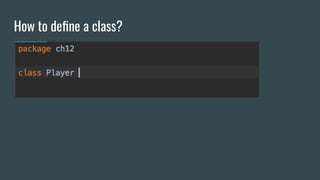
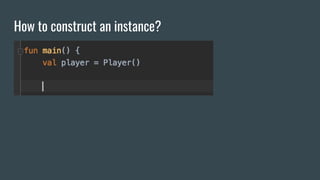
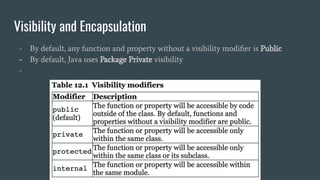
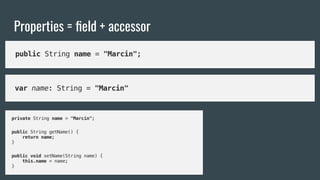
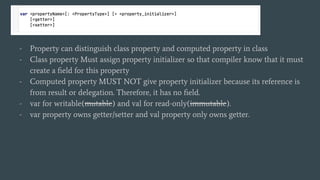
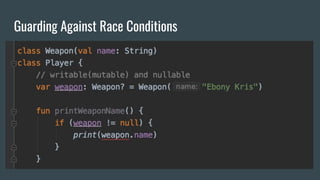
This document provides an outline for a Kotlin class definition lesson. It will cover how to define a class, construct class instances, define class functions and properties, set visibility and encapsulation, and use properties including class properties, computed properties, and guarding against race conditions. The presenter is John, an Android developer who has used Kotlin for 2 years.