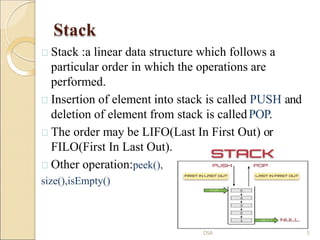
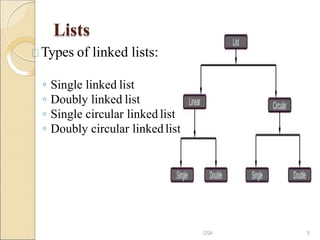
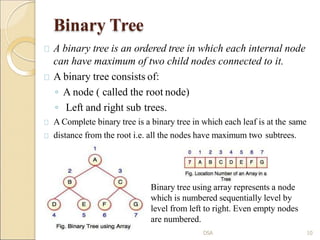
This document provides an introduction to various data structures. It discusses arrays, stacks, queues, lists, binary trees, and graphs. Arrays can be single-dimension, two-dimension, or multi-dimension. Stacks follow LIFO order while queues follow FIFO order. Lists are collections of nodes where each node contains data and a link to the next node. Binary trees have a root node and left and right subtrees, while graphs contain vertices connected by edges.