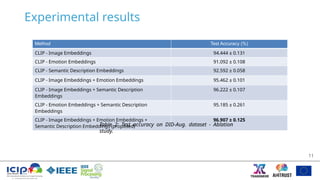
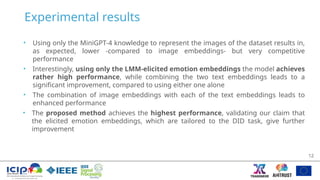
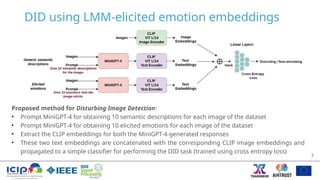
The document presents a method for detecting disturbing images using LMM-elicited emotion embeddings and the Minigpt-4 model, which combines image and text processing. The proposed approach significantly improves detection accuracy compared to existing models by leveraging semantic descriptions and emotion recognition in the classification of images. Experimental results show it outperforms state-of-the-art methods, addressing the significant challenges in disturbing image detection.

![Problem statement
• Disturbing Image Detection (DID): detecting content in images that can cause
trauma to viewers
• It may include images that depict violence, pornography, animal cruelty
• Such content elicits anxiety or/and fear to viewers
• DID is a task of significant importance
• Limited literature due to the challenging nature of creating datasets, restricting,
in turn, the generalization ability of the trained models
○ [1] proposed a framework that exploits large-scale multimedia datasets so as
to automatically extend initial training datasets with hard examples. An
EfficientNet-b1 is trained on the augmented dataset for addressing the DID
task.
3
[1] Sarridis, Ioannis, et al. "Leveraging large-scale multimedia datasets to refine content moderation models." 2022 IEEE
Eighth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM). IEEE, 2022.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icipw2024mezaris-241103150946-0c3be854/85/Disturbing-Image-Detection-Using-LMM-Elicited-Emotion-Embeddings-3-320.jpg)
![Motivation
• Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance in
several downstream vision recognition tasks
• Goal: Address the DID task exploiting knowledge encoded in LLMs and
particularly in Large Multimodal Models (LMMs)
• [2] proposed to use an LMM in order to extract semantic descriptions for the
images of a dataset, and use them in order to address generic image
classification tasks
• Apart from these generic semantic descriptions, we propose to extract responses
linked with a complementary task, i.e., emotion recognition
• We argue that we can advance the performance in the DID task by also extracting
LMM-elicited emotions for each image of the dataset
4
[2] Tzelepi, Maria, and Vasileios Mezaris. "Exploiting LMM-based knowledge for image classification tasks."
International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icipw2024mezaris-241103150946-0c3be854/85/Disturbing-Image-Detection-Using-LMM-Elicited-Emotion-Embeddings-4-320.jpg)
![Preliminaries: MiniGPT-4
• GPT-4 is the first model to accept both
text and image input, producing text
output, however the technical details
behind GPT-4 remain undisclosed
• MiniGPT-4 aligns a frozen visual
encoder with a frozen LLM, using a
single projection layer
- LLM: Vicuna
- Visual encoder: ViT-G/14 from
EVA- CLIP and a Q-Former network
• MiniGPT-4 only requires training the
linear projection layer to align the
visual features with the LLM
5
The MiniGPT-4 model [3]
[3] Zhu, Deyao, et al. "Minigpt-4: Enhancing vision-language understanding with advanced large language models."
arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.10592 (2023).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icipw2024mezaris-241103150946-0c3be854/85/Disturbing-Image-Detection-Using-LMM-Elicited-Emotion-Embeddings-5-320.jpg)
![Preliminaries: CLIP
• CLIP comprises of an image and text encoder
• It is trained with (image,text) pairs for
predicting which of the possible pairs actually
occurred
• To do so, it learns a multimodal embedding
space by jointly training the image and text
encoders to maximize the cosine similarity of
the real image and text embeddings, while
minimizing the cosine similarity of the
embeddings of the incorrect pairs
• CLIP provides outstanding zero-shot
classification performance
• Another approach is to use the CLIP image
encoder for extracting the corresponding
embeddings and use them with a classifier 6
The CLIP model [4]
[4] Radford, Alec, et al. "Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision." International
conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2021.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icipw2024mezaris-241103150946-0c3be854/85/Disturbing-Image-Detection-Using-LMM-Elicited-Emotion-Embeddings-6-320.jpg)

![Experimental results
10
• The proposed method significantly improves the baseline performance (using only
image embeddings) in terms of accuracy, accomplishing also superior performance
over current state-of-the-art
[1] Sarridis, Ioannis, et al. "Leveraging large-scale multimedia datasets to refine content moderation models." 2022 IEEE
Eighth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM). IEEE, 2022.
[4] Radford, Alec, et al. "Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision." International
conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2021.
Method Test Accuracy (%)
CLIP - Image Embeddings
[4]
94.444
EfficientNet-b1 [1] 95.000
CLIP - Proposed 96.907
Table 1: Test accuracy on DID-Aug. dataset - Comparison with state-of-
the-art.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icipw2024mezaris-241103150946-0c3be854/85/Disturbing-Image-Detection-Using-LMM-Elicited-Emotion-Embeddings-10-320.jpg)