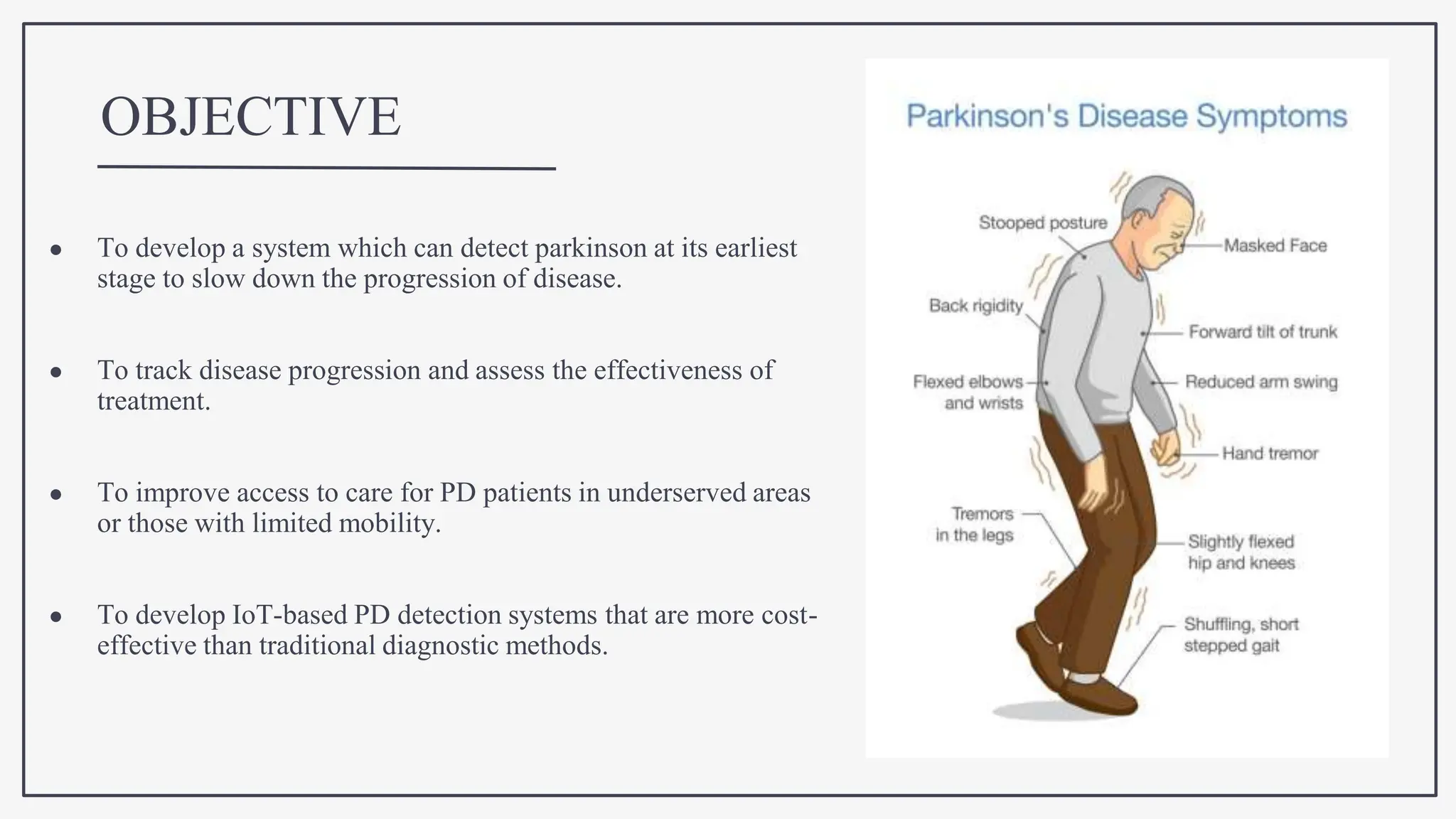
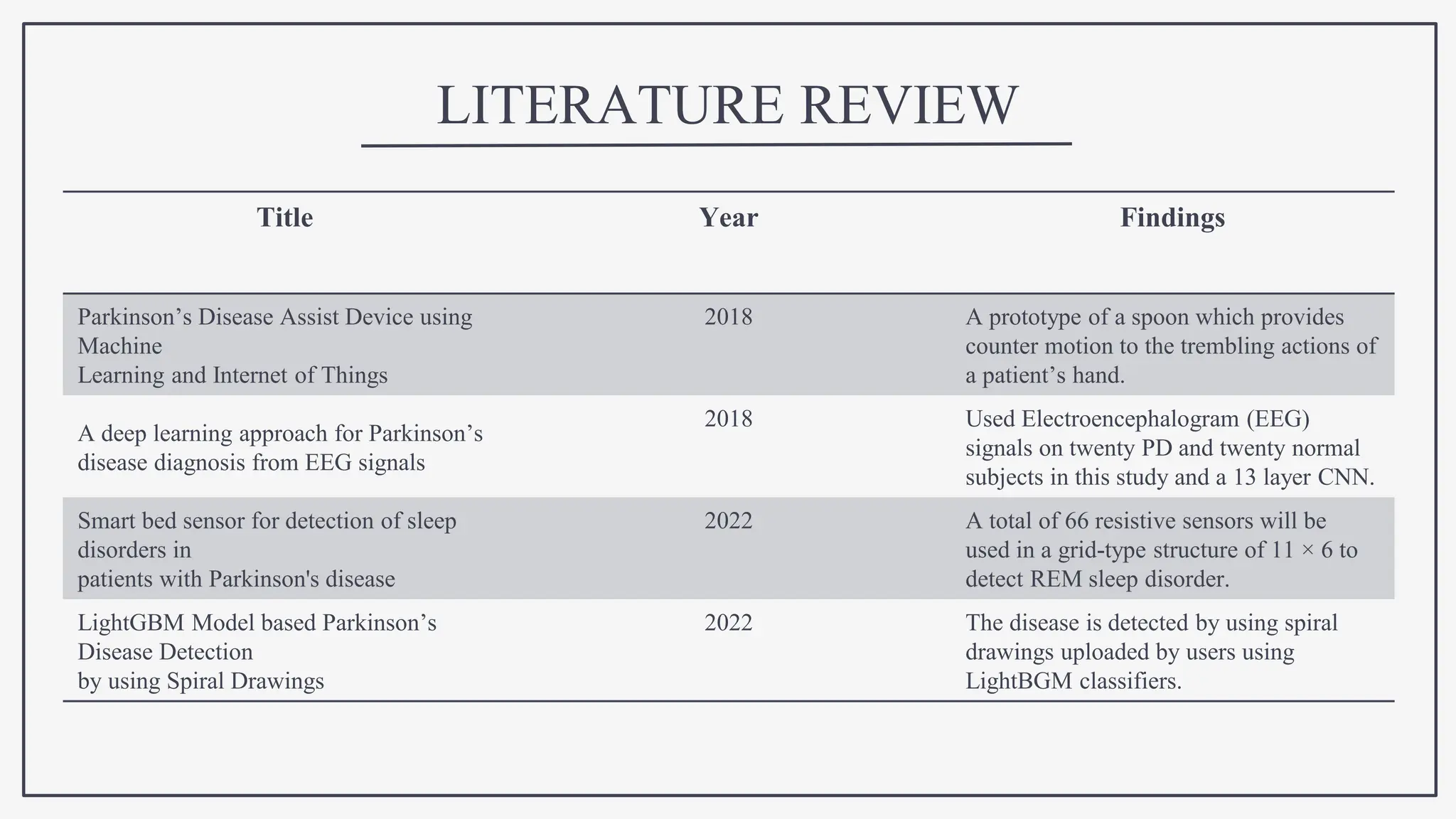
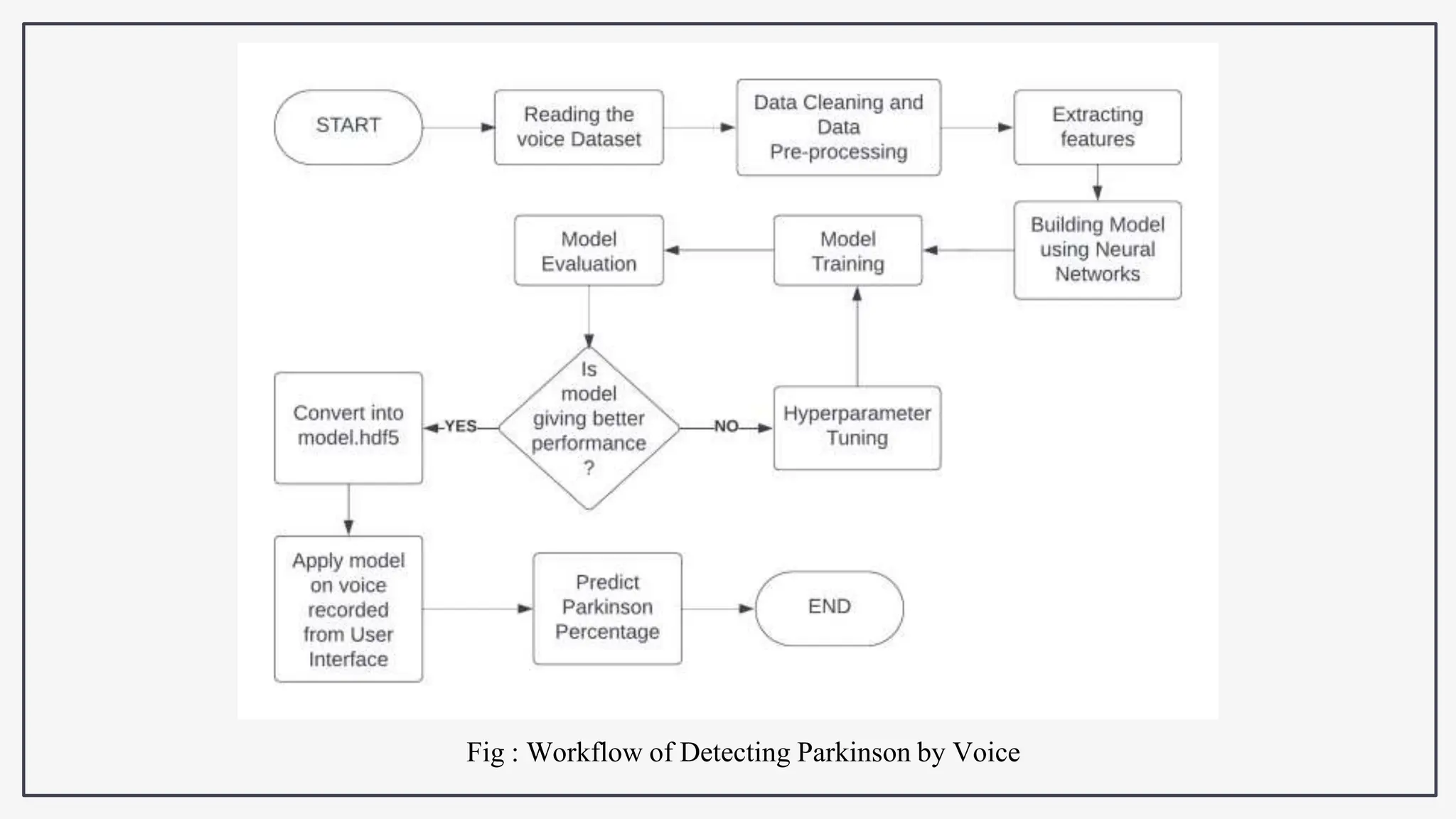
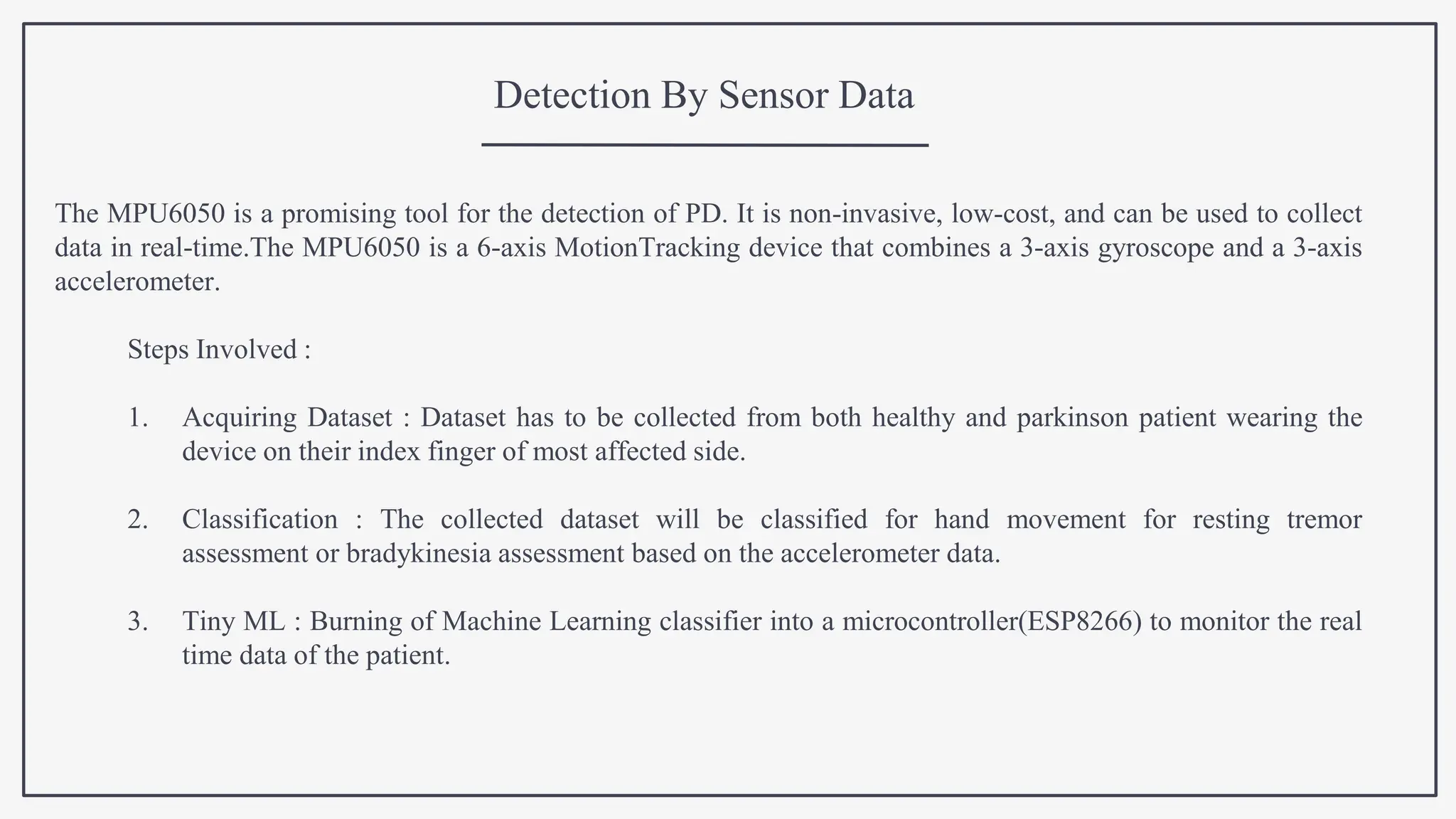
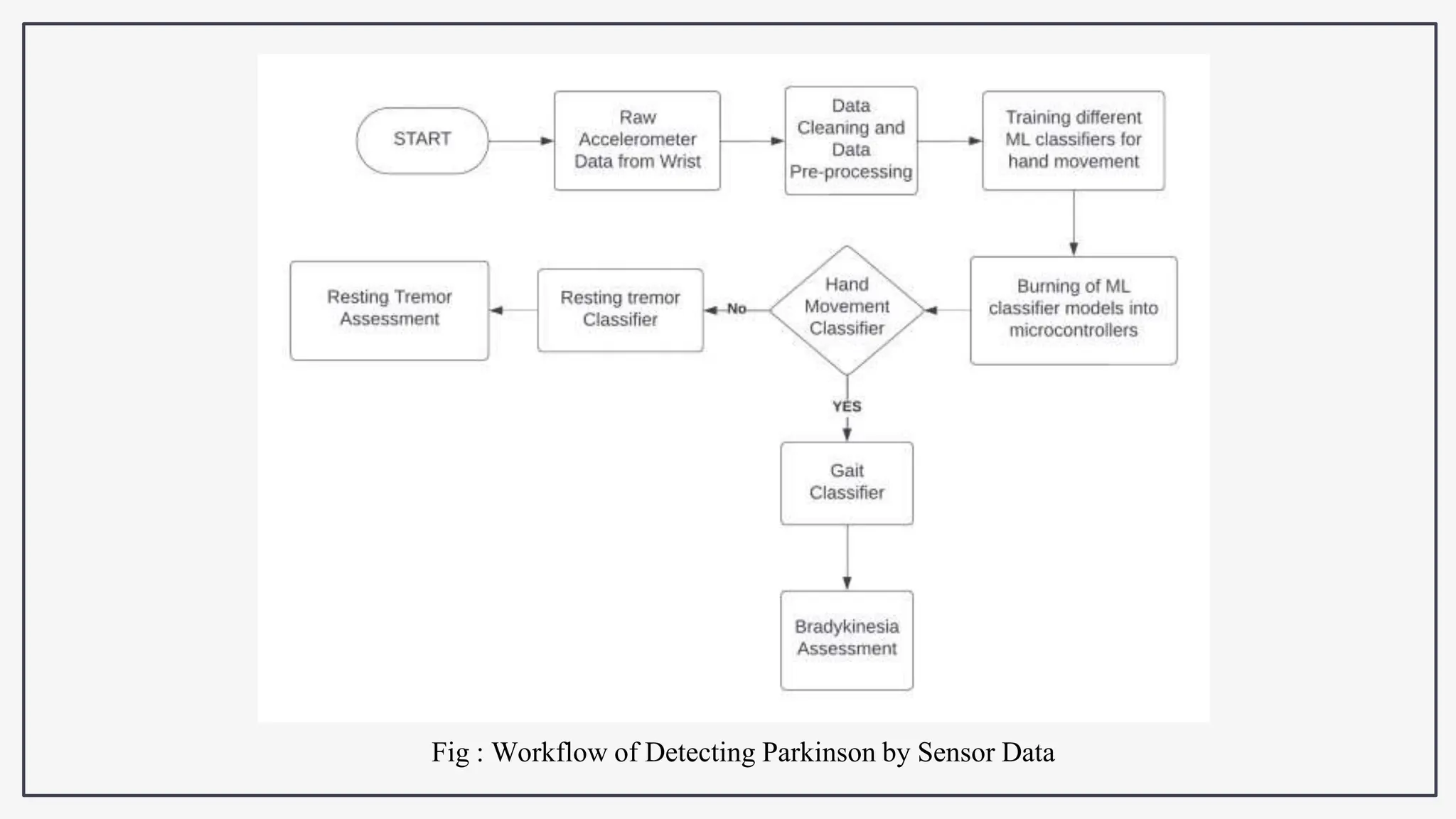
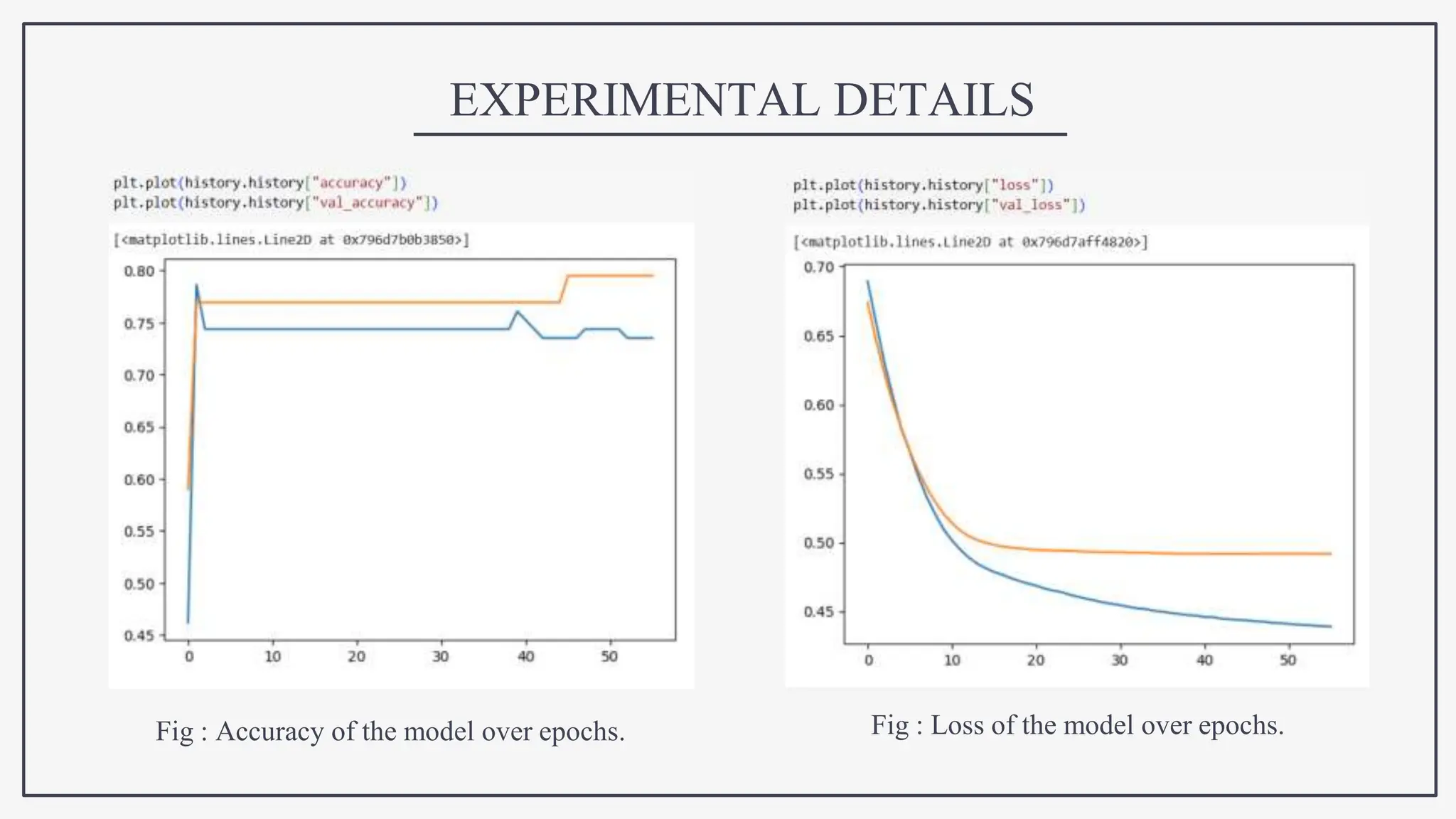
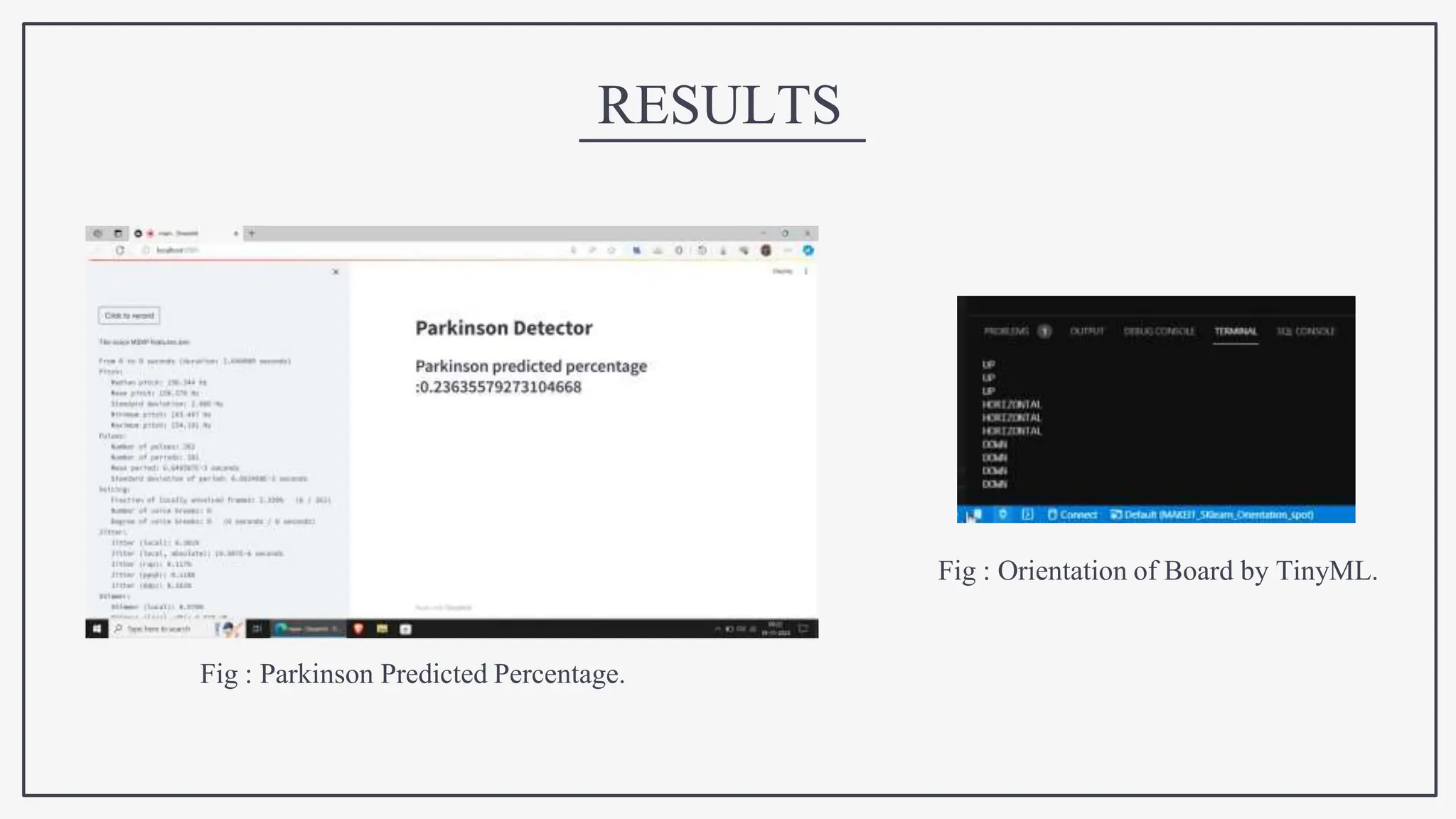
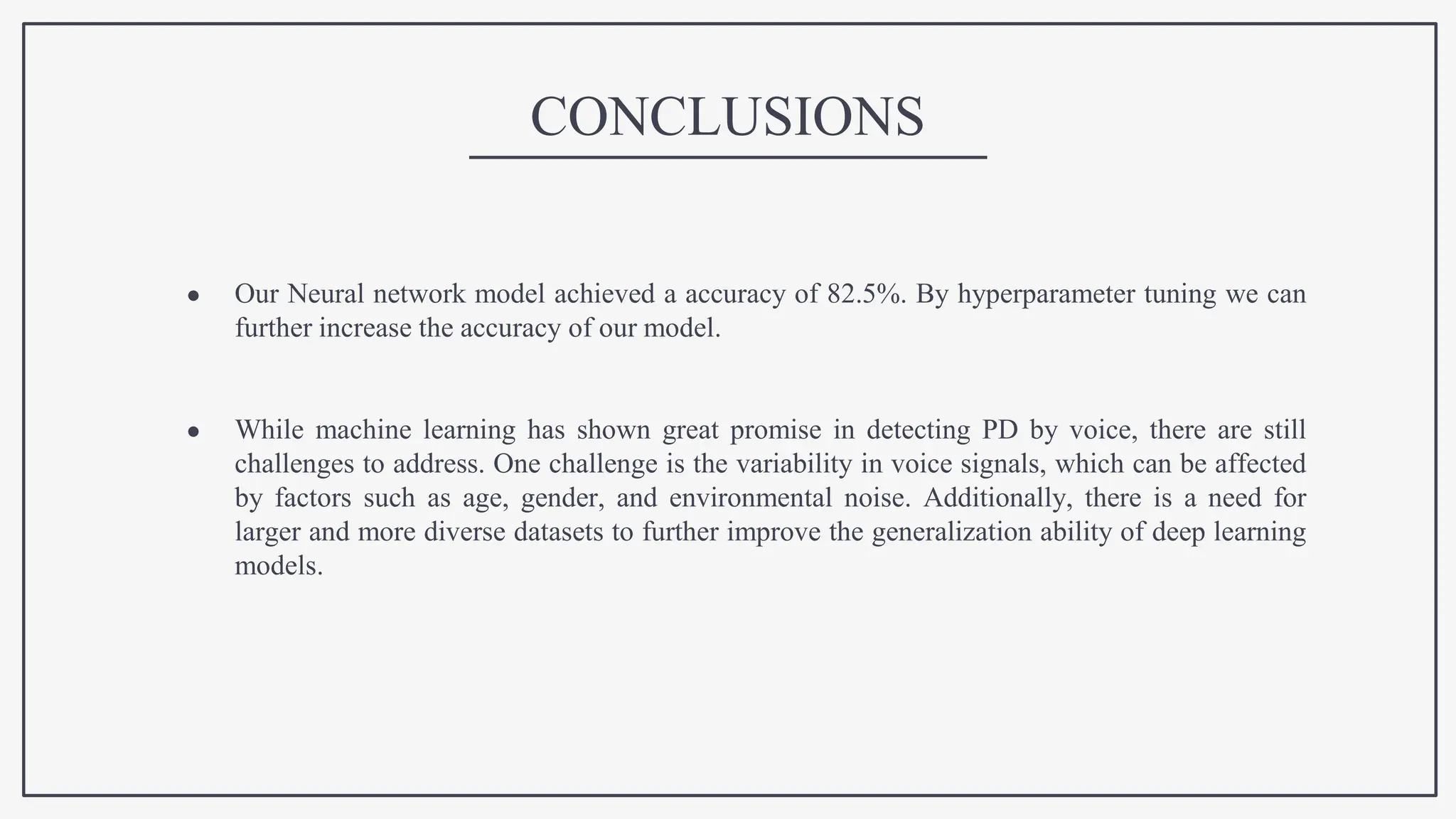
This document proposes using IoT sensors and machine learning to develop an early detection and monitoring system for Parkinson's disease. The objectives are to detect Parkinson's at its earliest stages to slow progression, track disease progression over time, and improve access to care. The proposed methodology uses voice analysis and sensors like accelerometers on the finger to detect movement patterns characteristic of Parkinson's. A neural network model achieved 82.5% accuracy in detecting Parkinson's from sensor data. Further research is needed to improve accuracy and address challenges like voice signal variability.