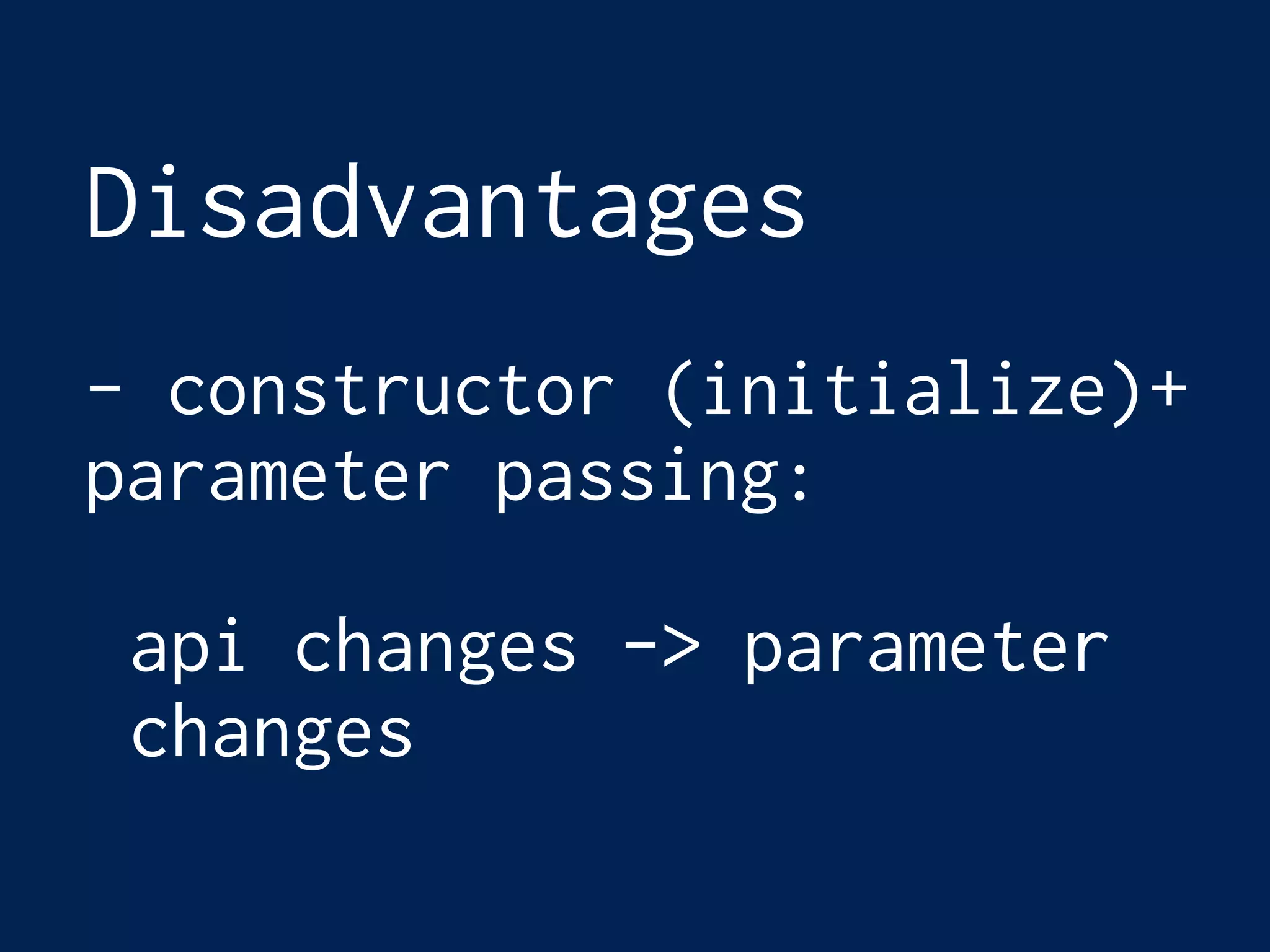
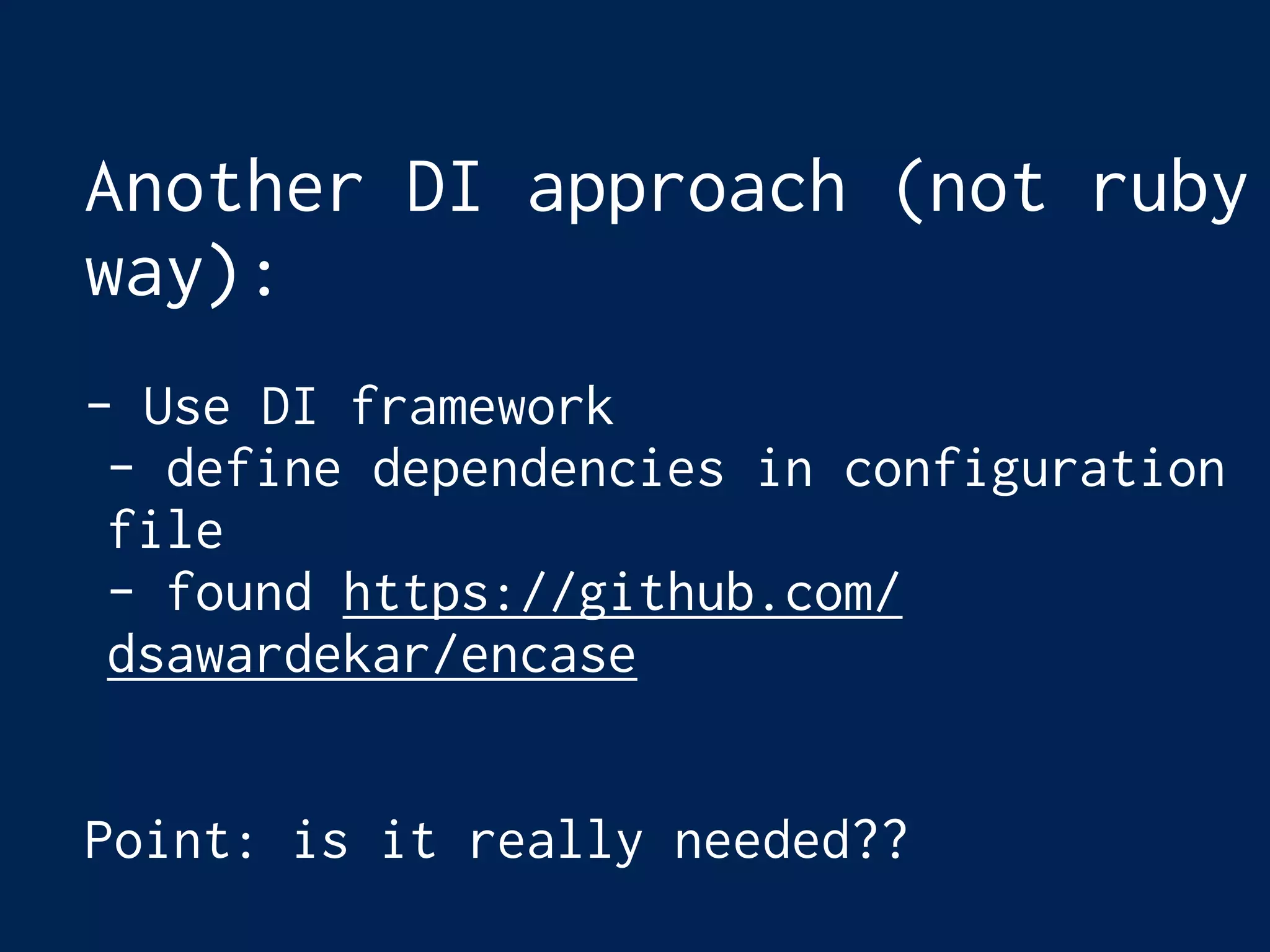
This document discusses dependency injection in Ruby. Dependency injection is when one part of code uses or relies on another part. In Ruby, common ways to implement dependency injection include using the constructor/initialize method and passing parameters, including modules, and inheritance. While these provide dependency injection, they can also introduce disadvantages like tight coupling, unexpected behavior from included modules, and rigid inheritance hierarchies. Dependency injection frameworks provide an alternative approach but may not be needed for many Ruby applications. The key benefits of dependency injection are improved testability, loose coupling between classes, and more extensible code.