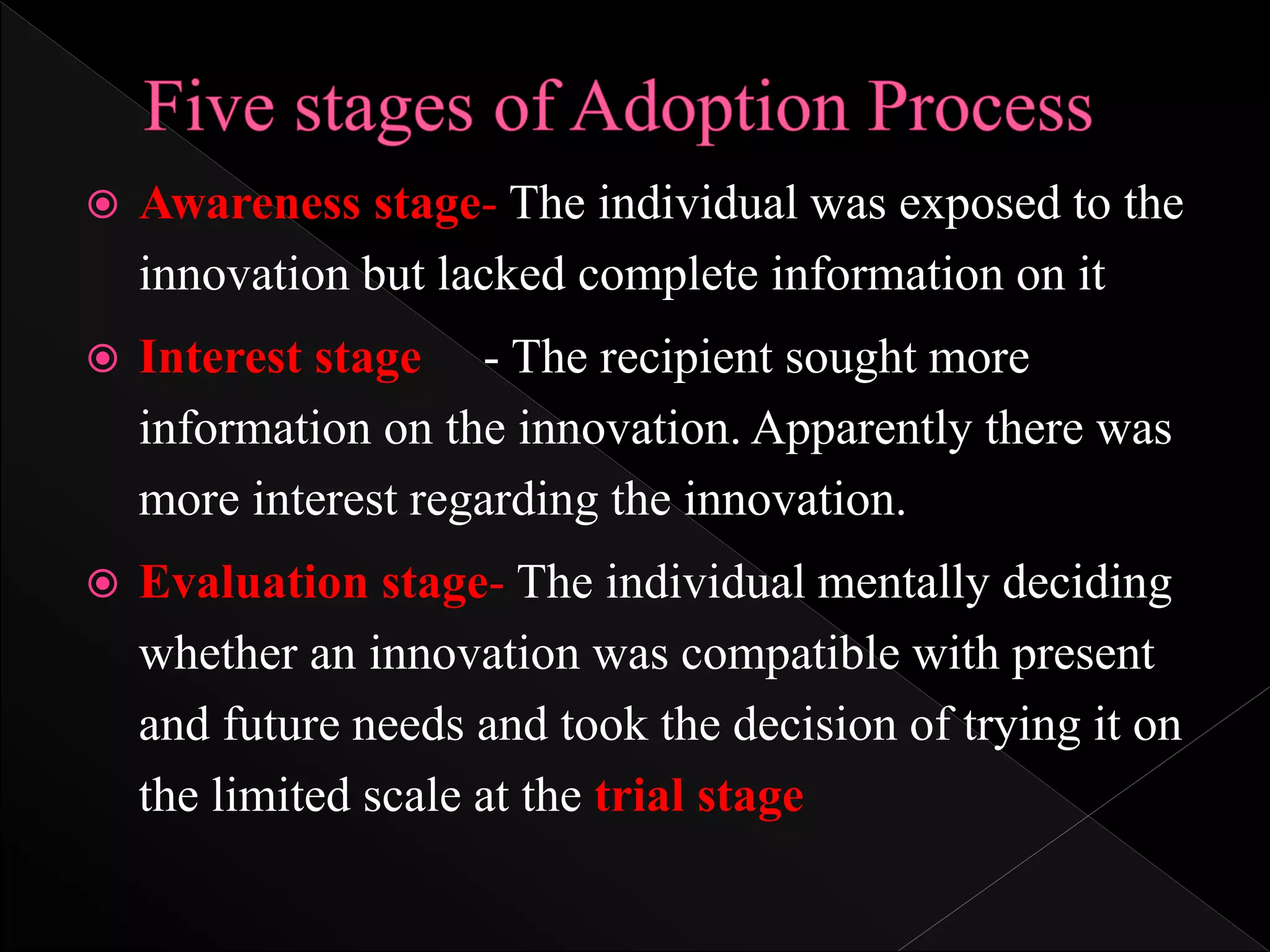
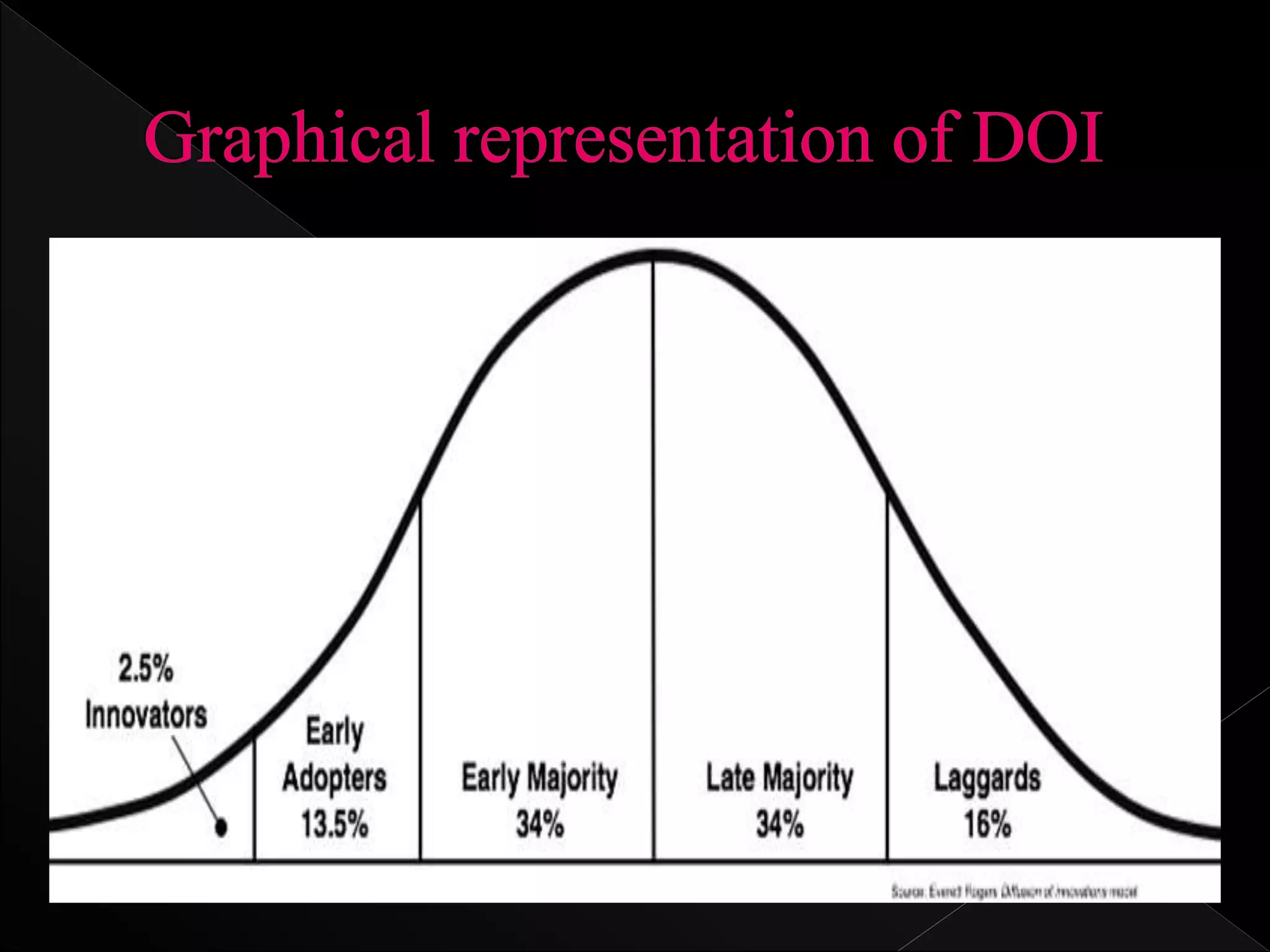
Diffusion is the process by which an innovation spreads through a social system over time through communication channels. It involves spreading new ideas and insights, such as what qualities make an innovation spread, the importance of peer networks, and understanding different user needs. Rogers developed the diffusion of innovation theory in 1962 to explain how, why, and at what rate new ideas and technologies spread through cultures. The theory describes the process of adoption where individuals first learn of an innovation, then form an opinion, make a decision, implement the innovation, and seek reinforcement. There are five stages of adoption - knowledge, persuasion, decision, implementation, and confirmation.