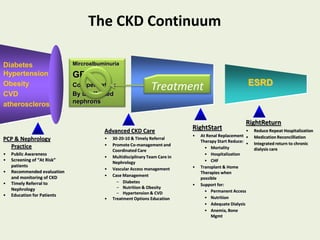
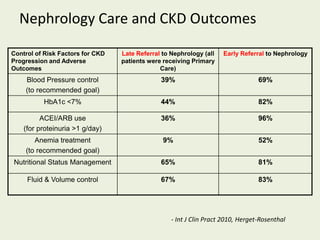
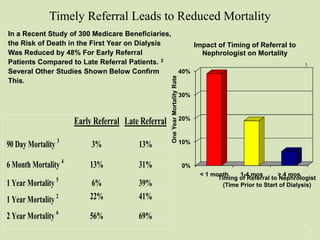
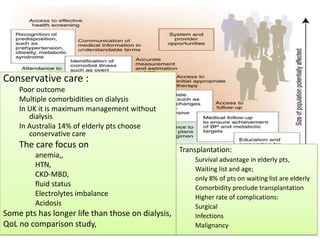
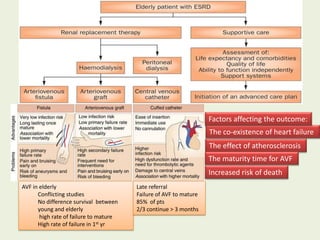
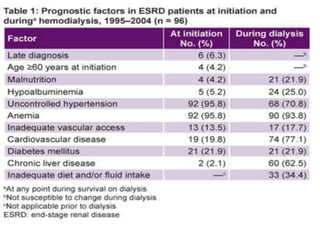
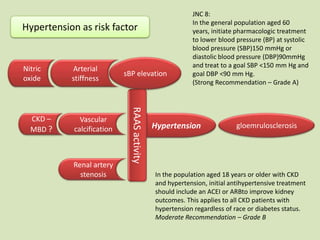
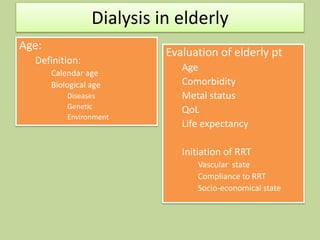
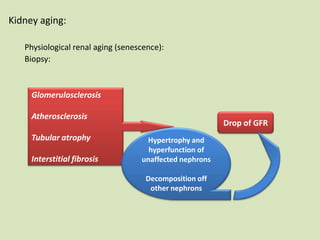
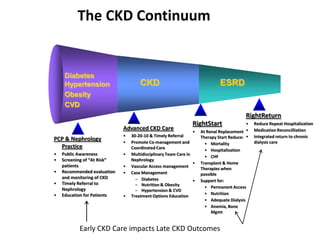
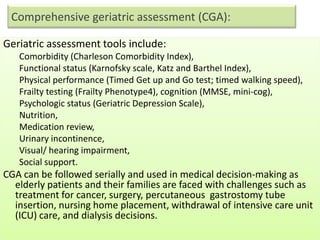
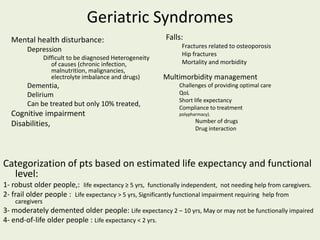
This document discusses dialysis in elderly patients. It notes that biological age is more important than calendar age when evaluating elderly patients for dialysis. Initiation of renal replacement therapy requires consideration of comorbidities, mental status, quality of life, life expectancy, vascular access, and socioeconomic factors. Dialysis in elderly patients is associated with higher rates of comorbidities like atherosclerosis and fewer vascular access options. Conservative care without dialysis is an alternative for some elderly patients with multiple comorbidities. Quality of life assessments are important when considering dialysis for elderly patients.

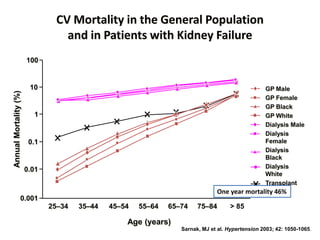


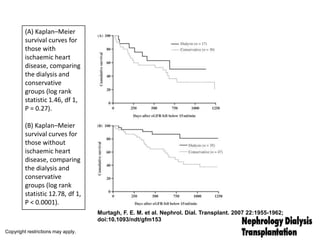
![Survival of patients aged ≥75 years initiating dialysis in Australia between January 2002 and
December 2005 (Kaplan–Meier curves) with 95% CIs compared with survival of 75- and 80-
year-olds from the general Australian population [23].
Foote C et al. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012;ndt.gfs096
© The Author 2012. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights
reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dialysisinelderlypatientswkd2014-140314124747-phpapp02/85/Dialysis-in-elderly-patients-wkd-2014-11-320.jpg)