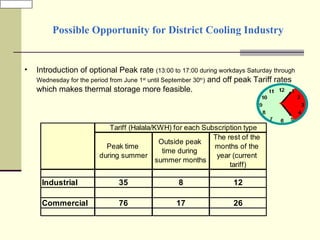
The document discusses the history and development of district cooling in the Middle East and Saudi Arabia. It notes that the first district cooling schemes were developed in the 1960s in Saudi Arabia, Lebanon and Kuwait. Key drivers for adopting district cooling in Saudi Arabia include rising electricity demand, availability of treated sewage water, large planned developments, and using district cooling to cool power plants. The prospects for future district cooling include over 800,000 tons of new capacity across various cities in the country. Challenges include a lack of land and electricity tariffs, but opportunities exist with peak pricing and thermal storage.