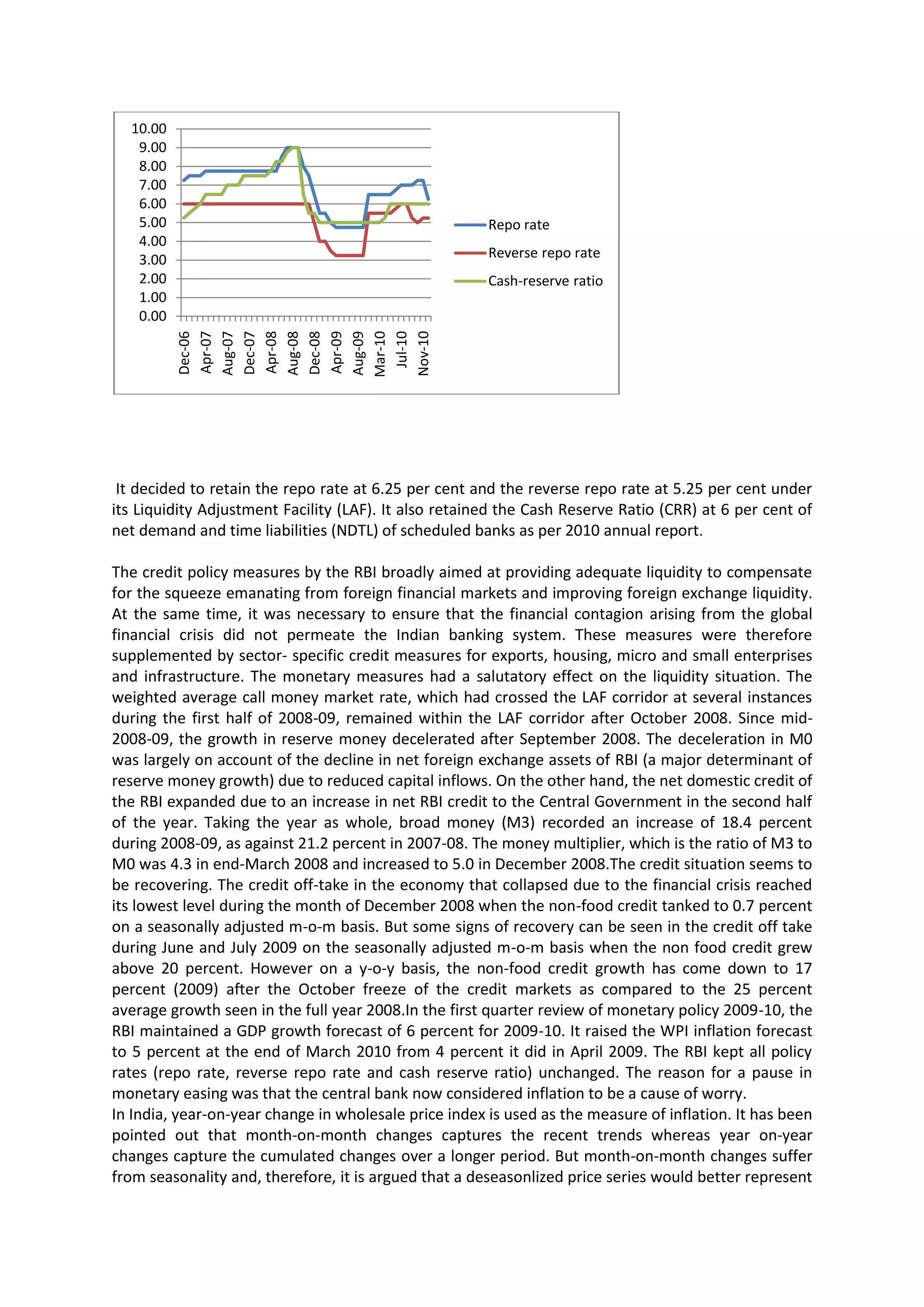
The Reserve Bank of India increased key policy rates and the cash reserve ratio to tighten monetary policy and curb inflationary pressures. The repo and reverse repo rates were increased by 25 basis points to 5.25% and 3.75% respectively, while the cash reserve ratio was also raised by 25 basis points to 6%. RBI projected GDP growth of 8% for 2010-2011, with inflation projected to moderate to 5.5%, but highlighted risks from commodity prices, the monsoon, and volatile capital flows. While seeking to contain inflation, RBI said it would ensure adequate liquidity to meet credit demands and support growth.