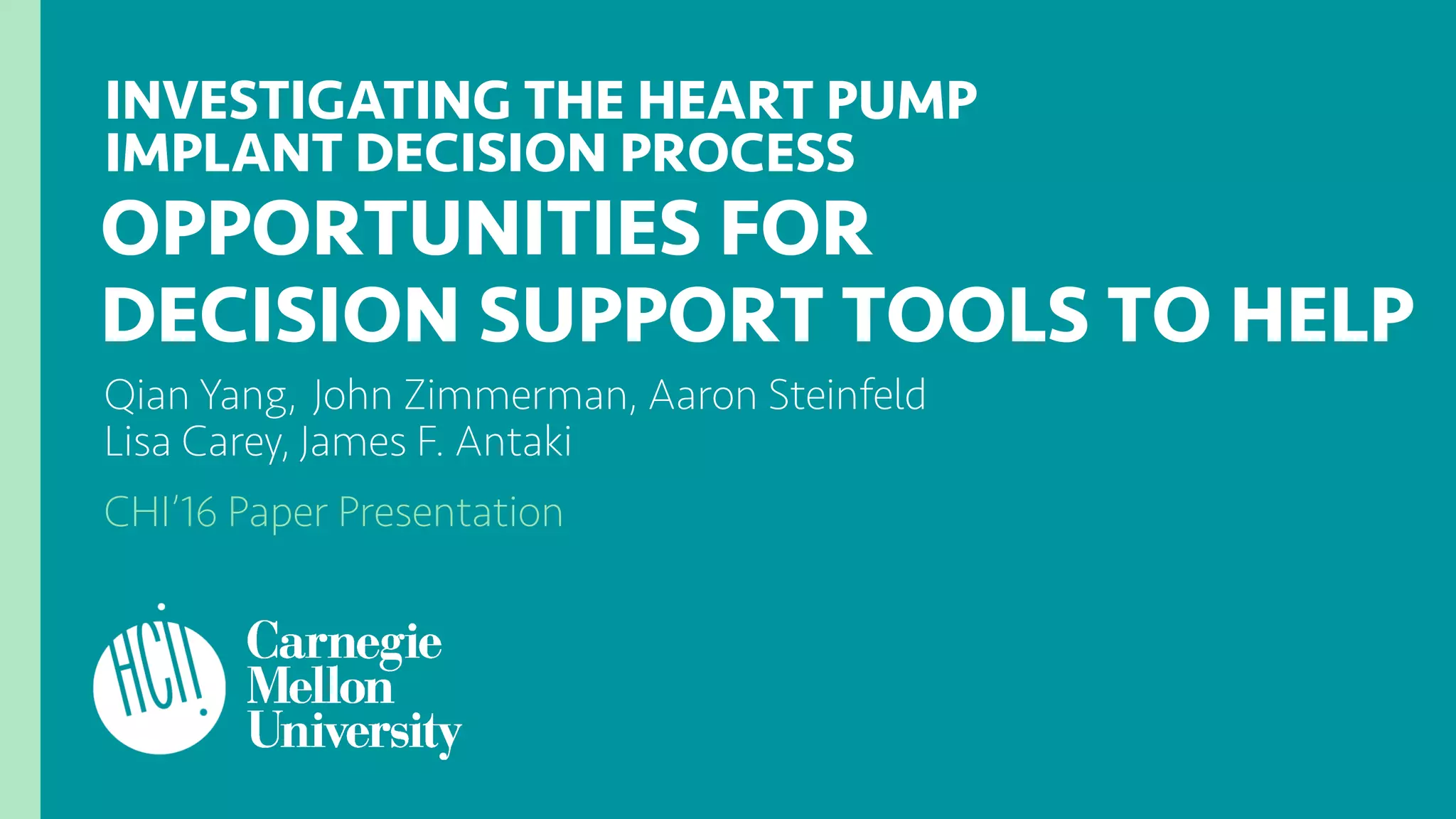
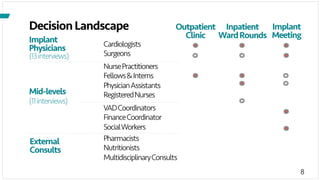
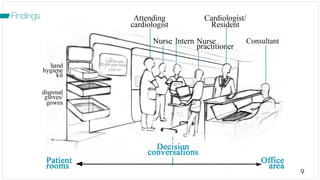
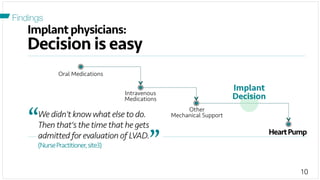
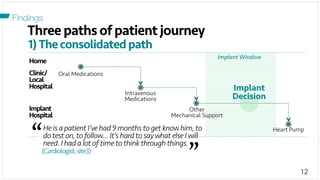
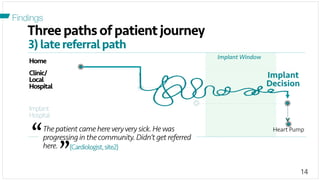
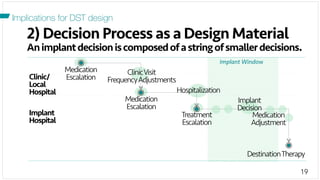
The document investigates the decision-making process surrounding the implantation of heart pumps (LVADs) in patients with advanced heart failure. It identifies barriers to the adoption of decision-support tools (DSTs) in clinical practice, such as lack of integration with workflow and physician skepticism about their usefulness. The findings highlight the need for DSTs that embrace clinical context and blend human and machine intelligence to better support clinicians in their decision-making processes.