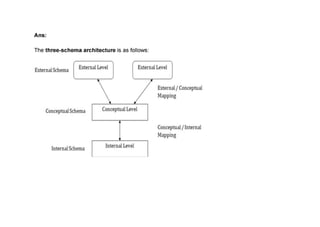
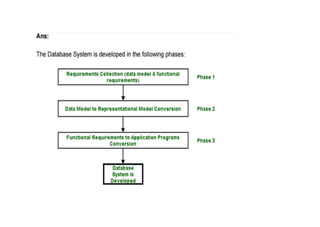
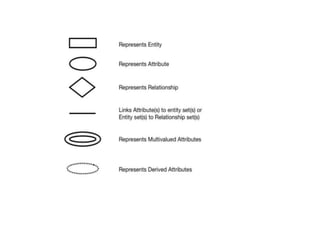
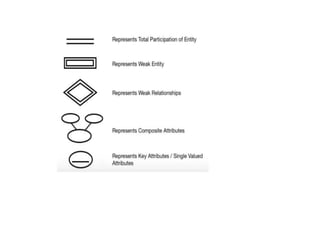
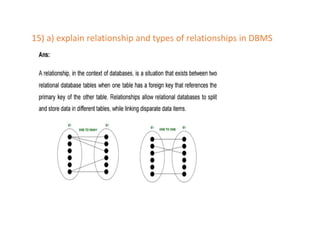
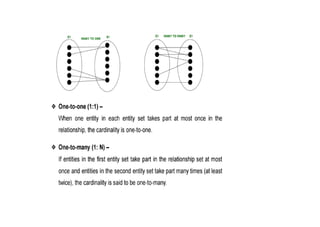
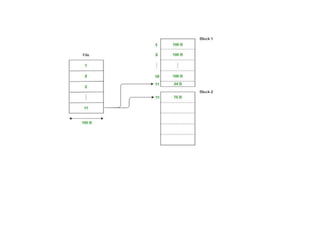
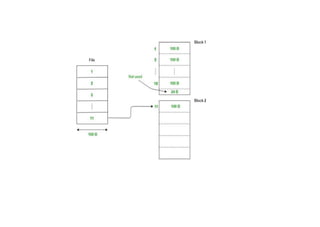
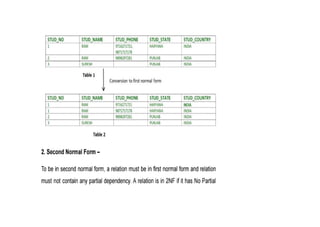
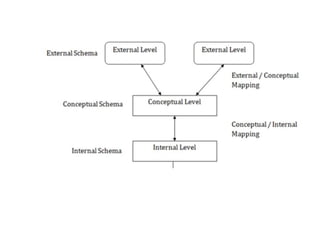
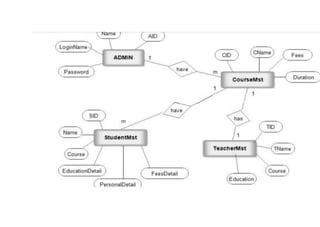
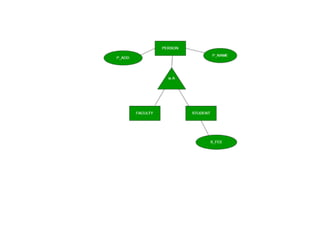
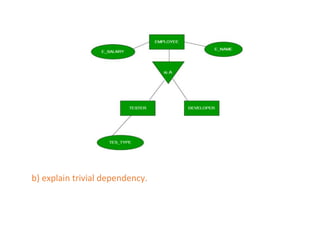
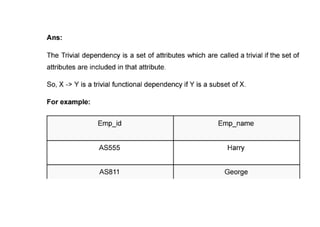
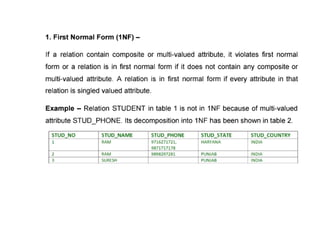
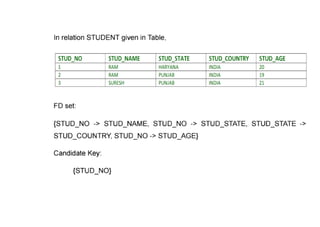
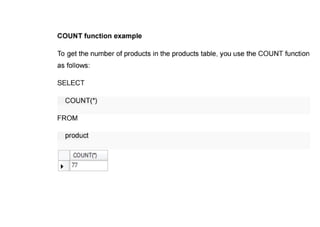
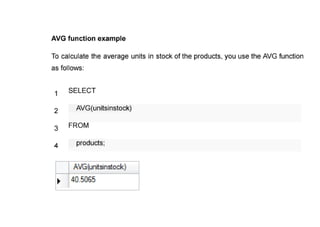
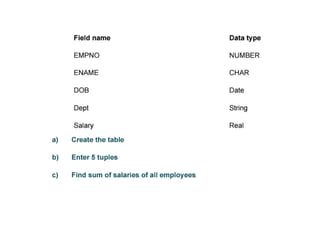
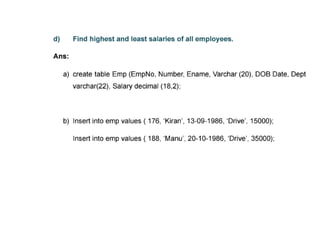
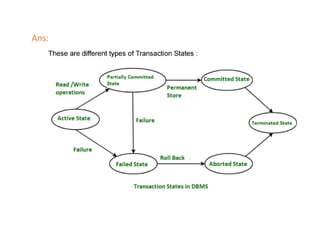
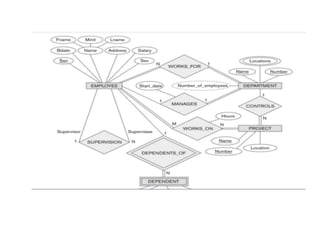
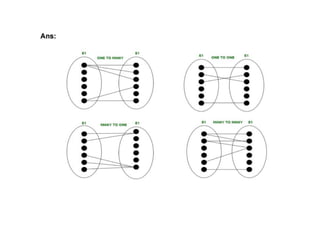
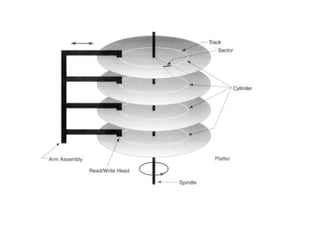
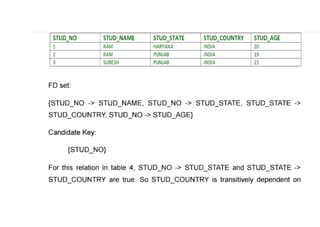
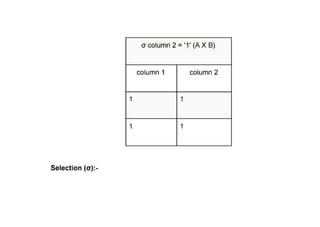
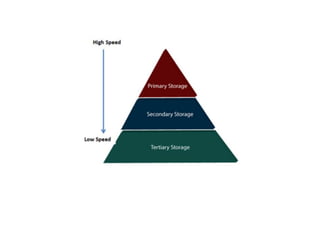
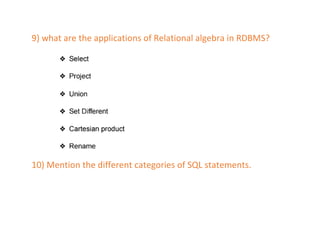
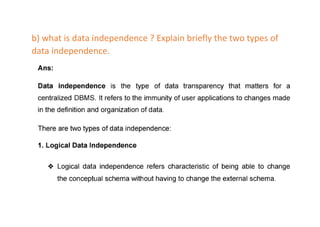
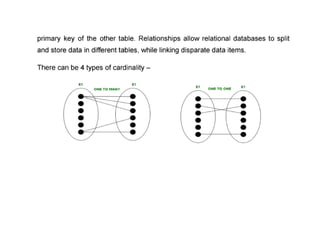
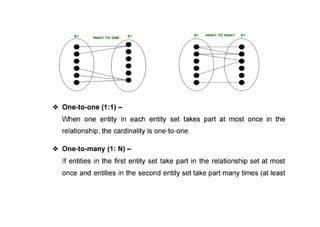
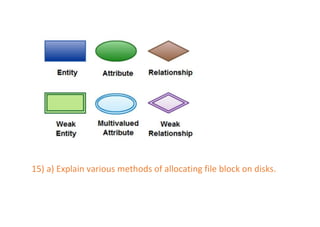
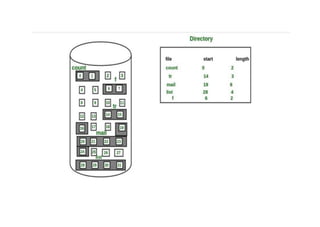
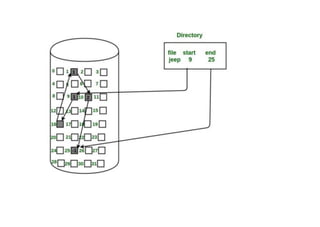
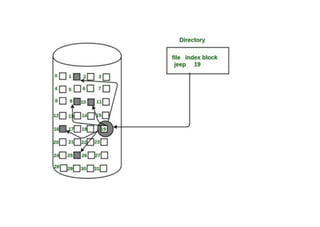
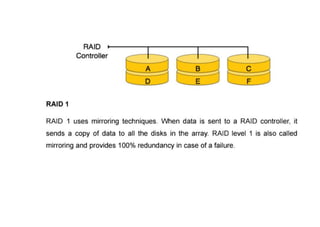
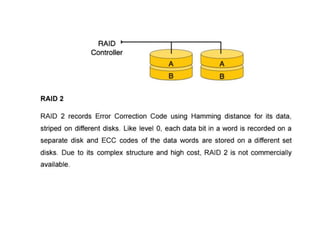
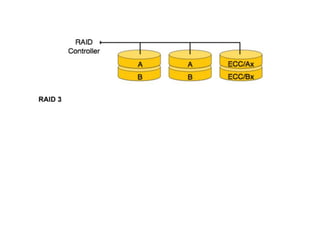
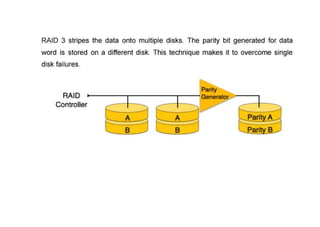
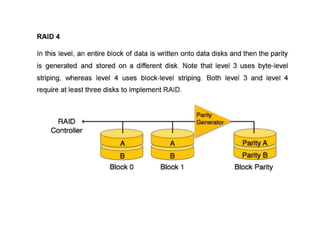
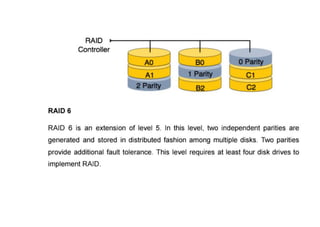
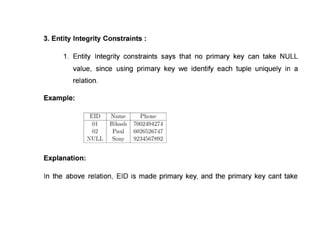
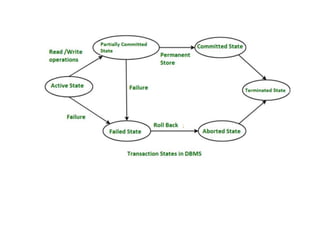
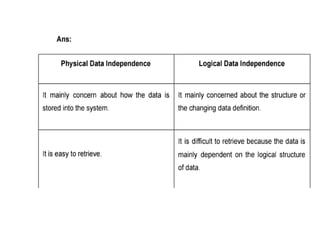
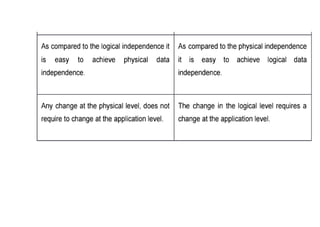
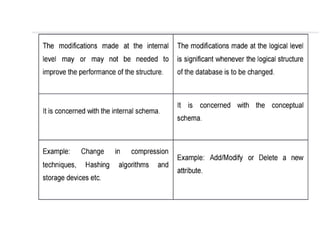
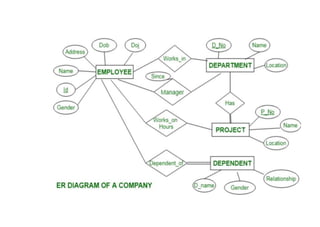
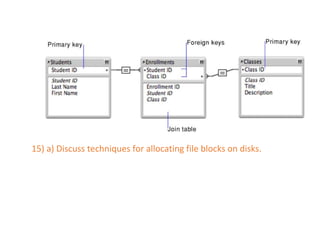
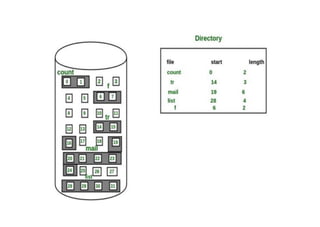
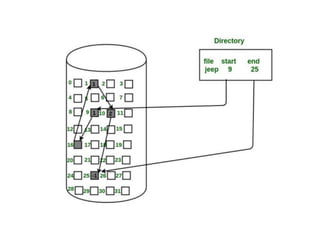
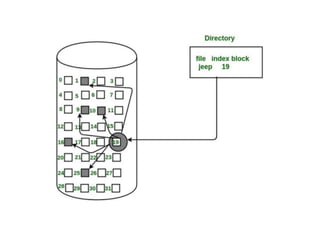
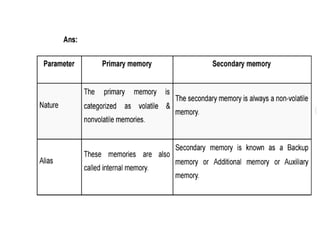
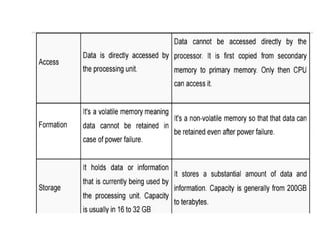
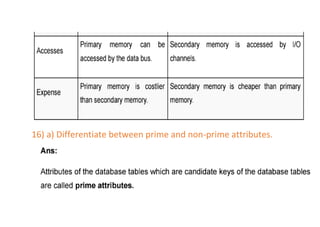
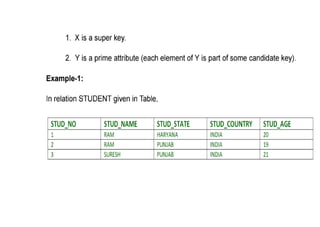
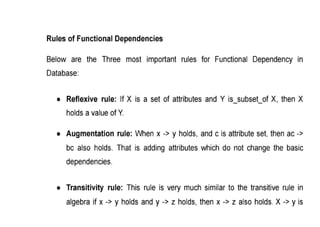
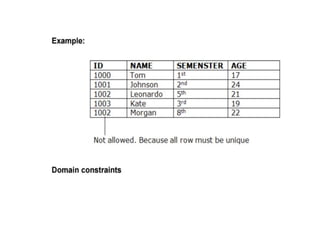
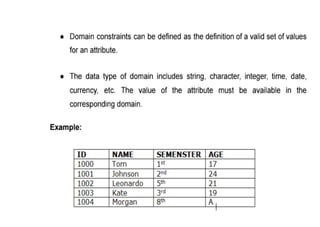
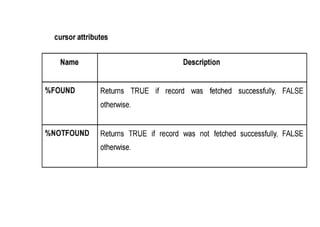
The document provides questions related to database management systems (DBMS). It asks to define key DBMS concepts like data models, attributes, cardinality ratio, normalization, functional dependency, and distributed databases. It also asks about database design topics such as entity-relationship diagrams, schema design, and integrity rules. Additional questions cover SQL, transactions, concurrency control, and PL/SQL.