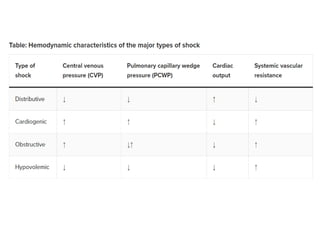
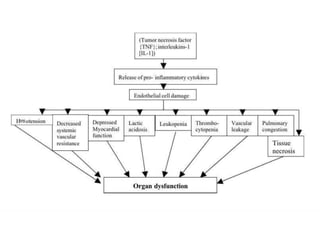
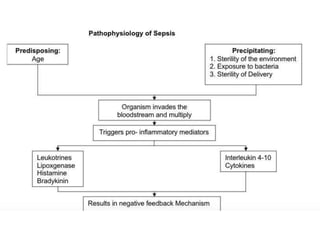
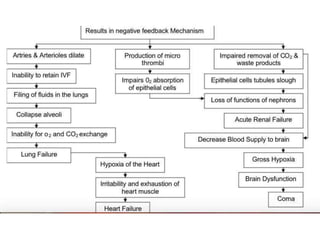
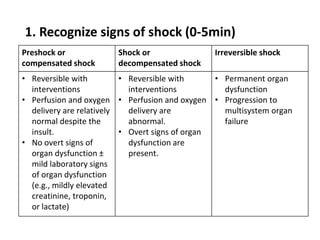
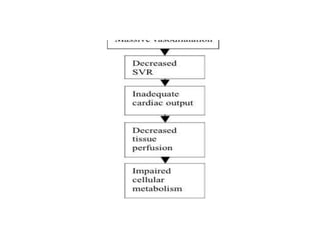
1. Distributive shock is caused by inadequate tissue perfusion despite normal cardiac output and blood volume due to maldistribution of blood flow. Common causes include septic shock, anaphylactic shock, and neurogenic shock.
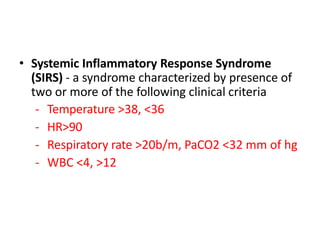
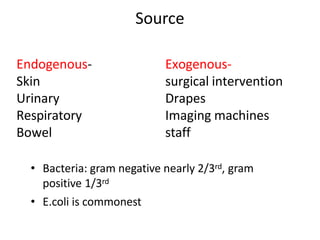
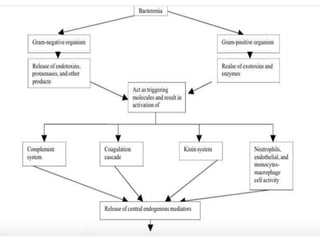
2. Septic shock occurs when sepsis leads to dysfunction of the cardiovascular system and tissues due to systemic inflammation. It requires prompt fluid resuscitation and vasopressor treatment to maintain blood pressure and tissue perfusion.
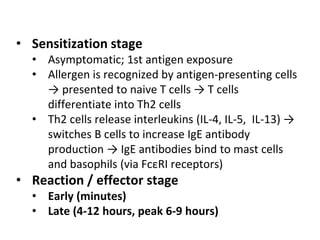
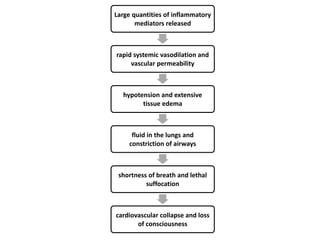
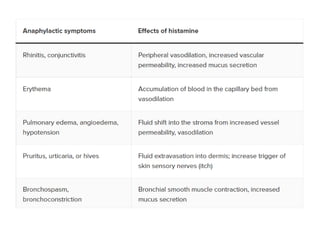
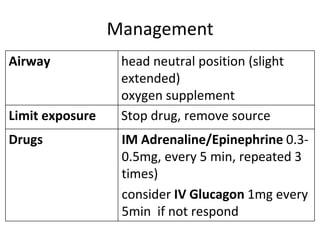
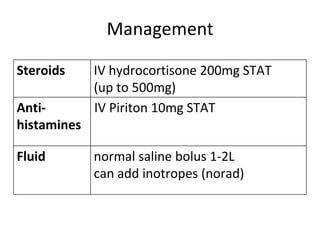
3. Anaphylactic shock results from a systemic allergic reaction. It causes rapid hypotension, bronchospasm, and edema. Treatment involves epinephrine, steroids, fluids, and monitoring for biphasic reactions.
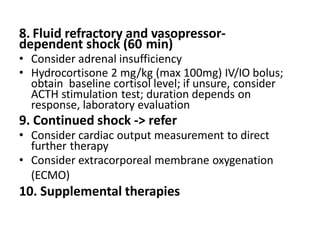
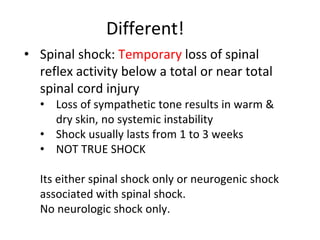
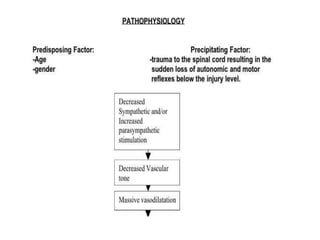
4. Neurogenic