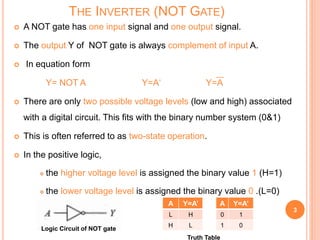
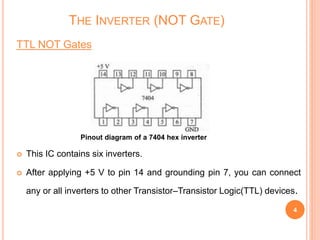
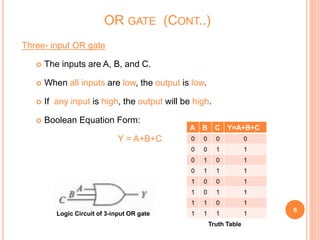
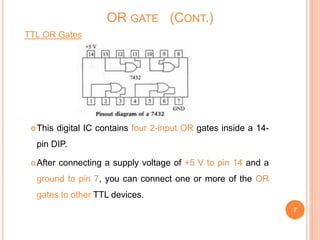
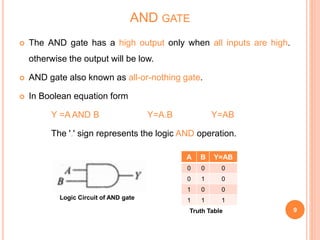
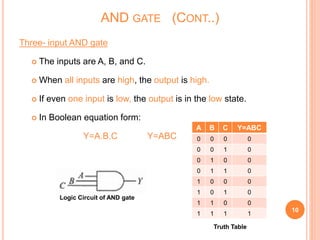
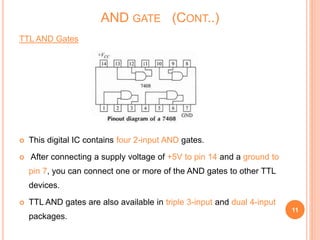
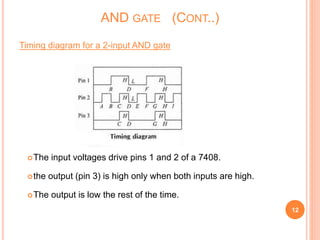
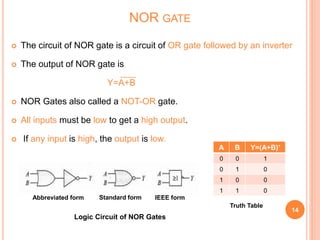
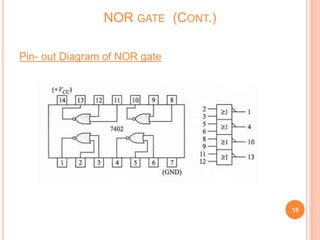
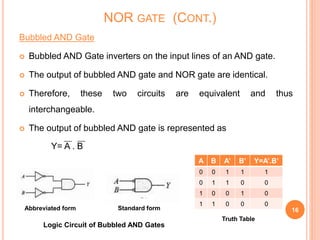
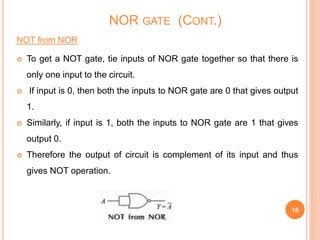
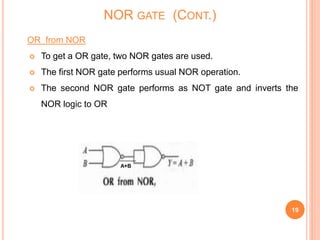
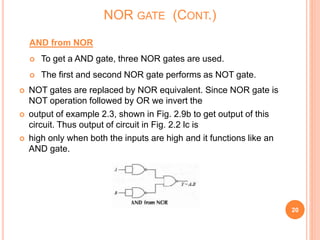
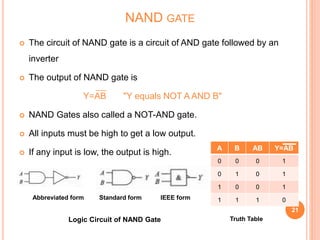
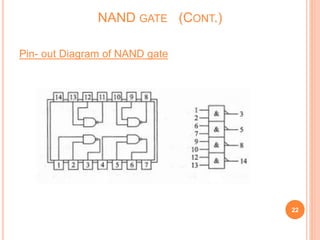
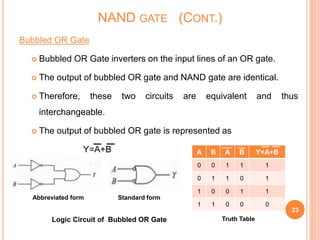
This document discusses digital logic gates. It begins by defining a gate as a digital circuit with one or more inputs and one output. The three basic gates are described as the NOT, OR, and AND gates. Additional universal gates, the NAND and NOR gates, are introduced. Truth tables are provided to explain the output of each gate for all possible input combinations. The document also discusses how to derive different gate functions using NAND and NOR gates alone through De Morgan's theorems.