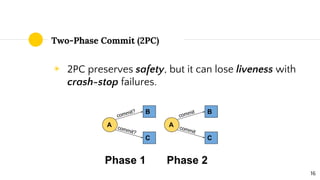
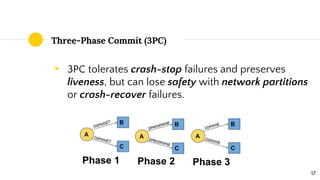
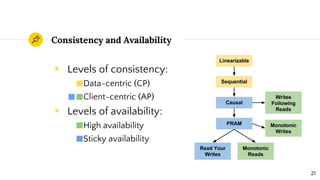
Distributed systems theory can help understand challenges like scalability, fault tolerance, and consistency. Key concepts include interaction models, failure modes, and consensus algorithms. The CAP theorem states that a distributed system cannot achieve both consistency and availability during network partitions. Hazelcast uses an eventually consistent asynchronous replication model, providing sticky availability with the possibility of losing consistency during failures. Understanding fundamental distributed systems principles prepares engineers for an ever-changing landscape of technologies.