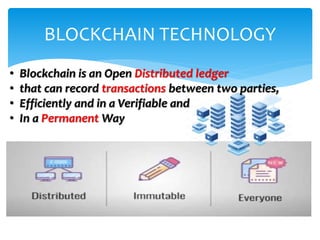
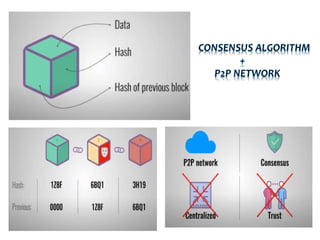
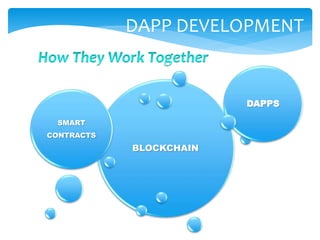
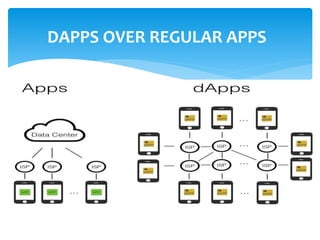
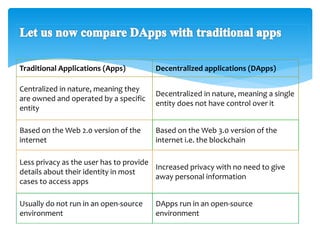
The document provides an overview of decentralized applications (dapps), explaining their nature, advantages over traditional apps, and their development. It discusses key aspects such as blockchain technology, smart contracts, types of dapps, and common drawbacks, while highlighting examples like Augur and Uniswap. The dapps market is projected to grow significantly, driven by their transparency, reliability, and evolving technology opportunities.