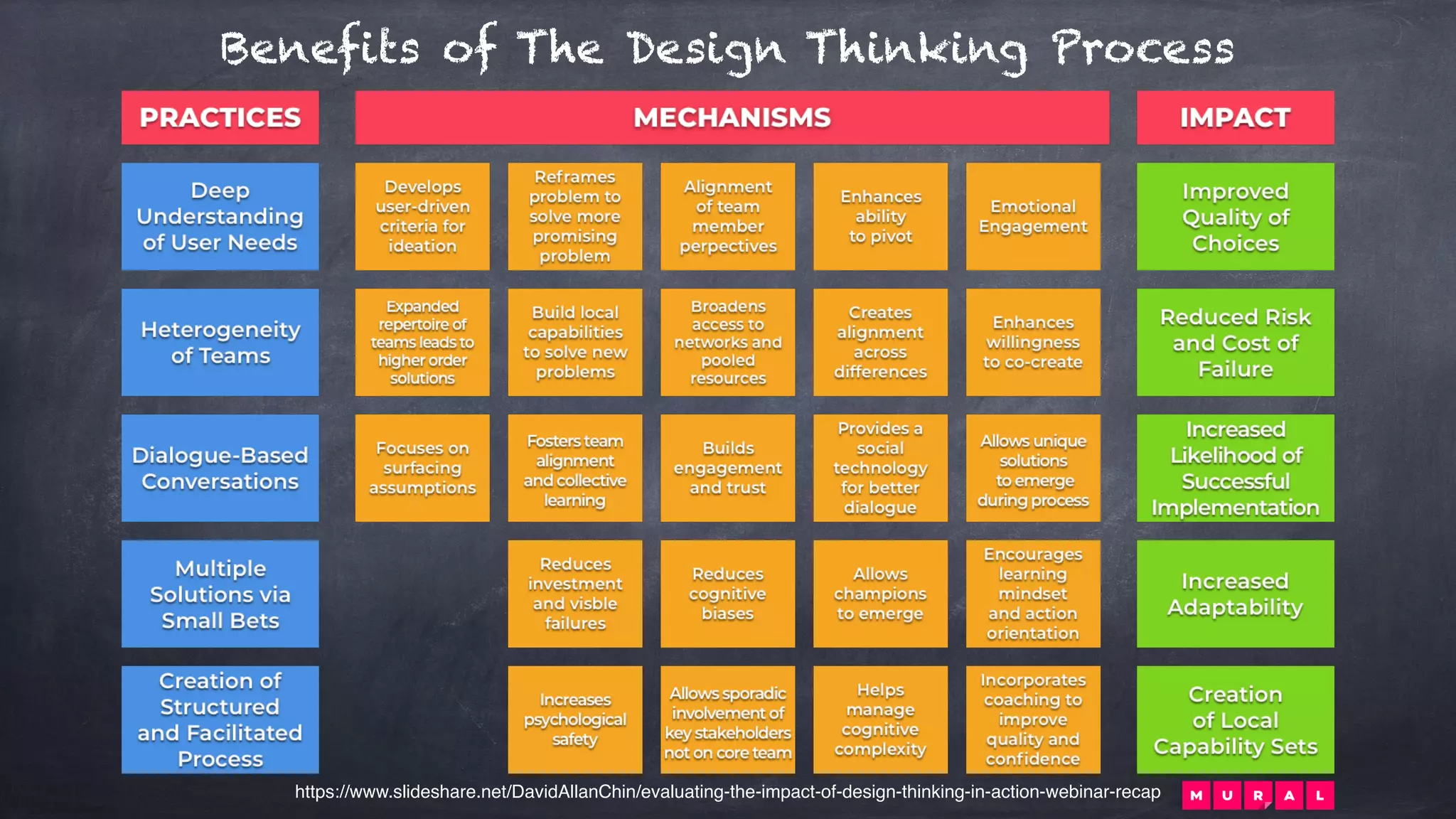
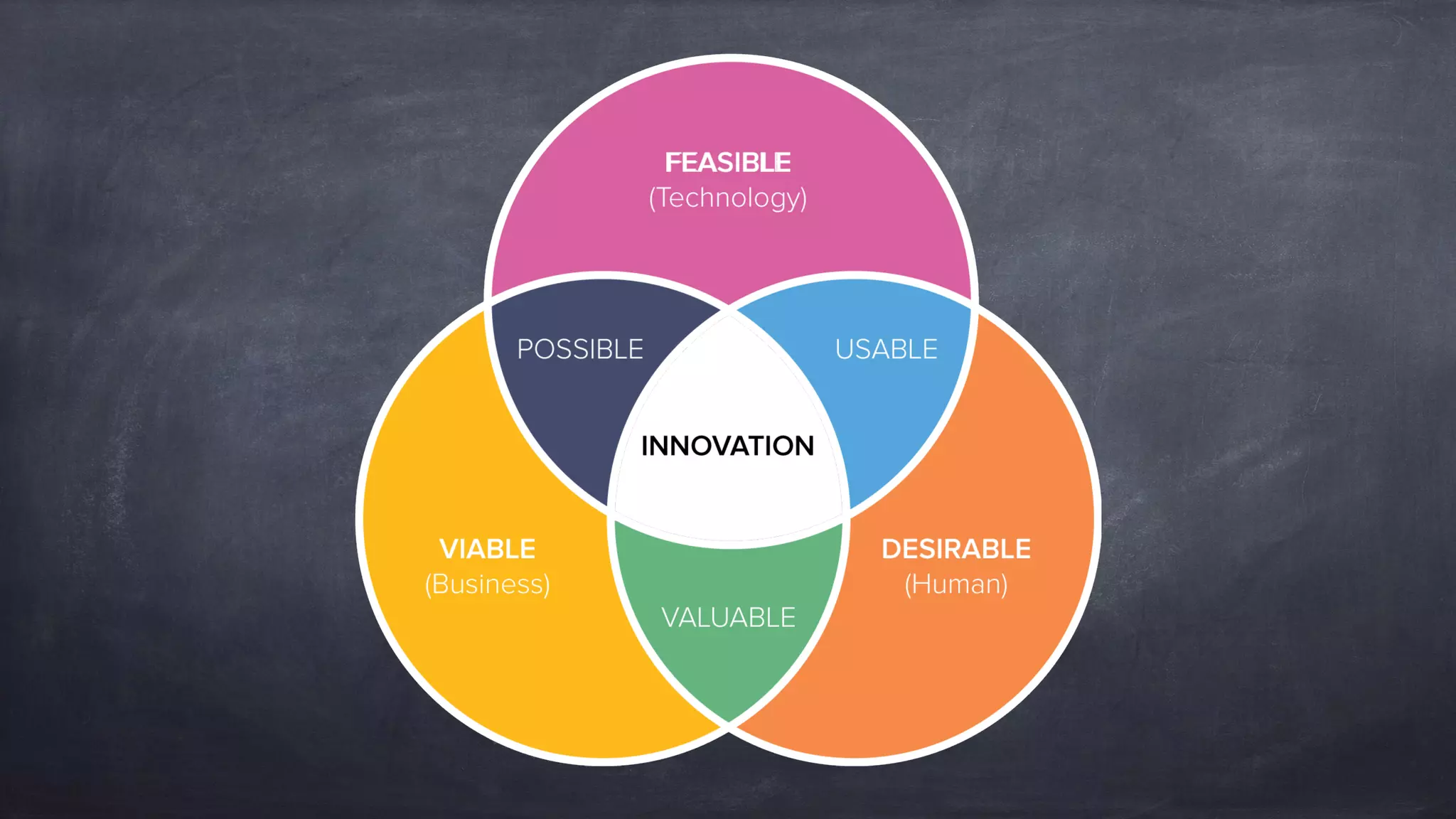
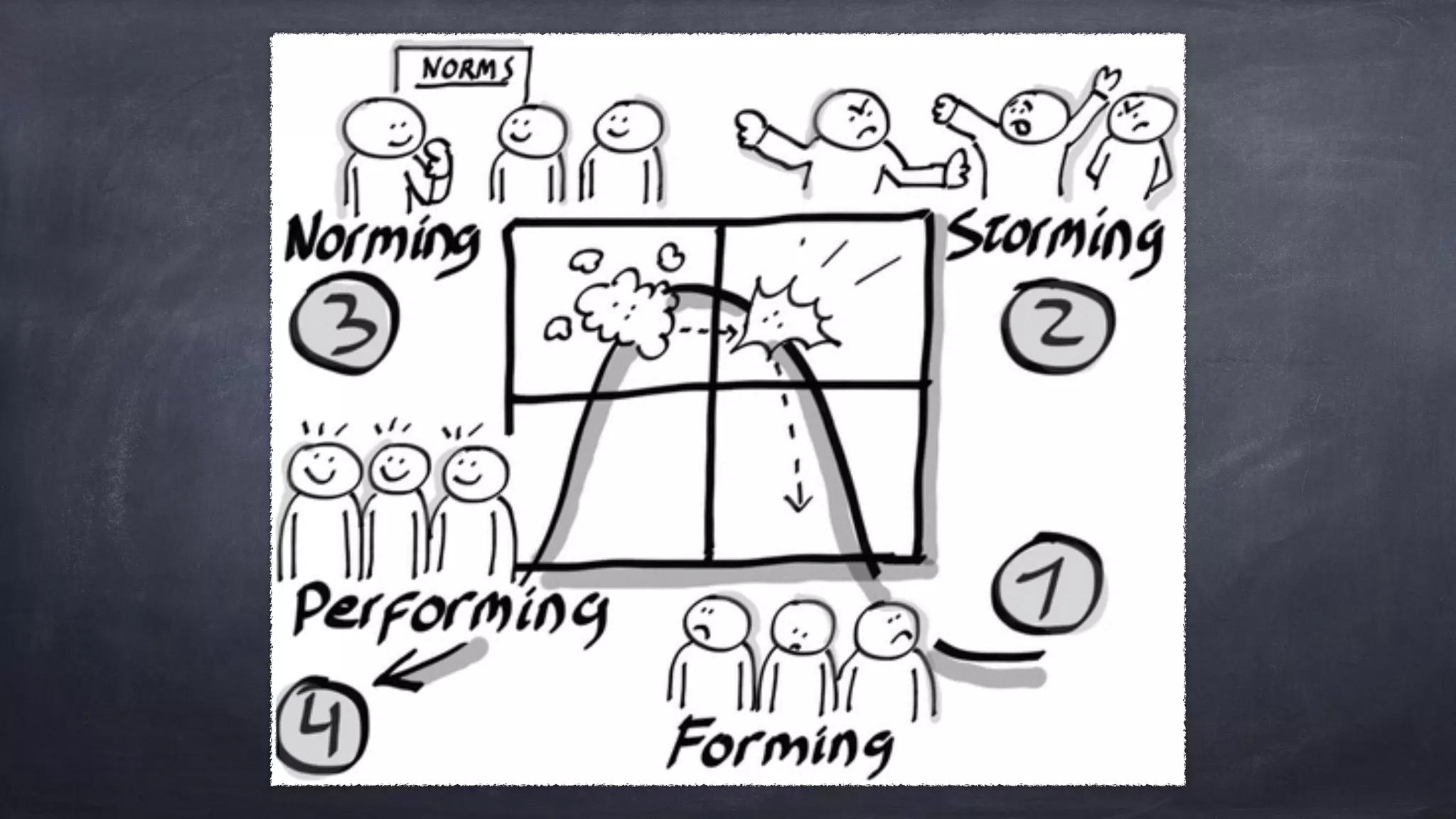
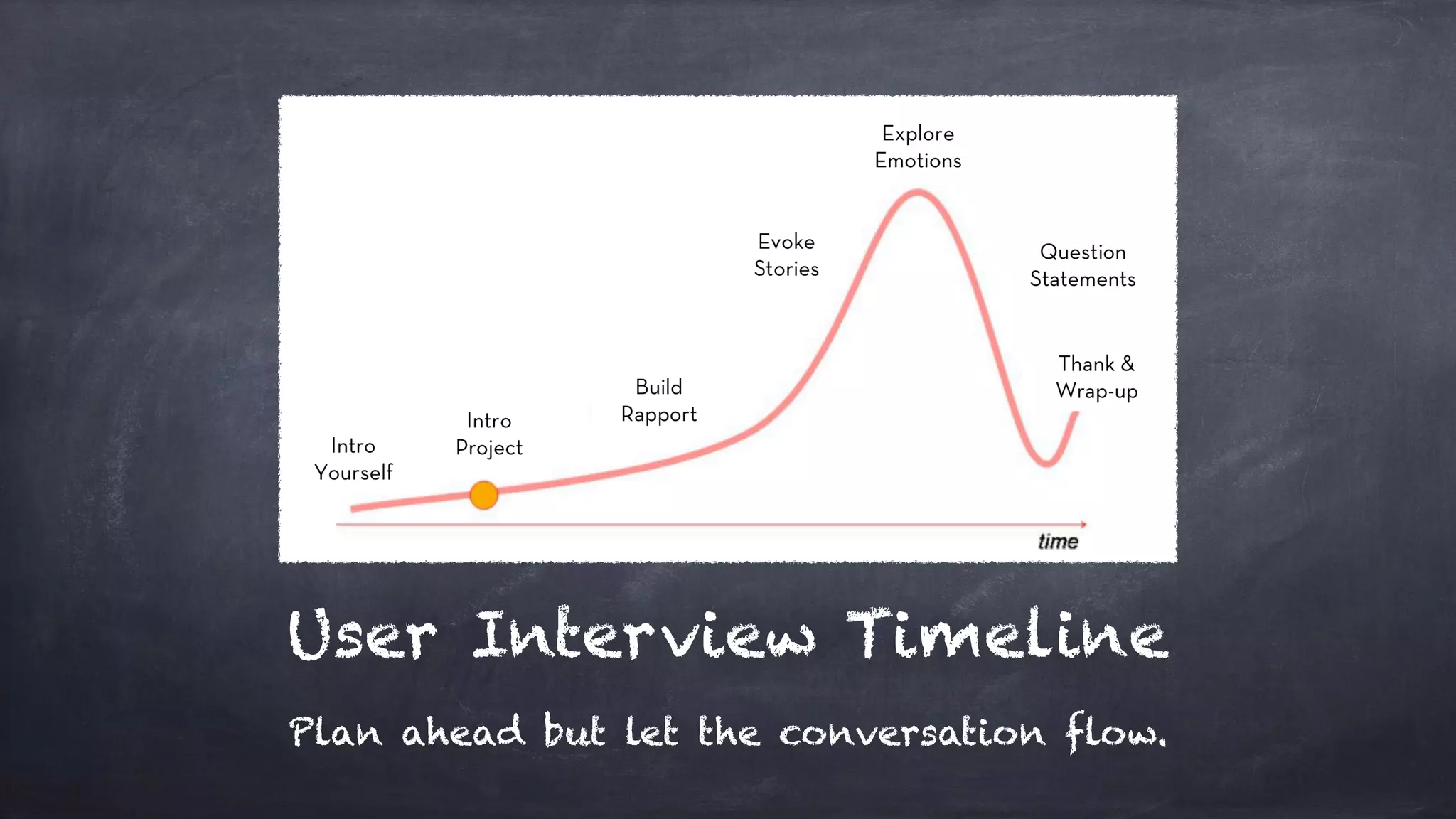
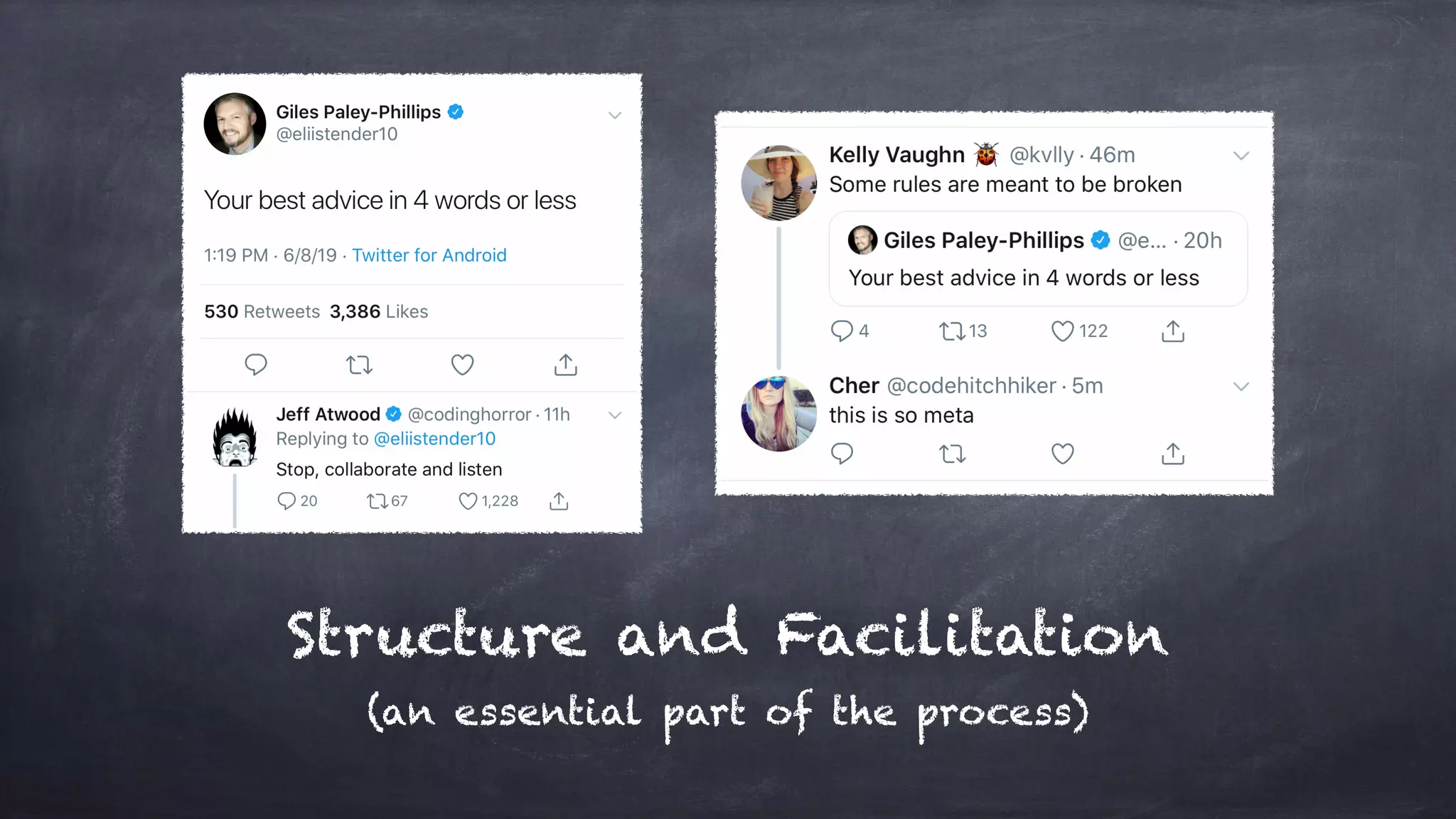
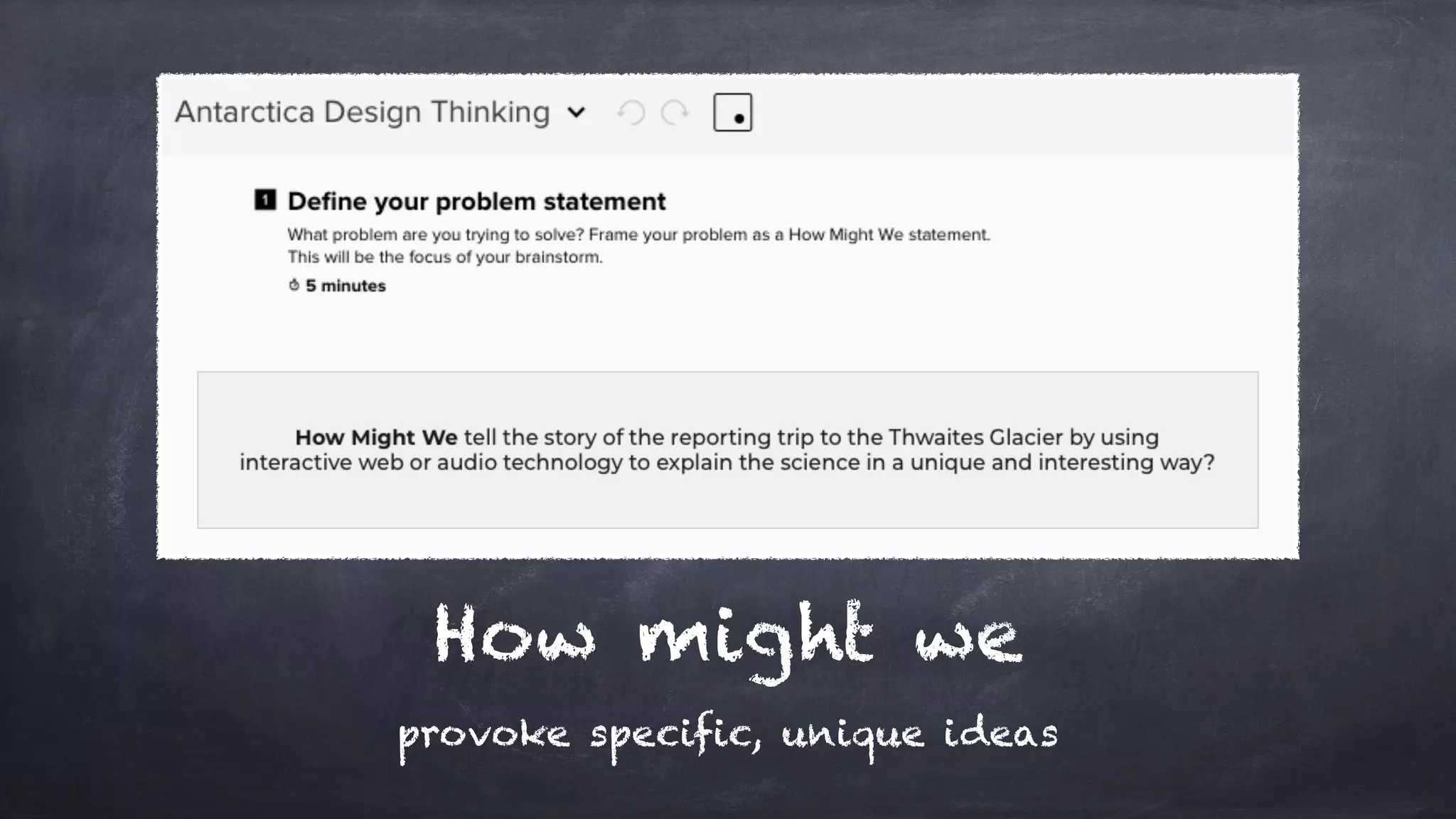
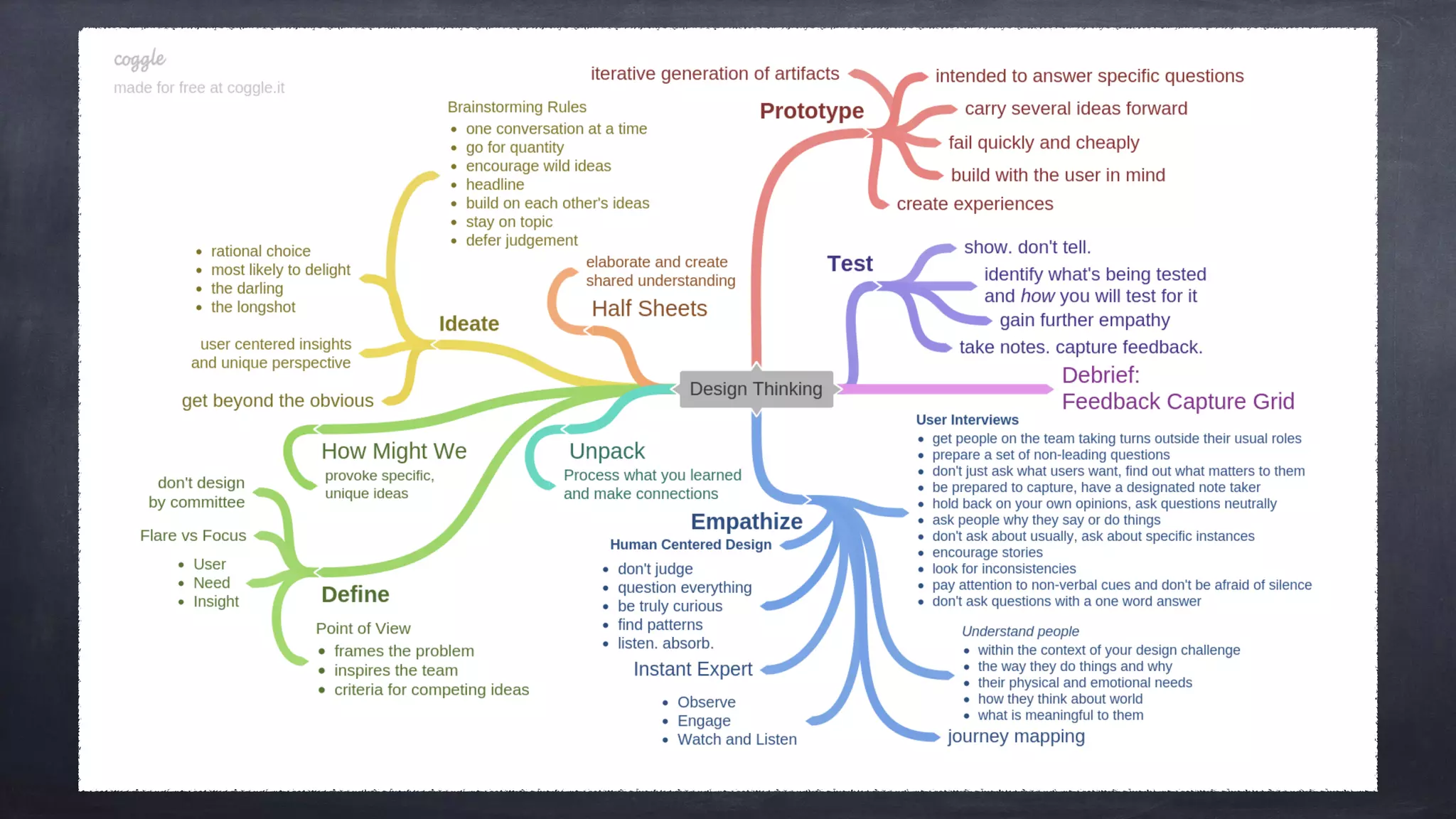
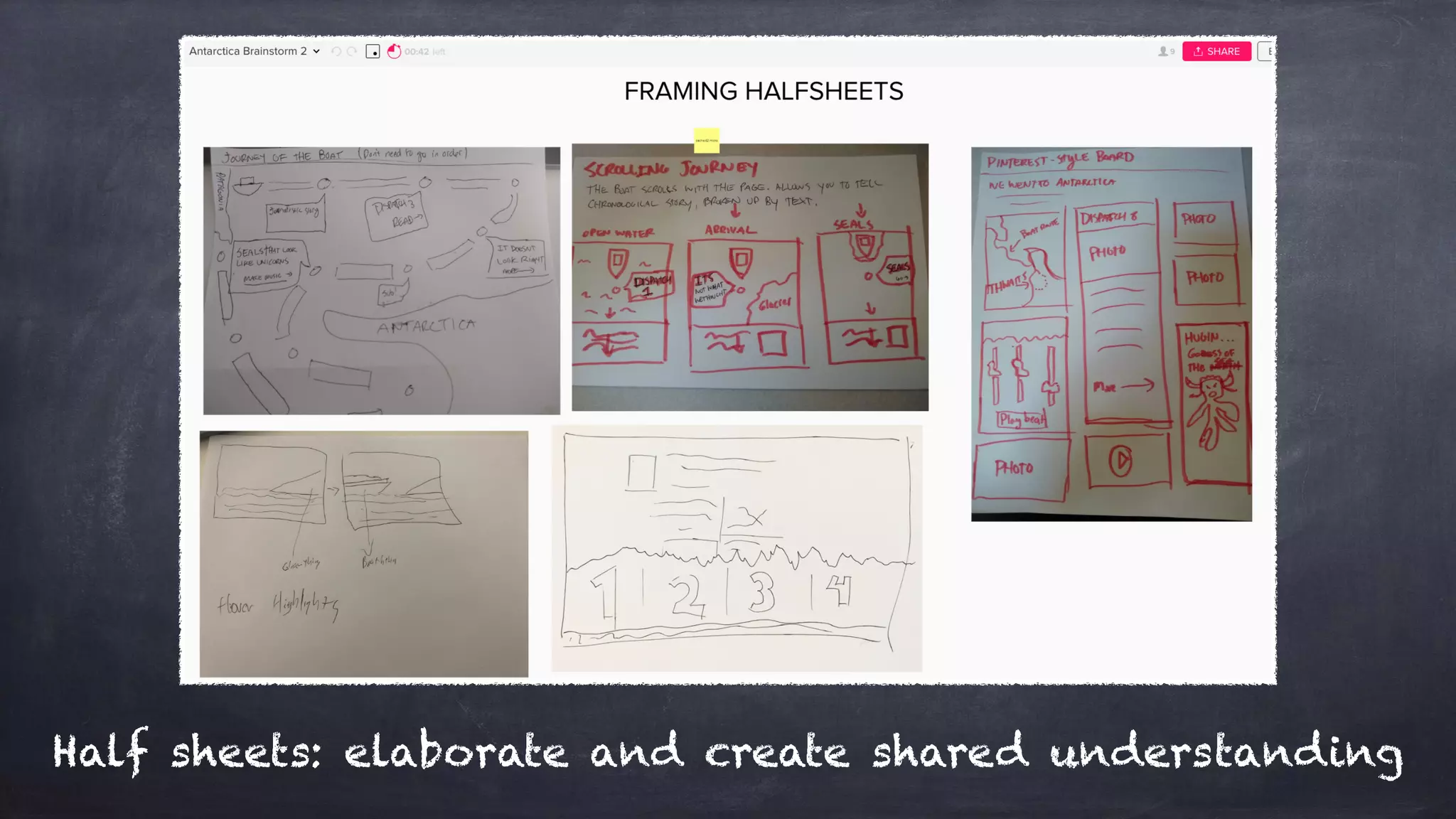
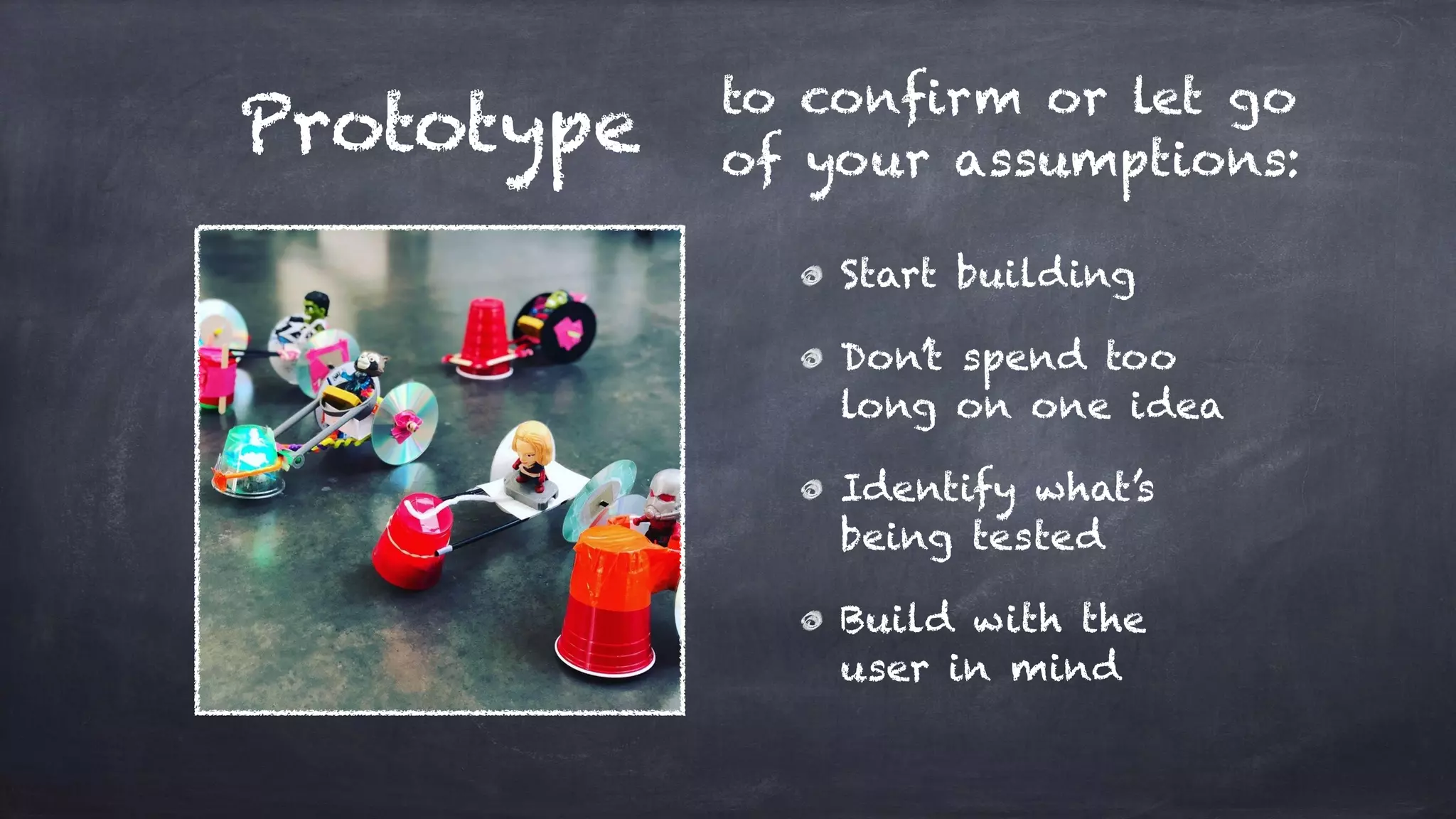
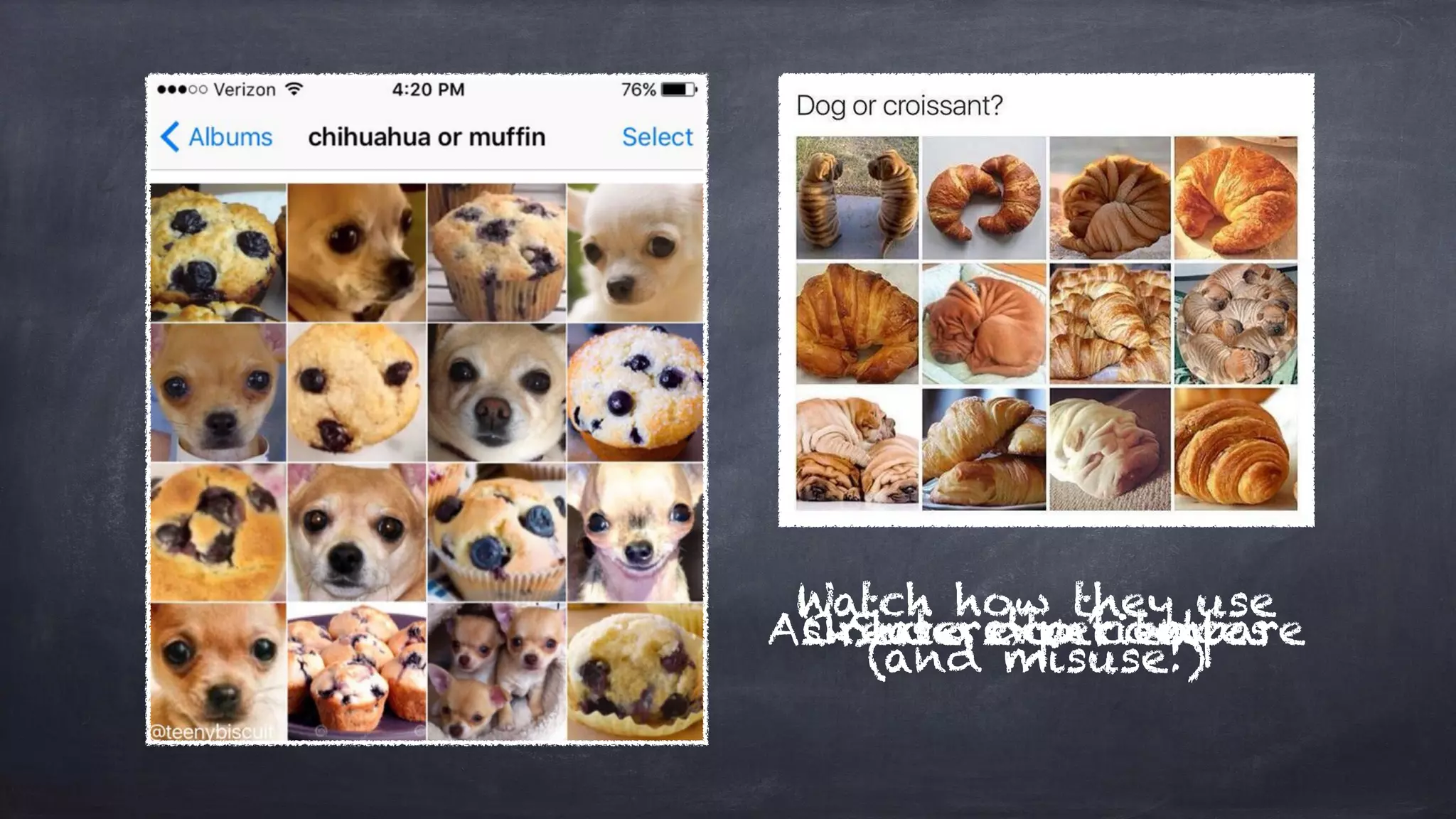
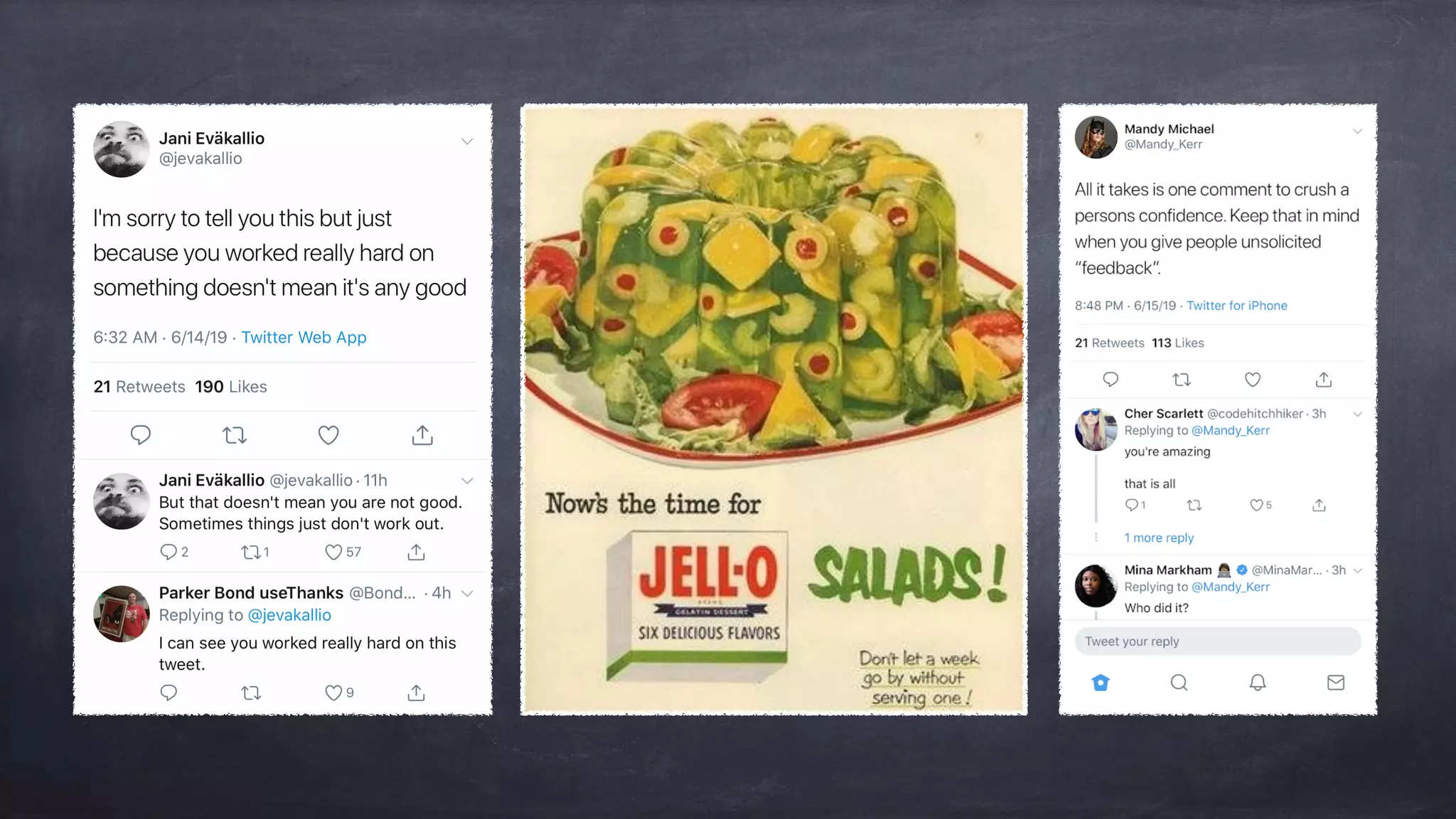
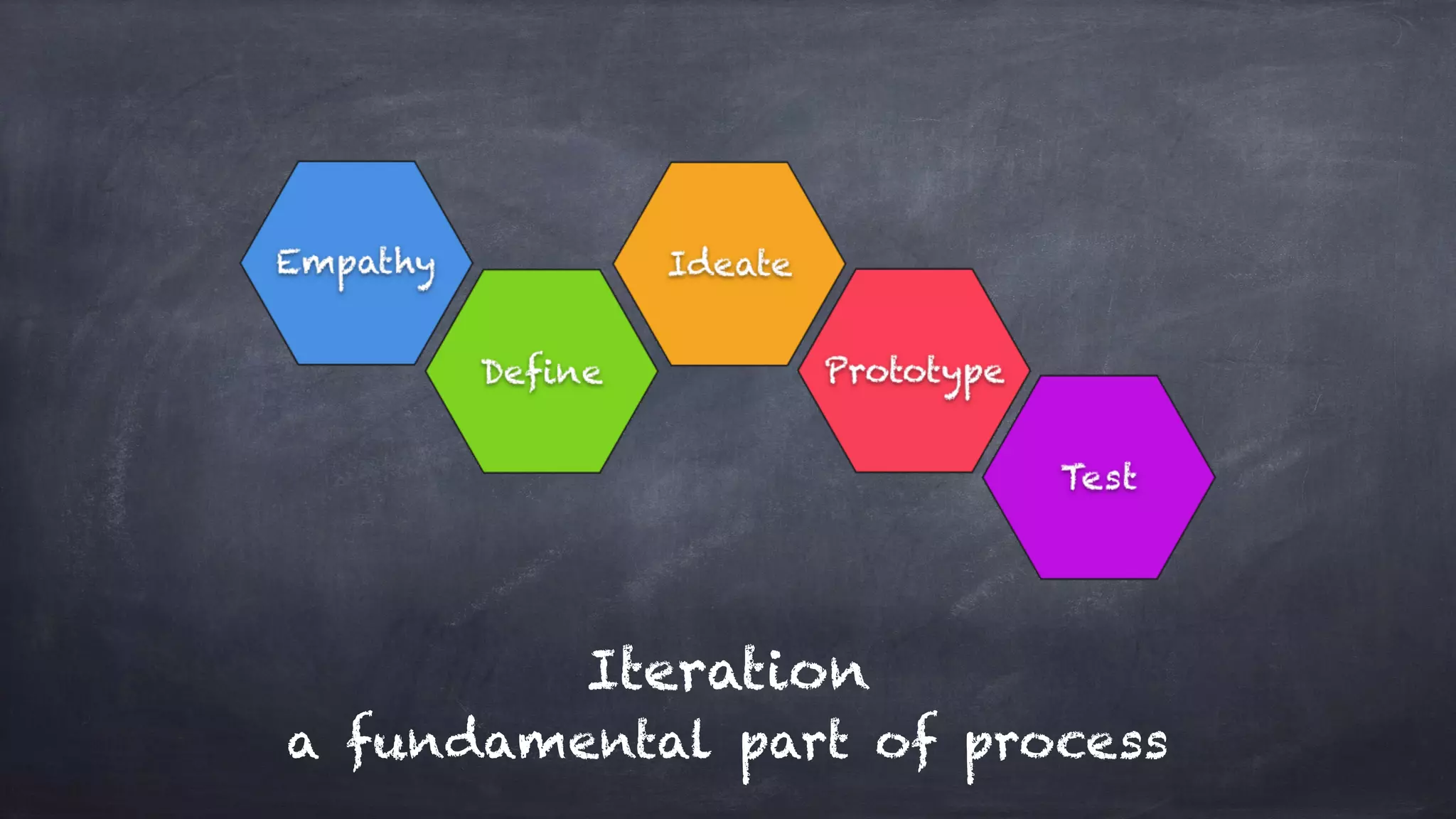
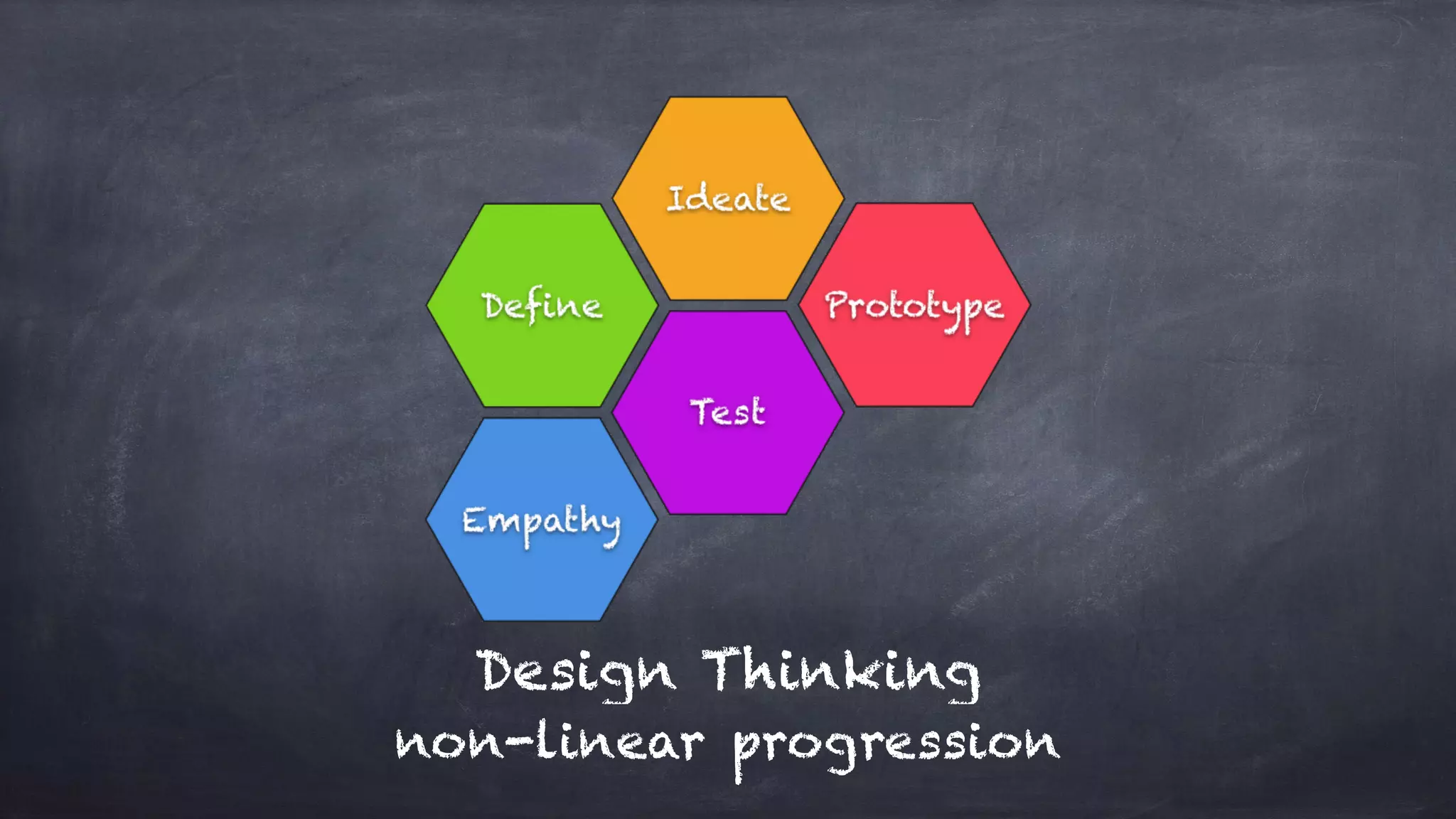
The document outlines the design thinking process focusing on inclusive collaboration, emphasizing user empathy, effective interviews, and the importance of an open mindset. It details strategies for brainstorming, prototyping, and user testing, highlighting the need for a culture of safety and the ability to navigate ambiguity. Key components include actively engaging users, crafting meaningful problem statements, and iterating solutions based on feedback.