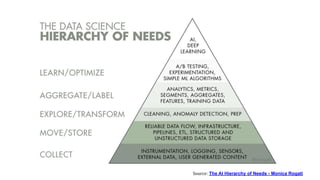
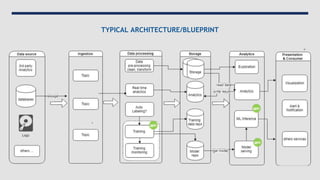
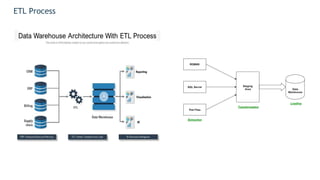
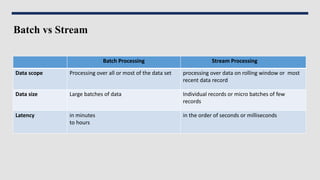
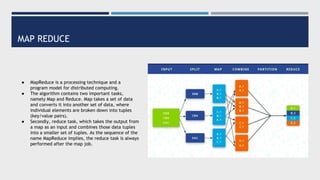
Data engineering involves designing and building pipelines to transform and transport data into a highly usable format for data scientists and analysts. This includes collecting data from multiple sources into a single data warehouse. Data engineers prepare big data infrastructure for analysis by setting up extract, transform, load processes and frameworks like Spark and Hadoop. They must understand batch and stream processing, unstructured and structured data types, relational databases and document stores, and perform demos to showcase their work.