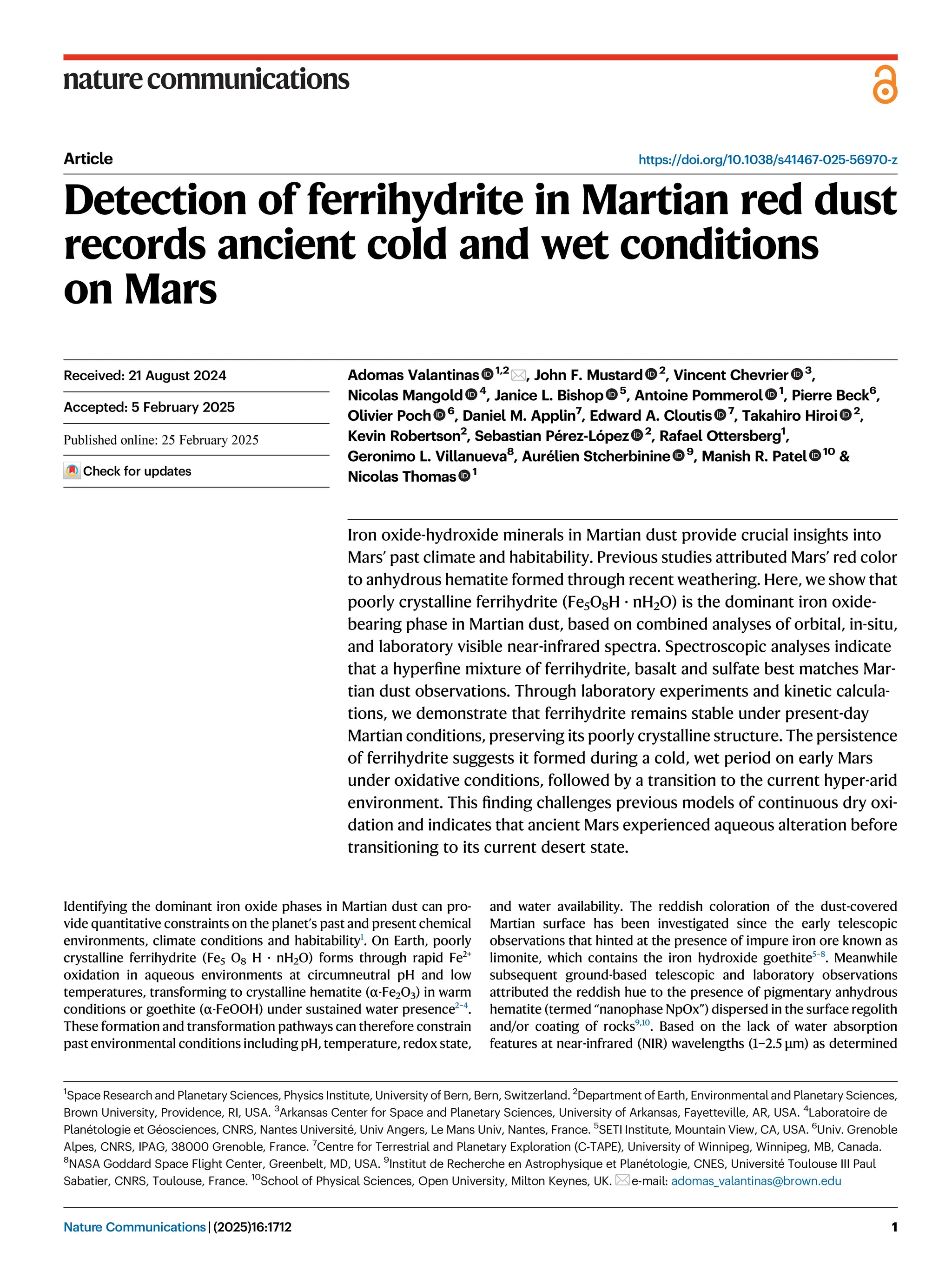
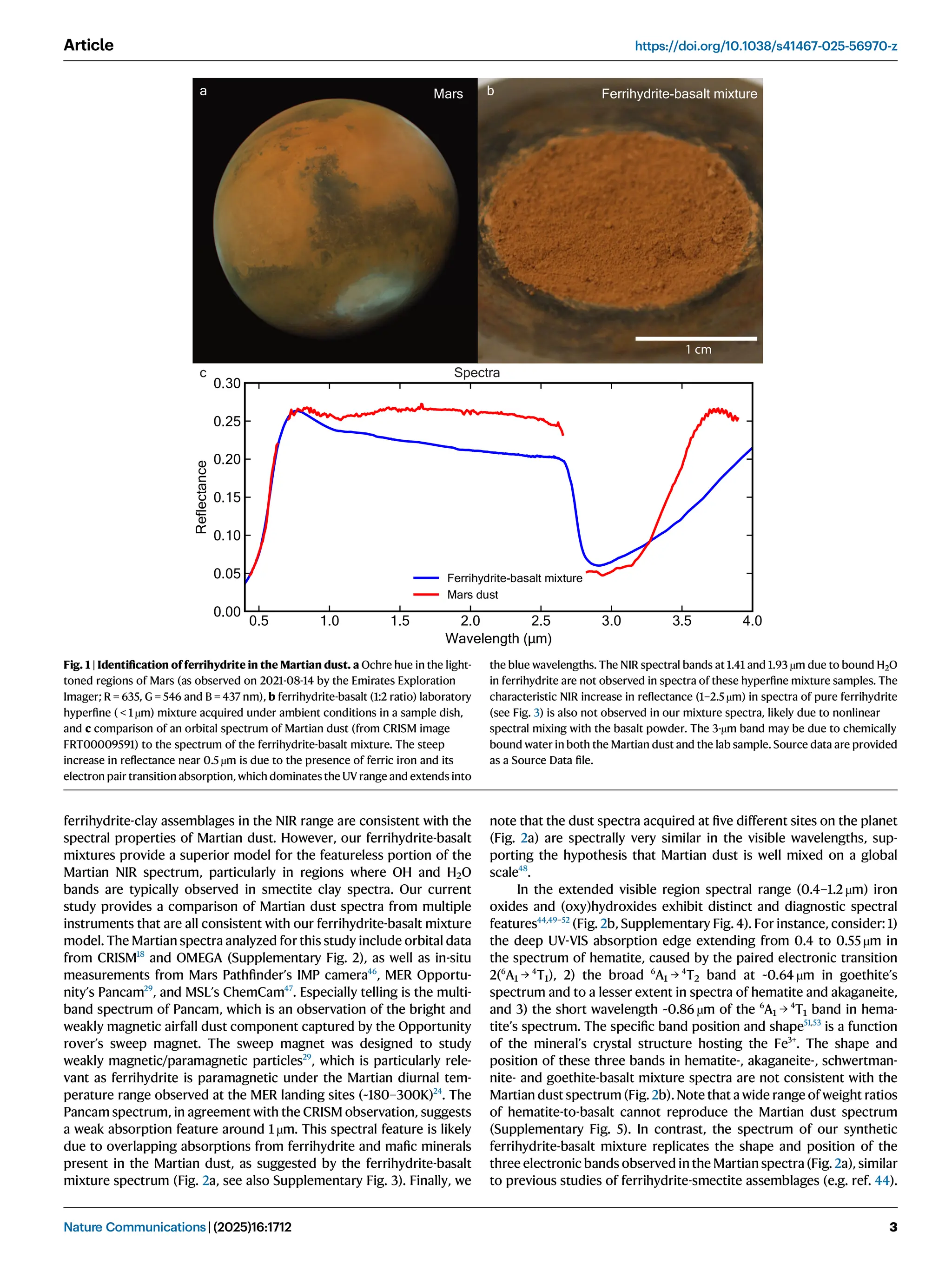
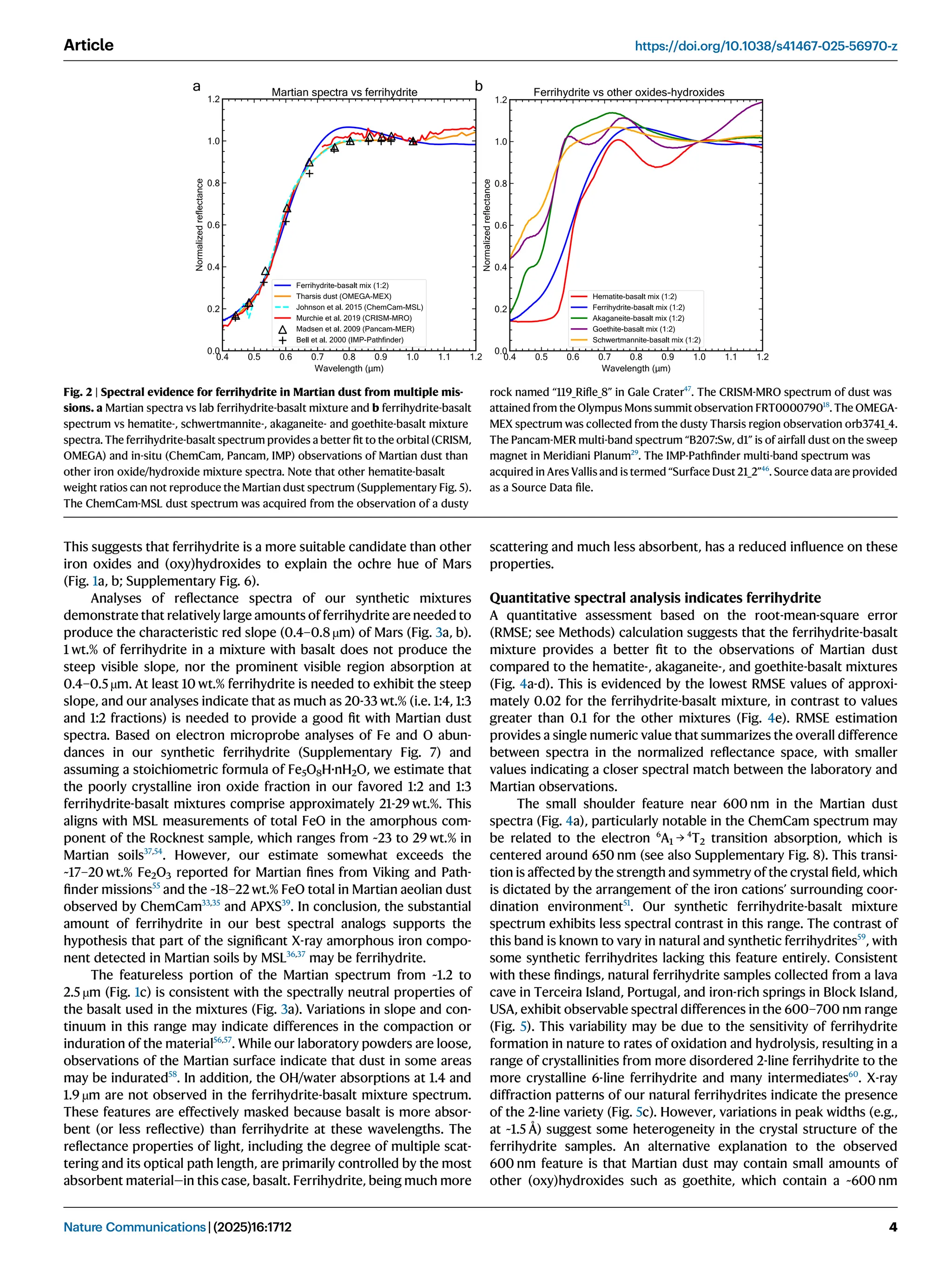
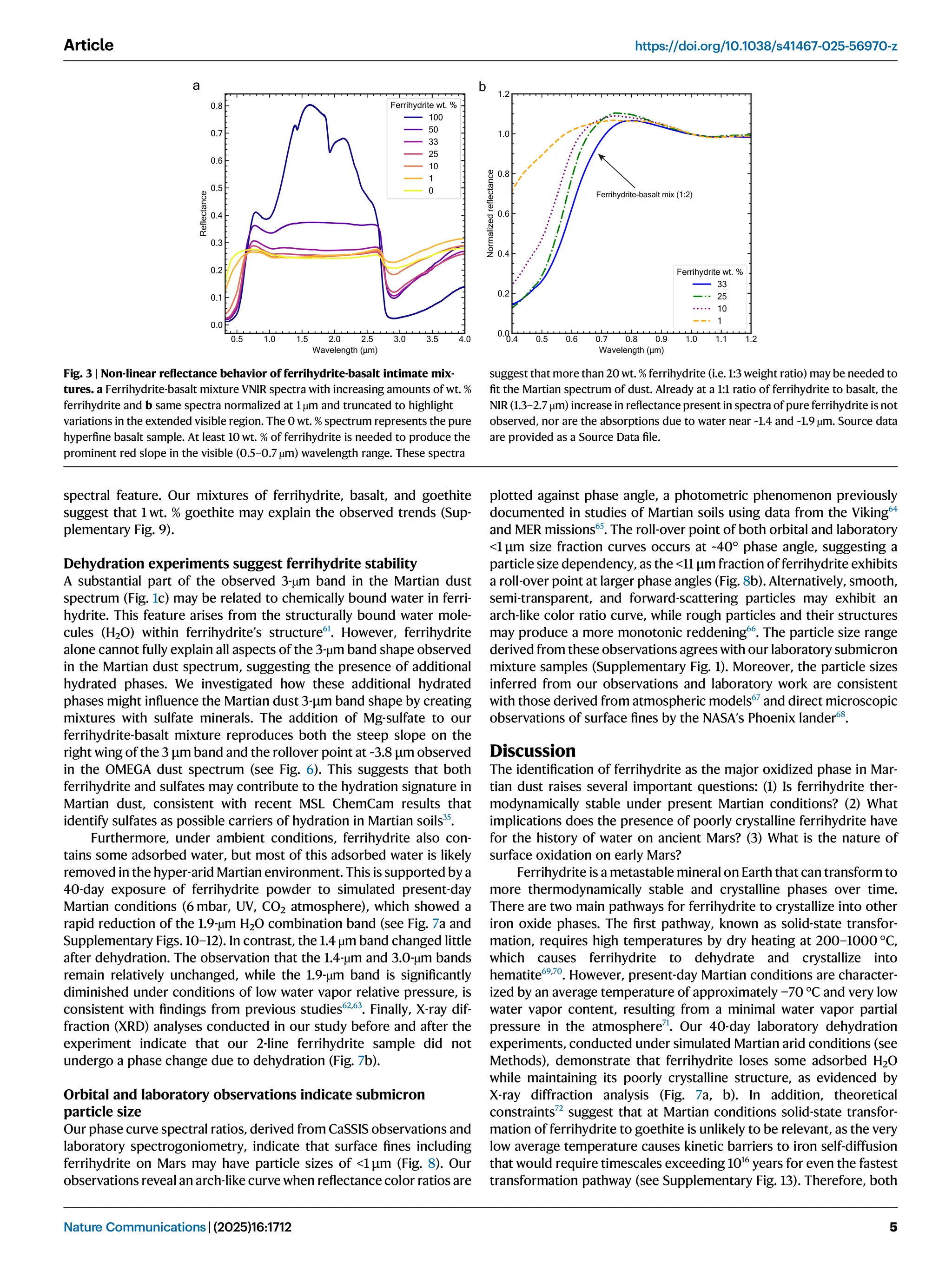
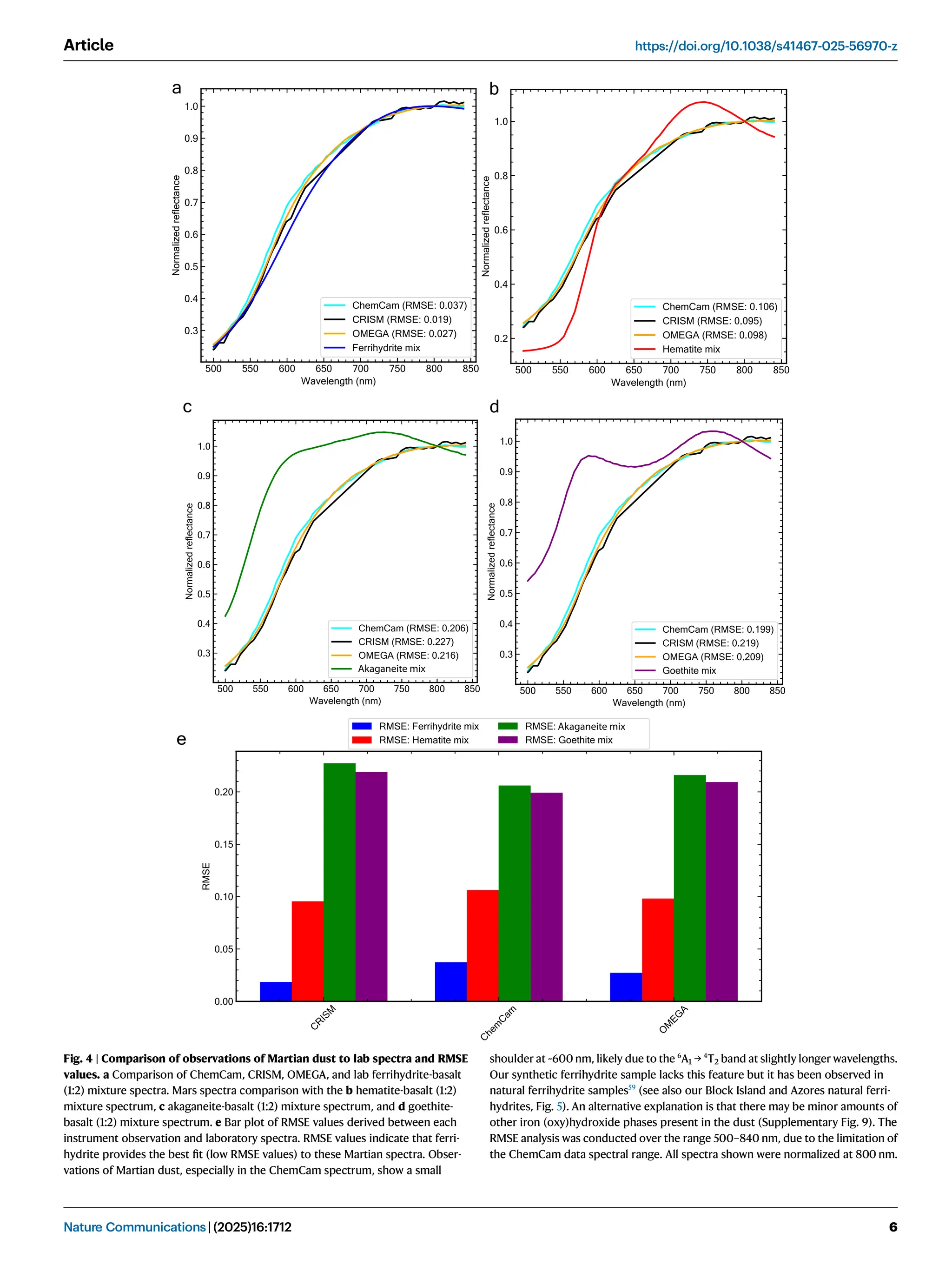
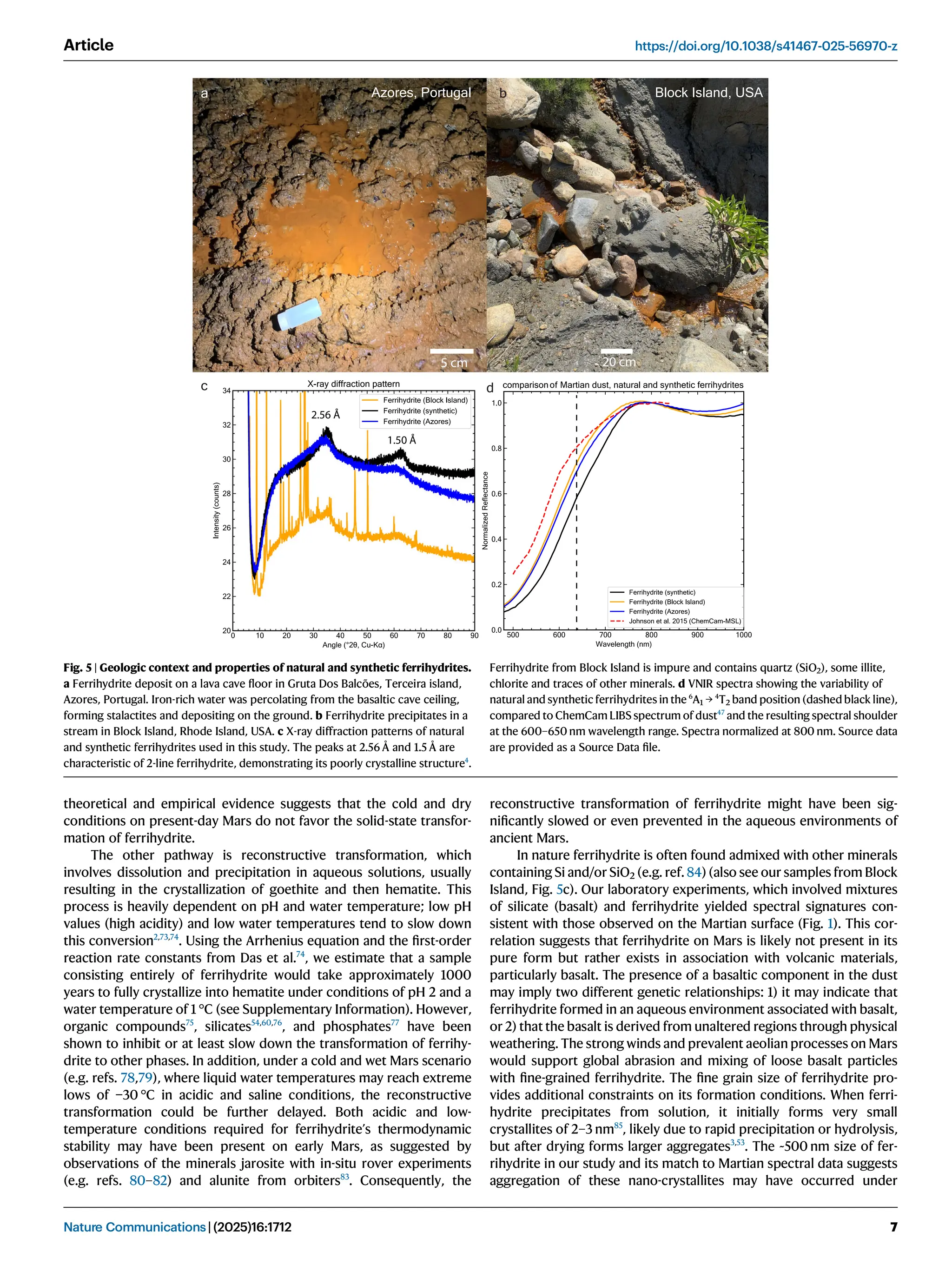
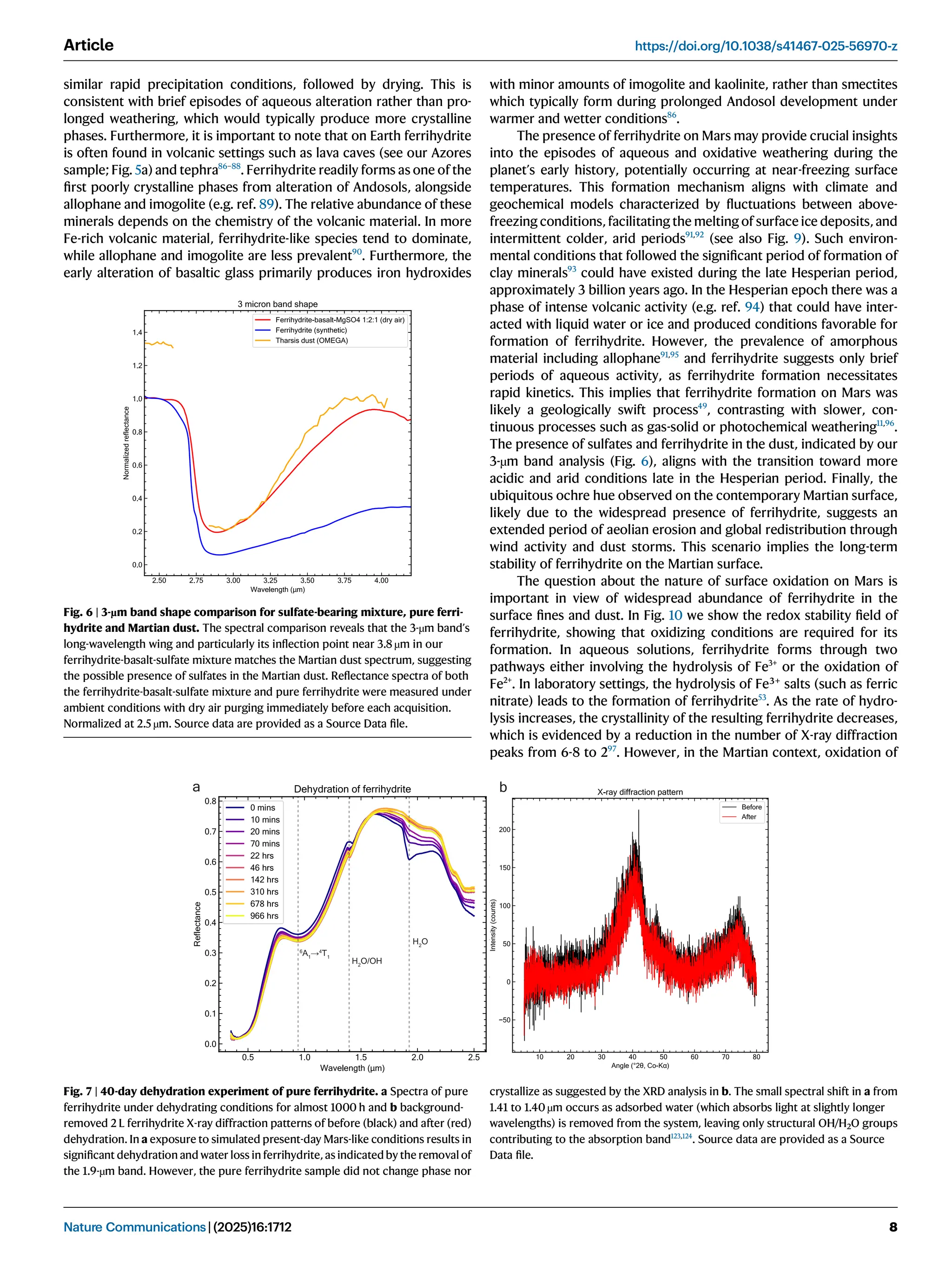
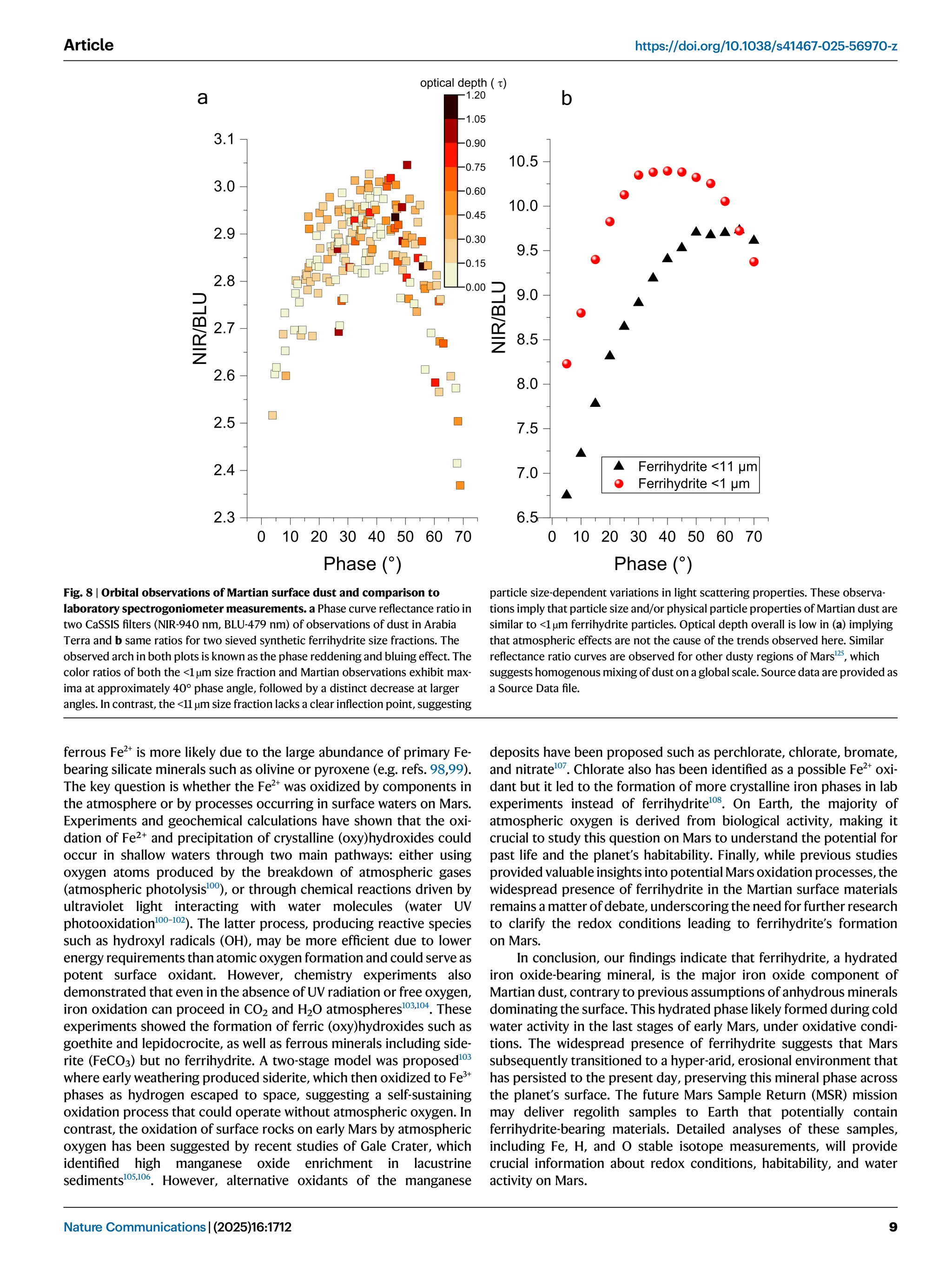
Iron oxide-hydroxide minerals in Martian dust provide crucial insights into
Mars’ past climate and habitability. Previous studies attributed Mars’ red color
to anhydrous hematite formed through recent weathering. Here, we show that
poorly crystalline ferrihydrite (Fe5O8H · nH2O) is the dominant iron oxidebearing phase in Martian dust, based on combined analyses of orbital, in-situ,
and laboratory visible near-infrared spectra. Spectroscopic analyses indicate
that a hyperfine mixture of ferrihydrite, basalt and sulfate best matches Martian dust observations. Through laboratory experiments and kinetic calculations, we demonstrate that ferrihydrite remains stable under present-day
Martian conditions, preserving its poorly crystalline structure. The persistence
of ferrihydrite suggests it formed during a cold, wet period on early Mars
under oxidative conditions, followed by a transition to the current hyper-arid
environment. This finding challenges previous models of continuous dry oxidation and indicates that ancient Mars experienced aqueous alteration before
transitioning to its current desert state.