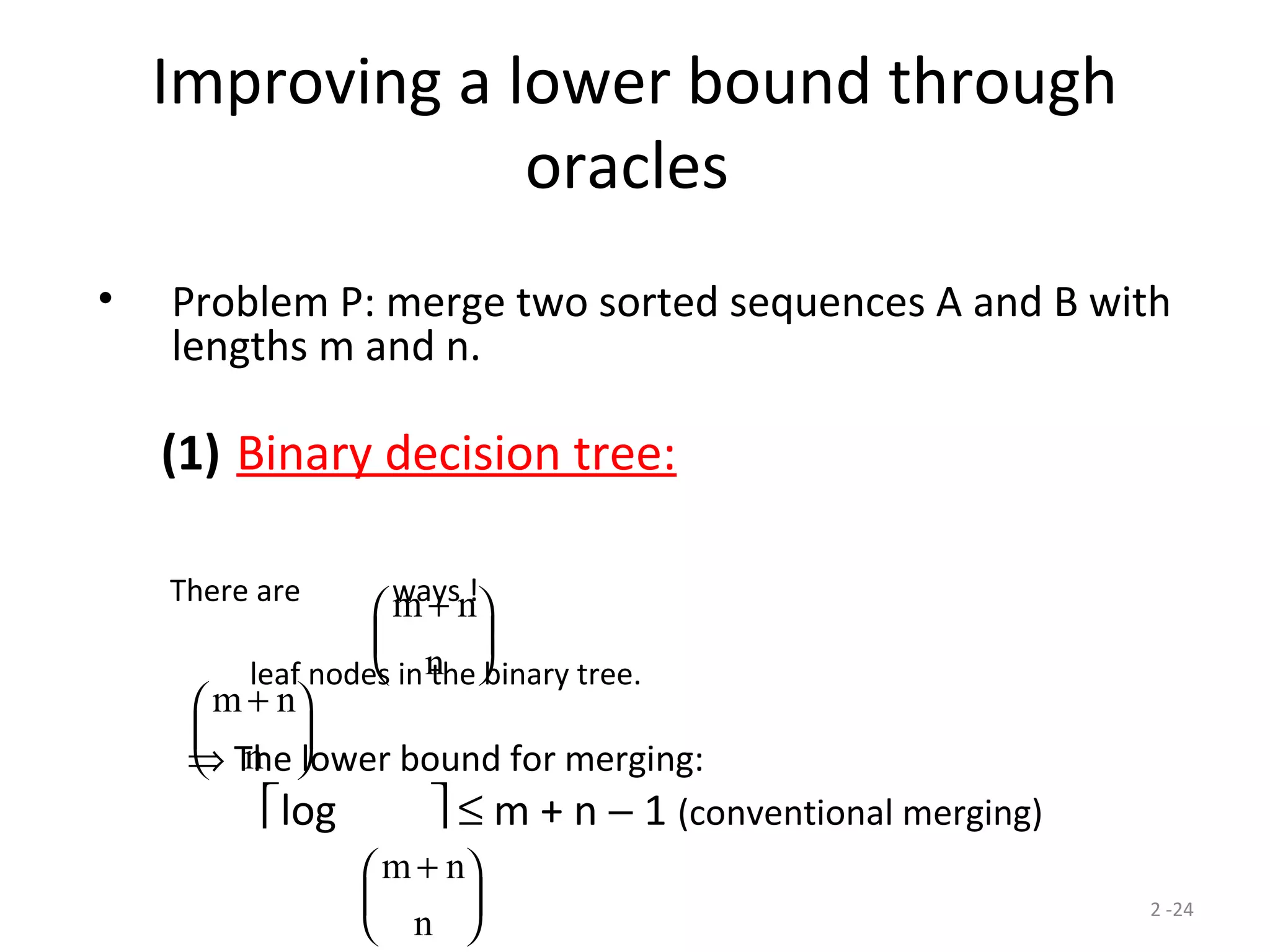
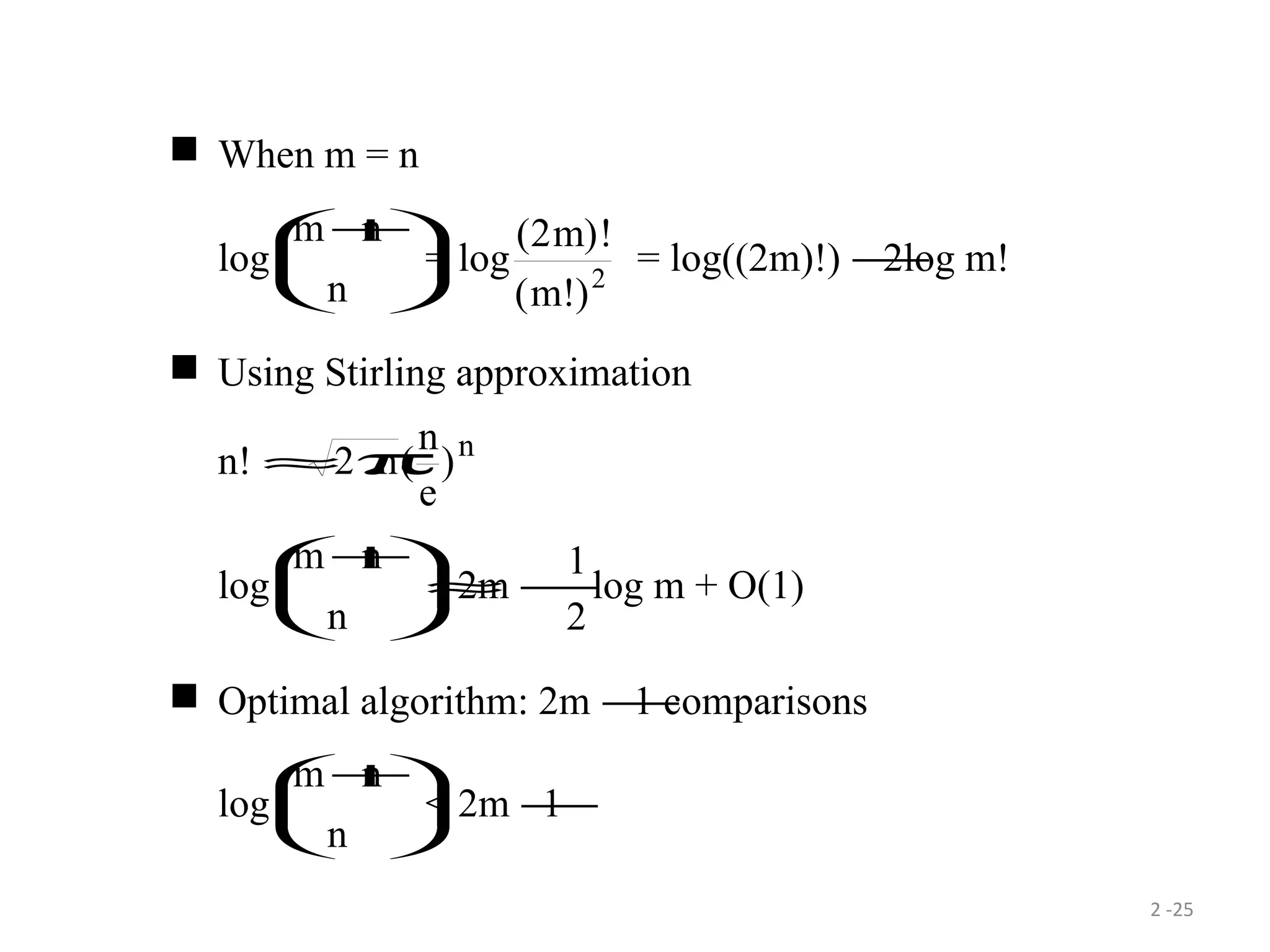
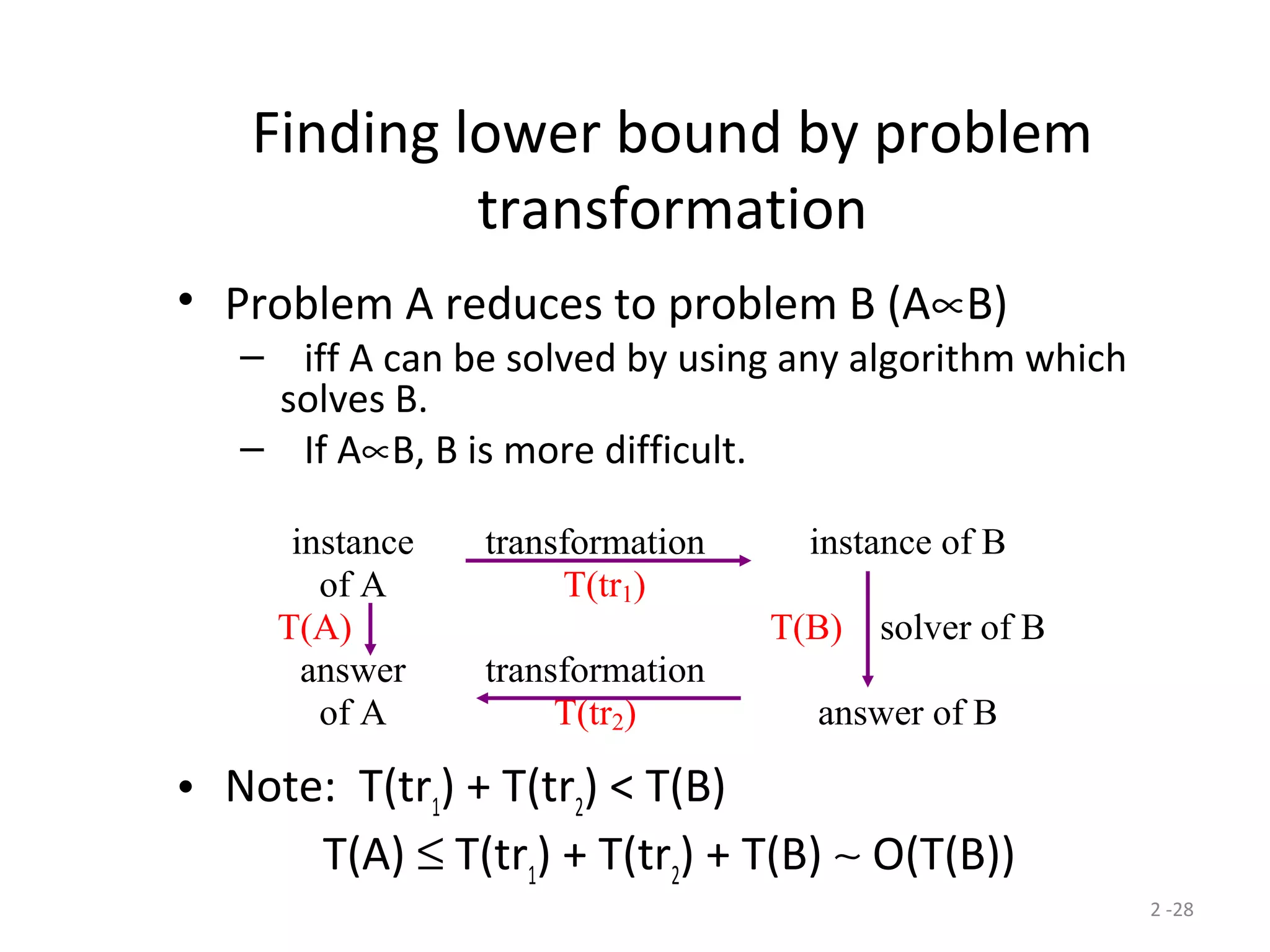
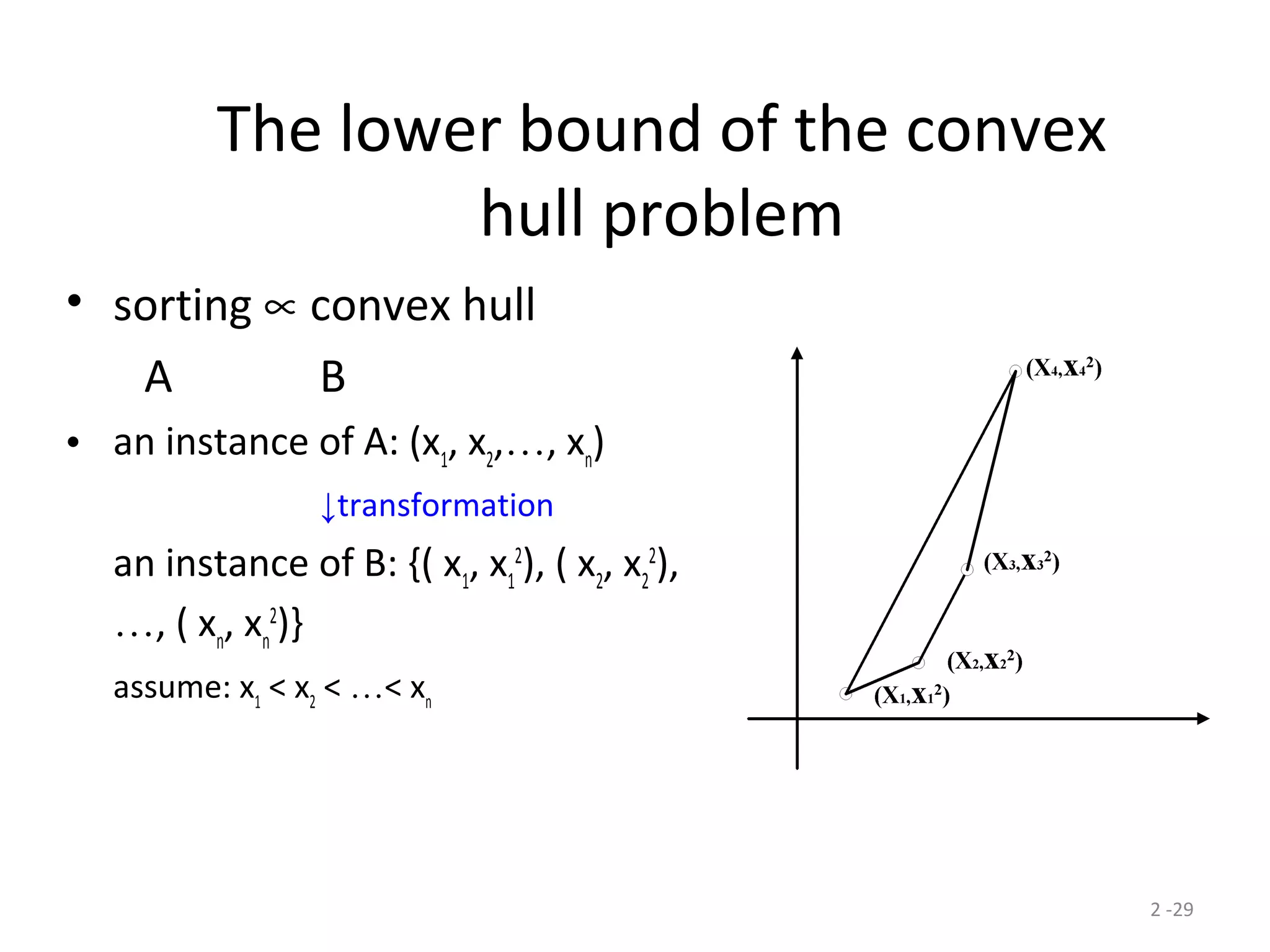
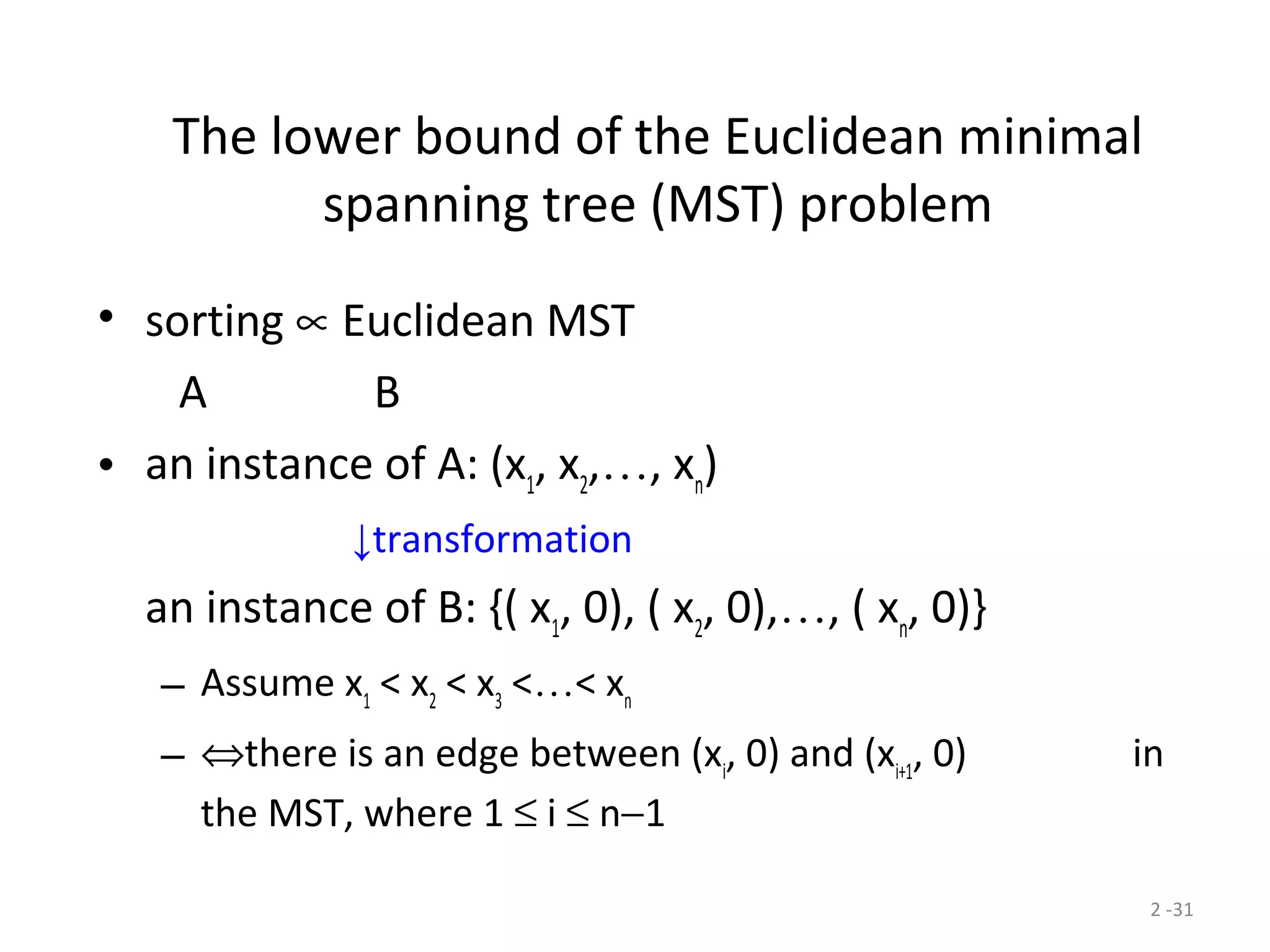
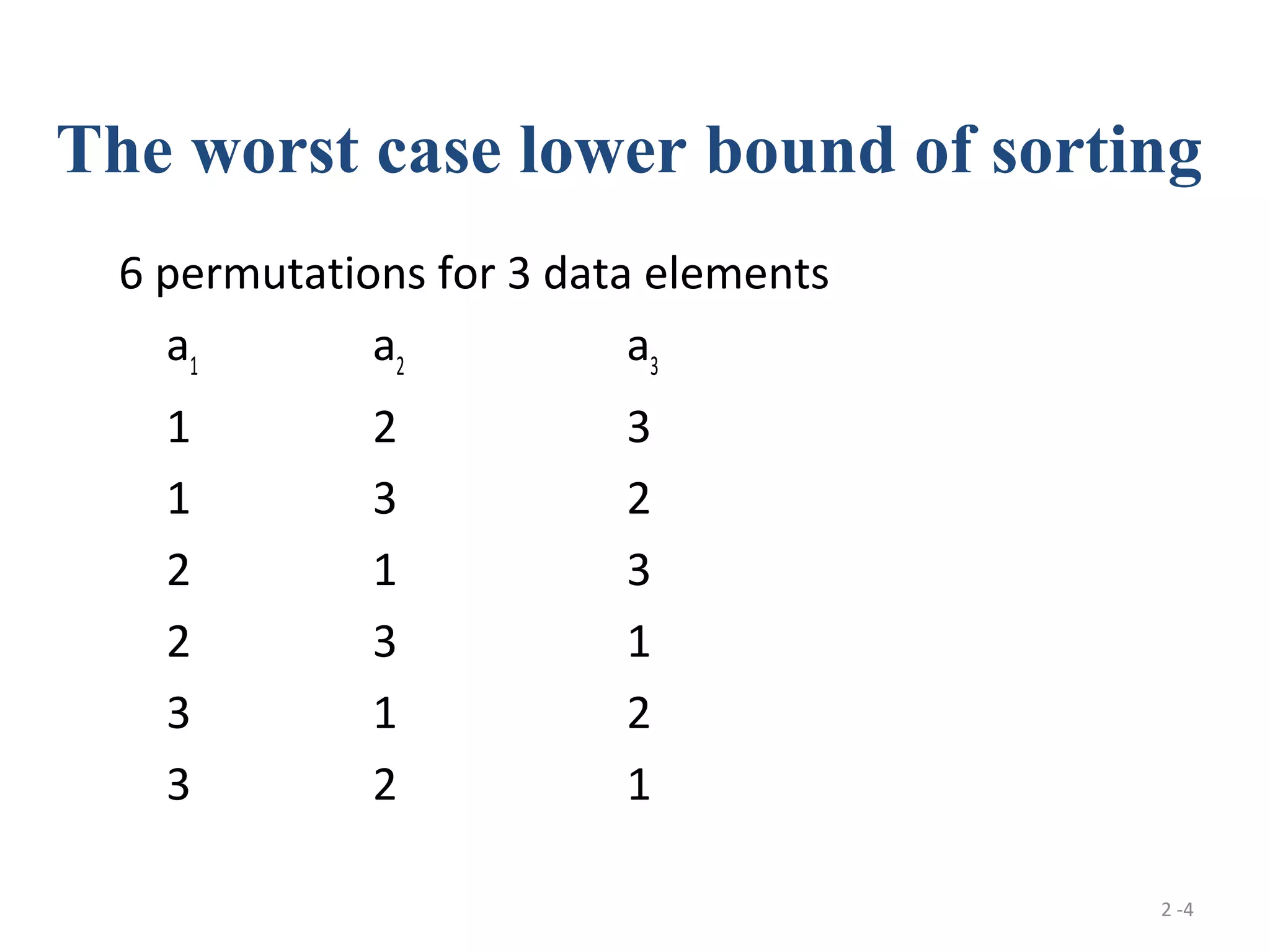
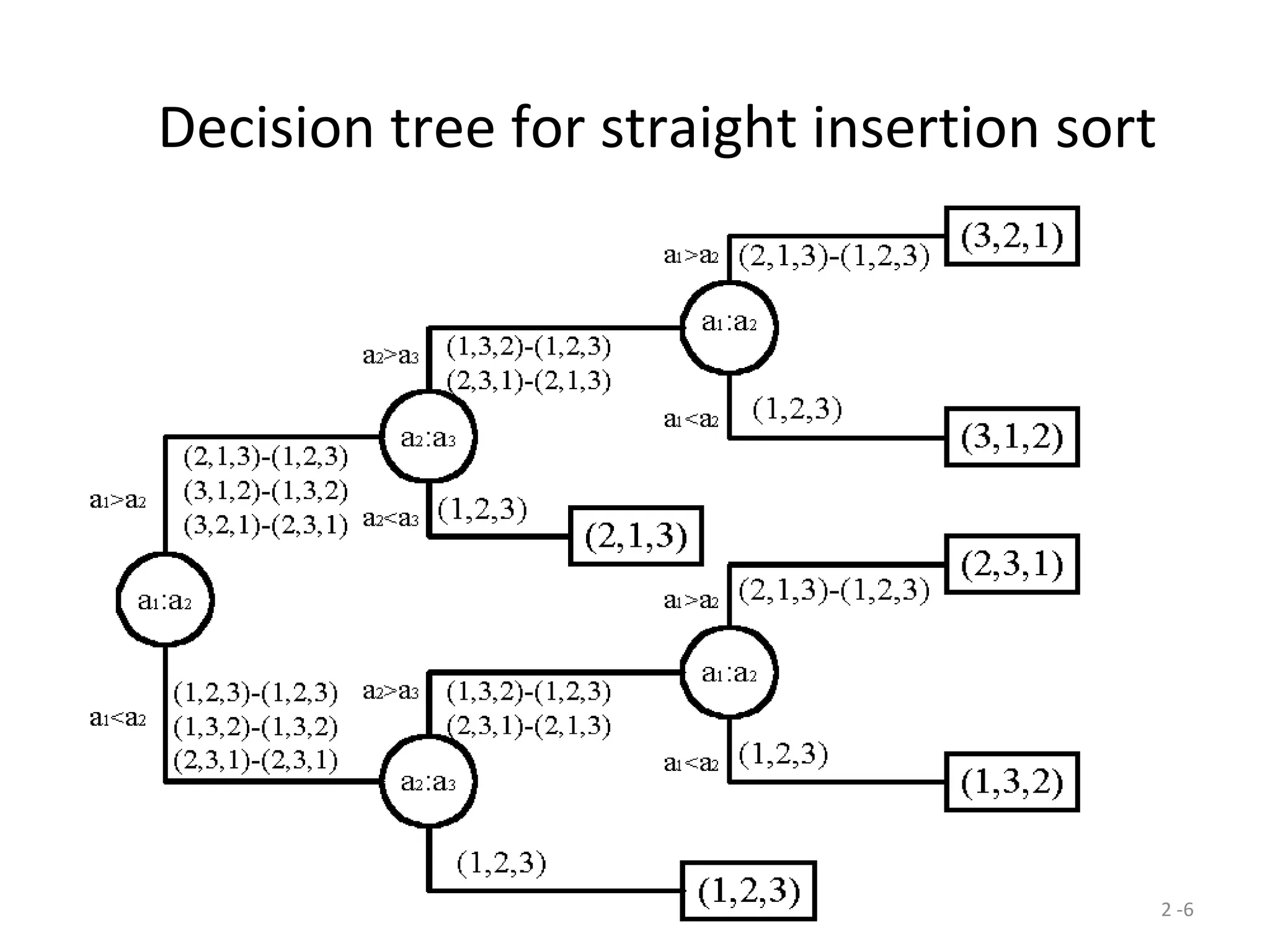
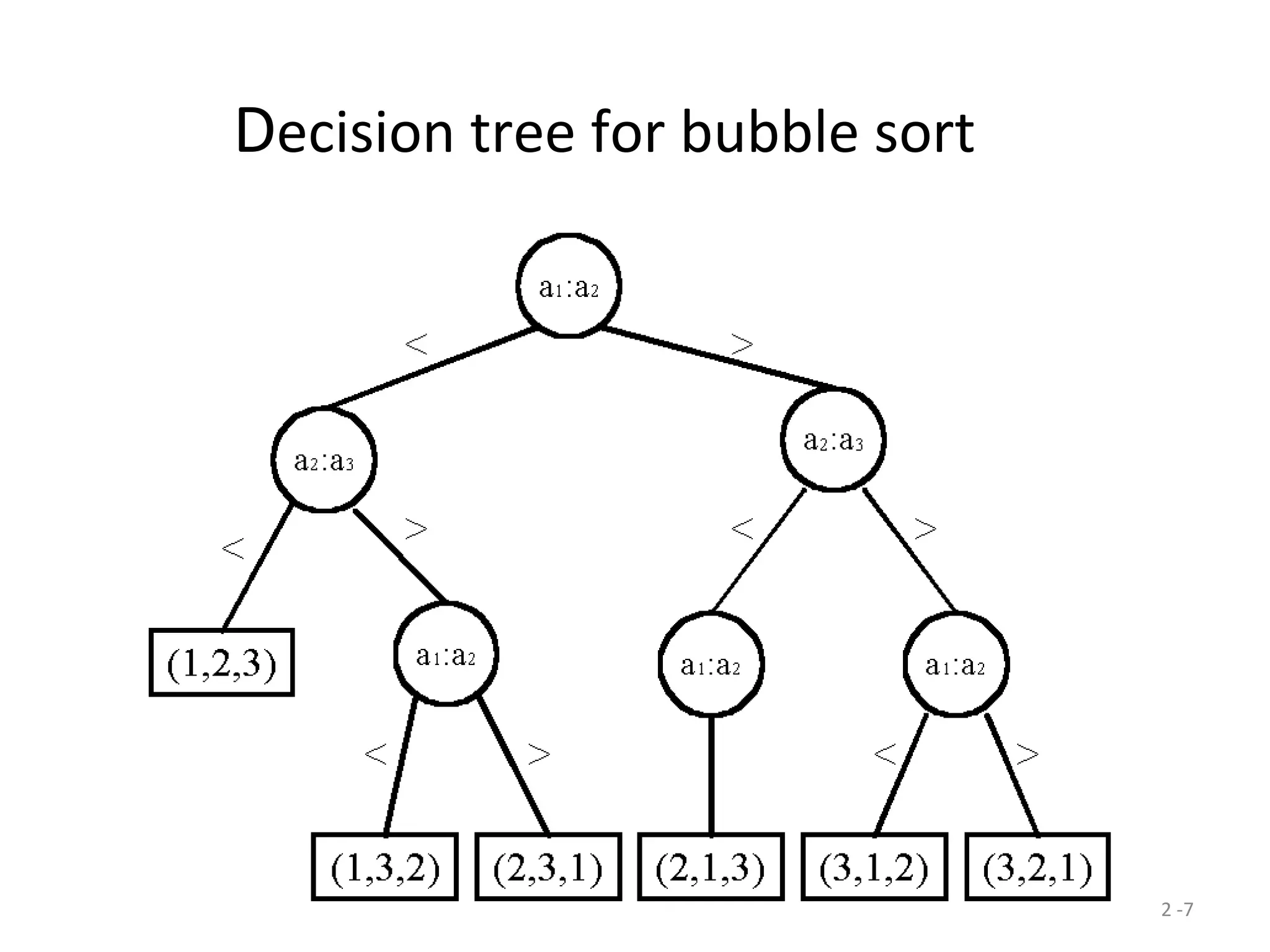
The document discusses lower bounds for sorting algorithms. It shows that the worst case and average case lower bounds for sorting are both Ω(n log n). This lower bound is derived by analyzing the minimum depth of balanced binary decision trees required to represent the n! possible permutations of n elements. Several algorithms, including heapsort, are shown to achieve the optimal time complexity of O(n log n), matching this lower bound. Problem transformations are also introduced as a method for proving lower bounds.





![2 -9
Method 1:
log(n!) = log(n(n− 1)…1)
= log2 + log3 +…+ log n
> log xdx
n
1∫
= log e ln xdx
n
1∫
= log e[ ln ]x x x n
− 1
= log e(n ln n − n + 1)
= n log n − n log e + 1.44
≥ n log n − 1.44n
=Ω (n log n)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/divideandconquer-surfinglowerbounds-170213041011/75/Divide-and-conquer-surfing-lower-bounds-9-2048.jpg)