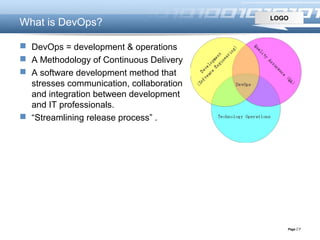
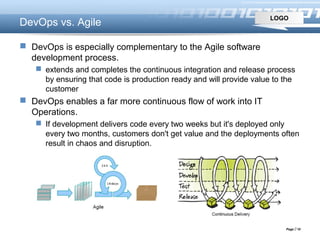
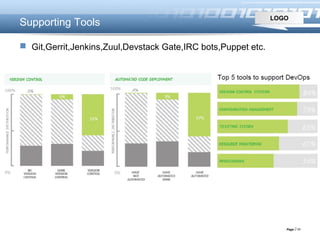
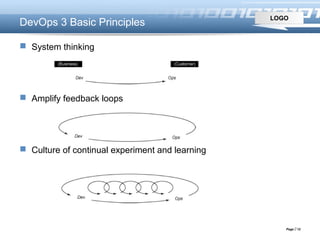
This document introduces DevOps, including how the DevOps movement took place originating from practices like continuous integration and infrastructure as code. It describes challenges of traditional software delivery approaches and how DevOps aims to reduce gaps through practices like integrating development and operations processes. DevOps benefits continuous delivery through collaboration between dev and ops and supporting tools. It promotes principles like system thinking, amplifying feedback loops, and continual learning.