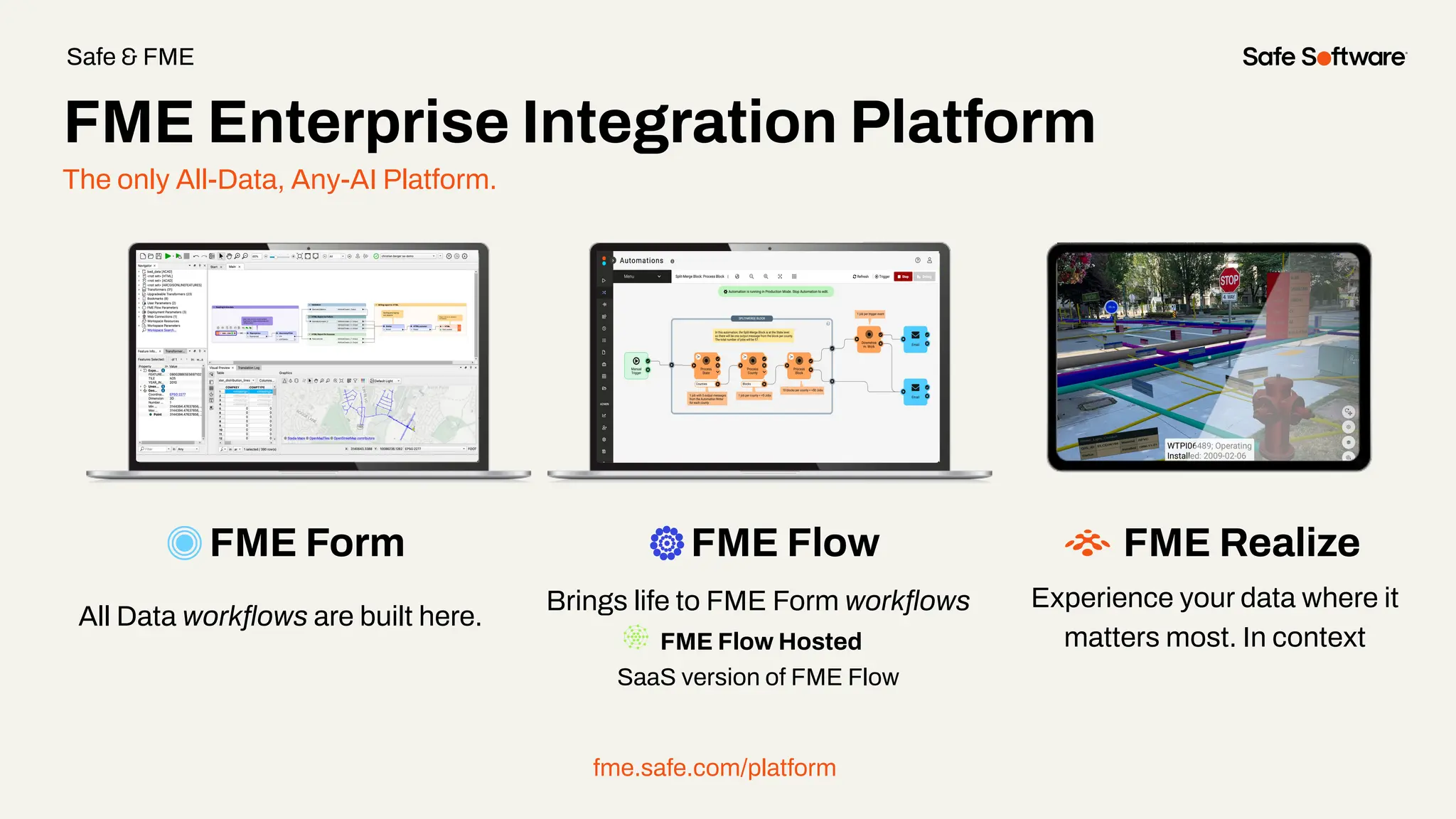
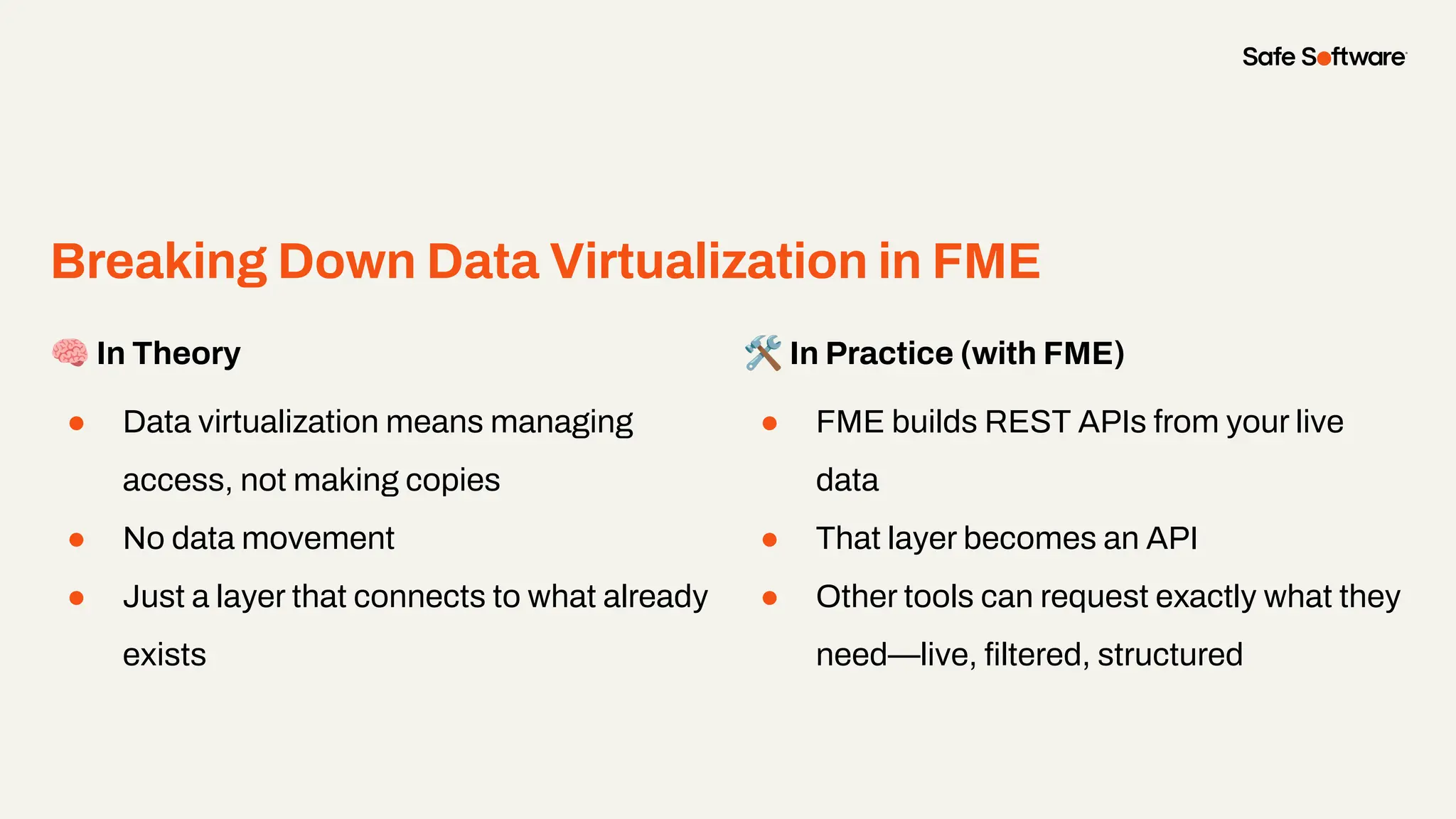
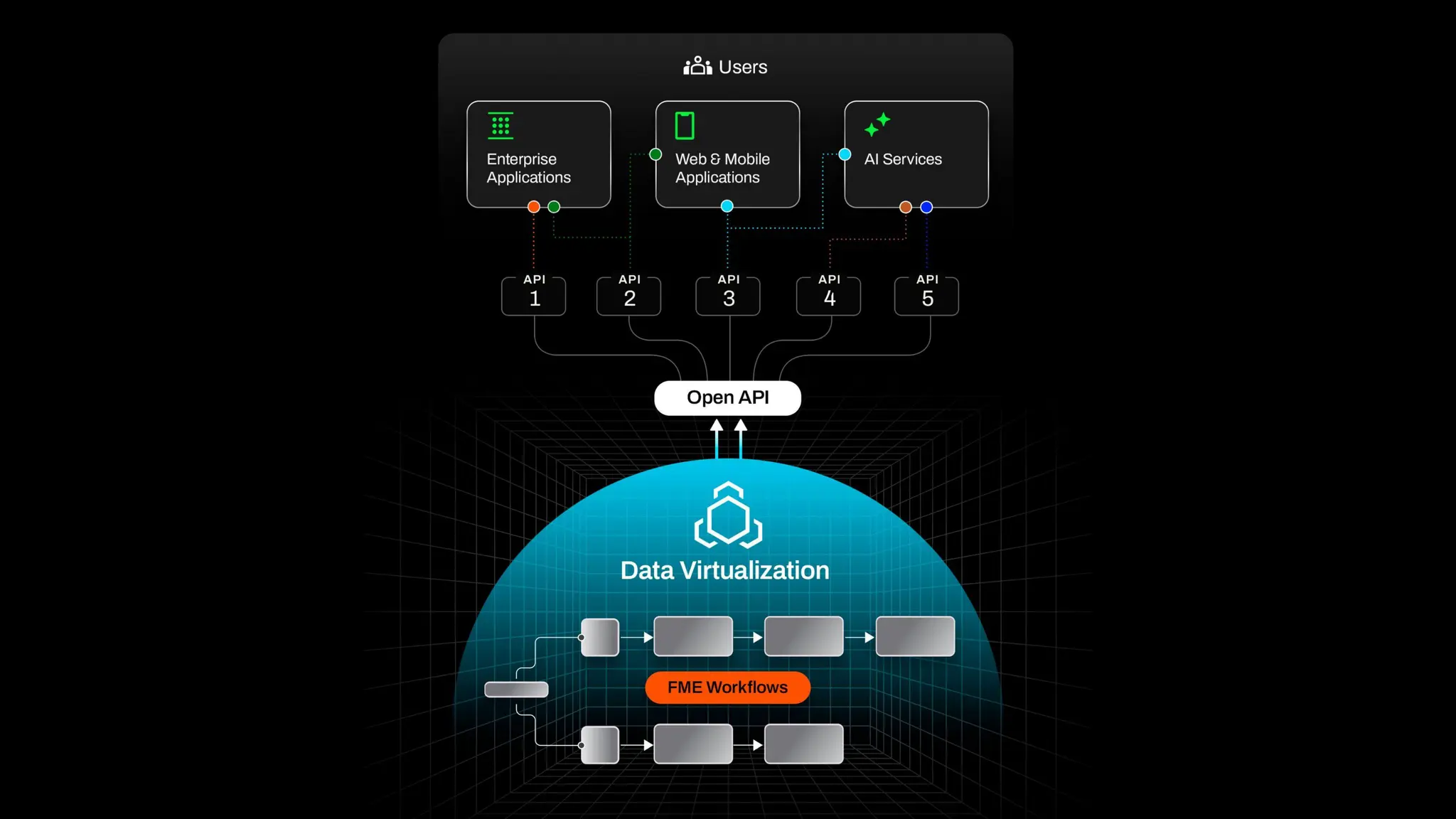
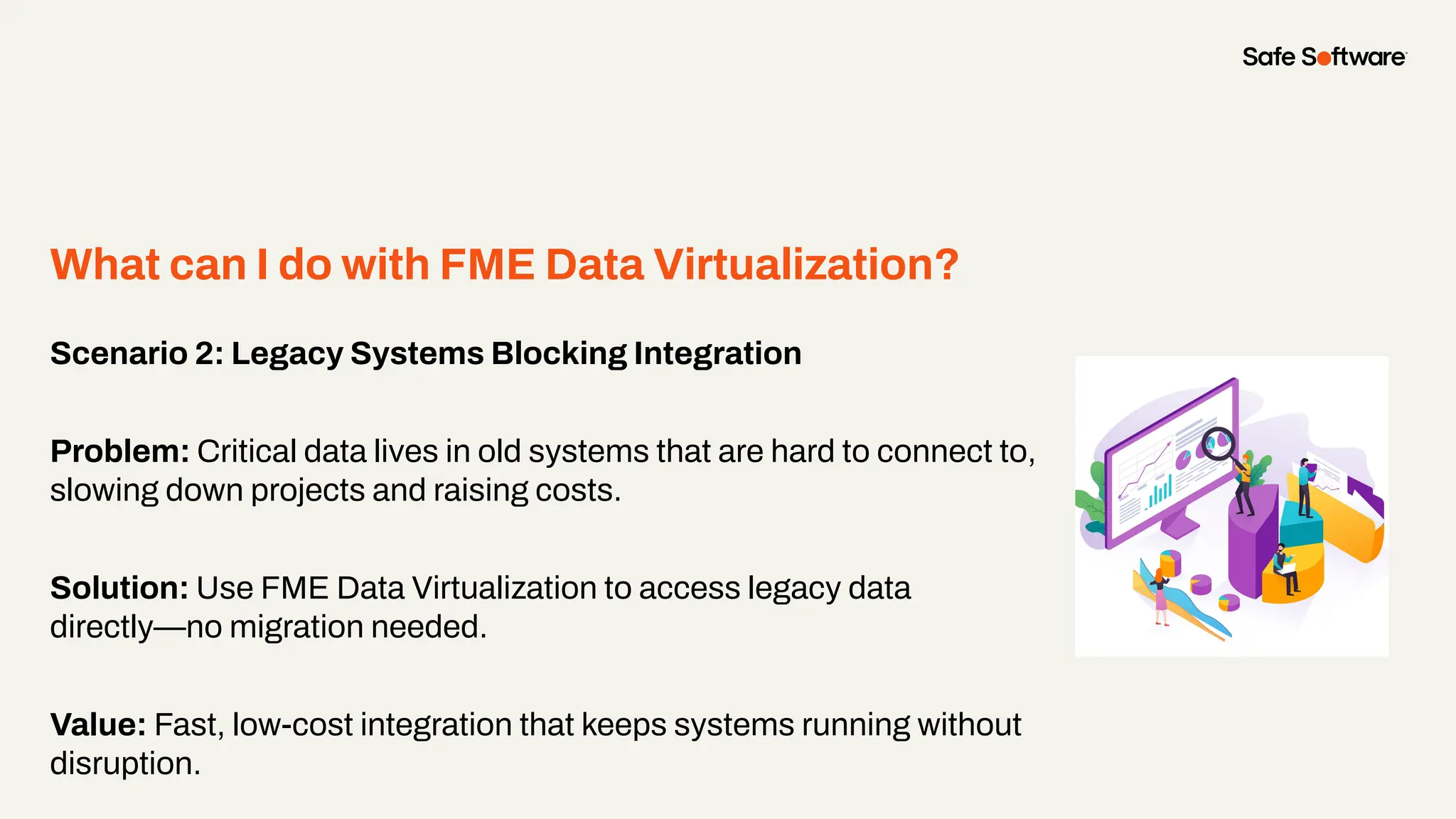
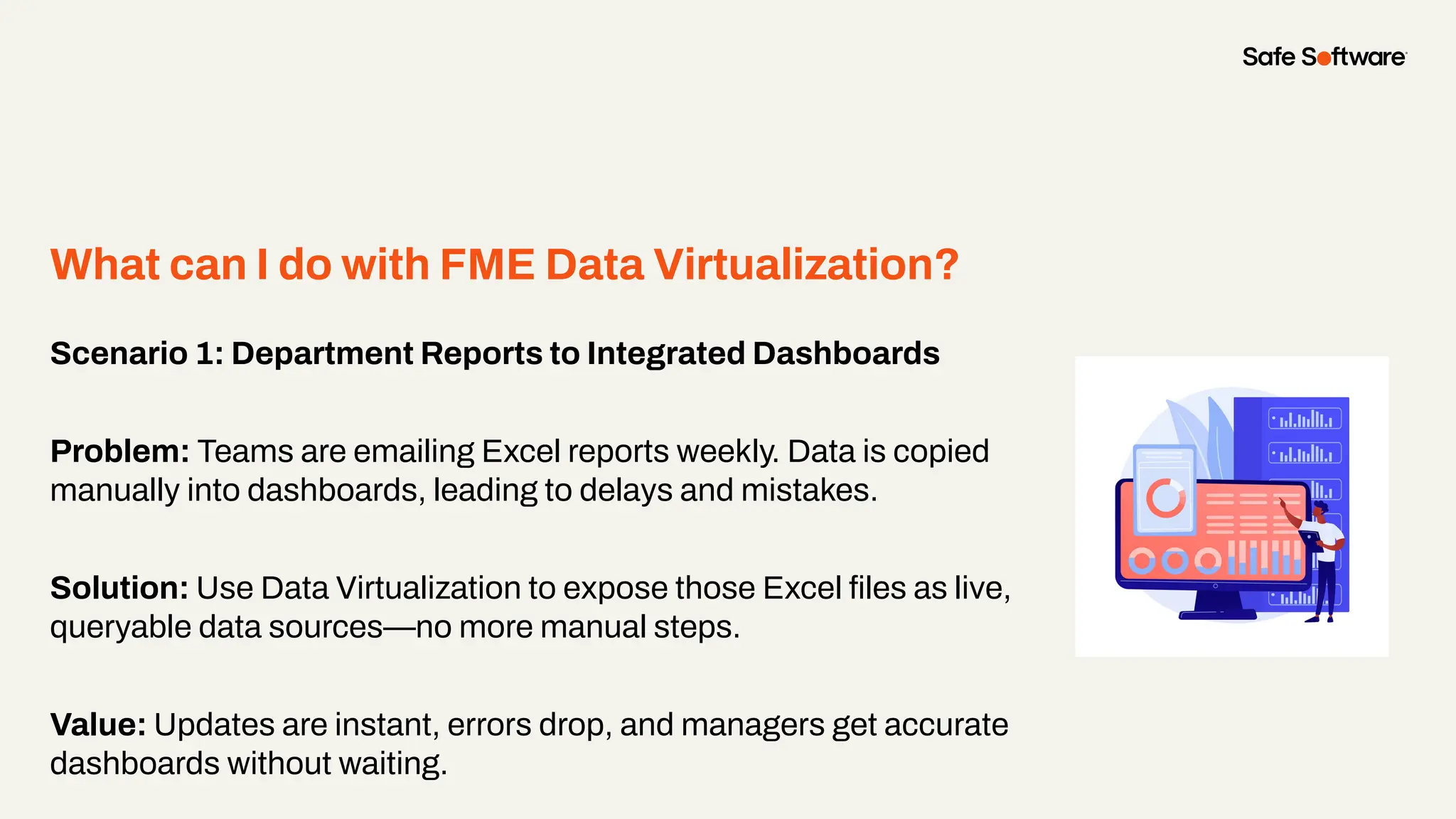
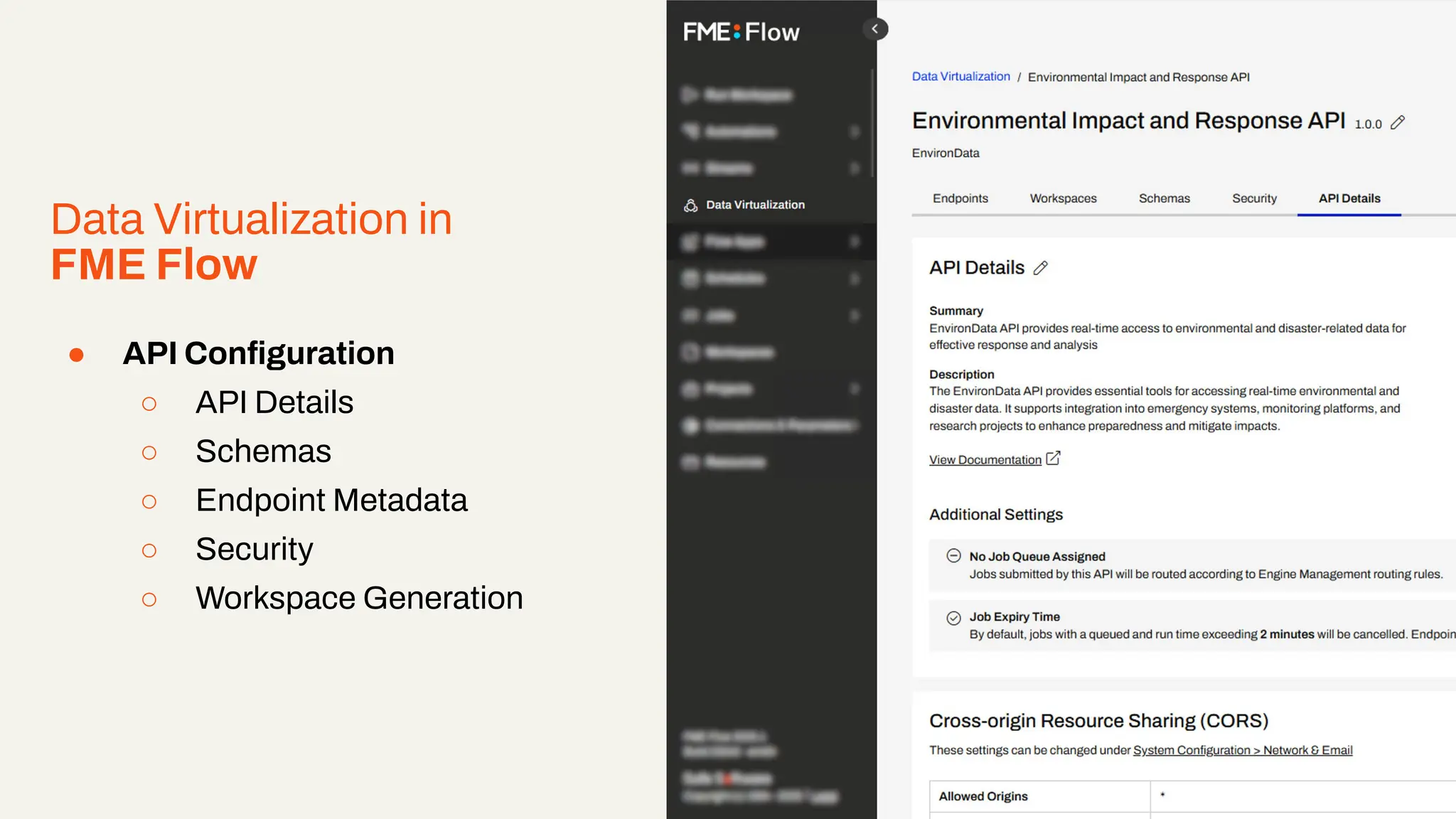
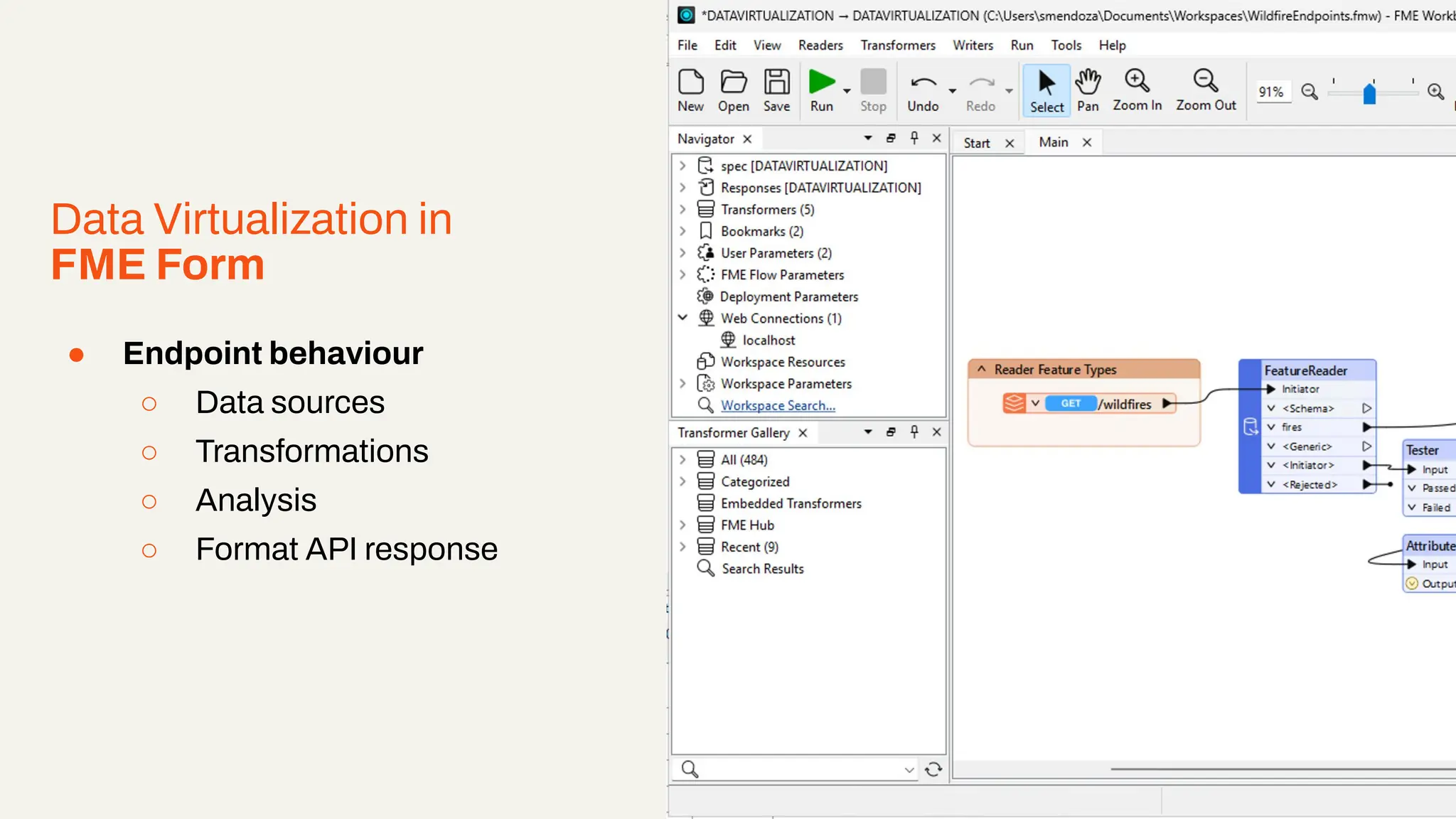
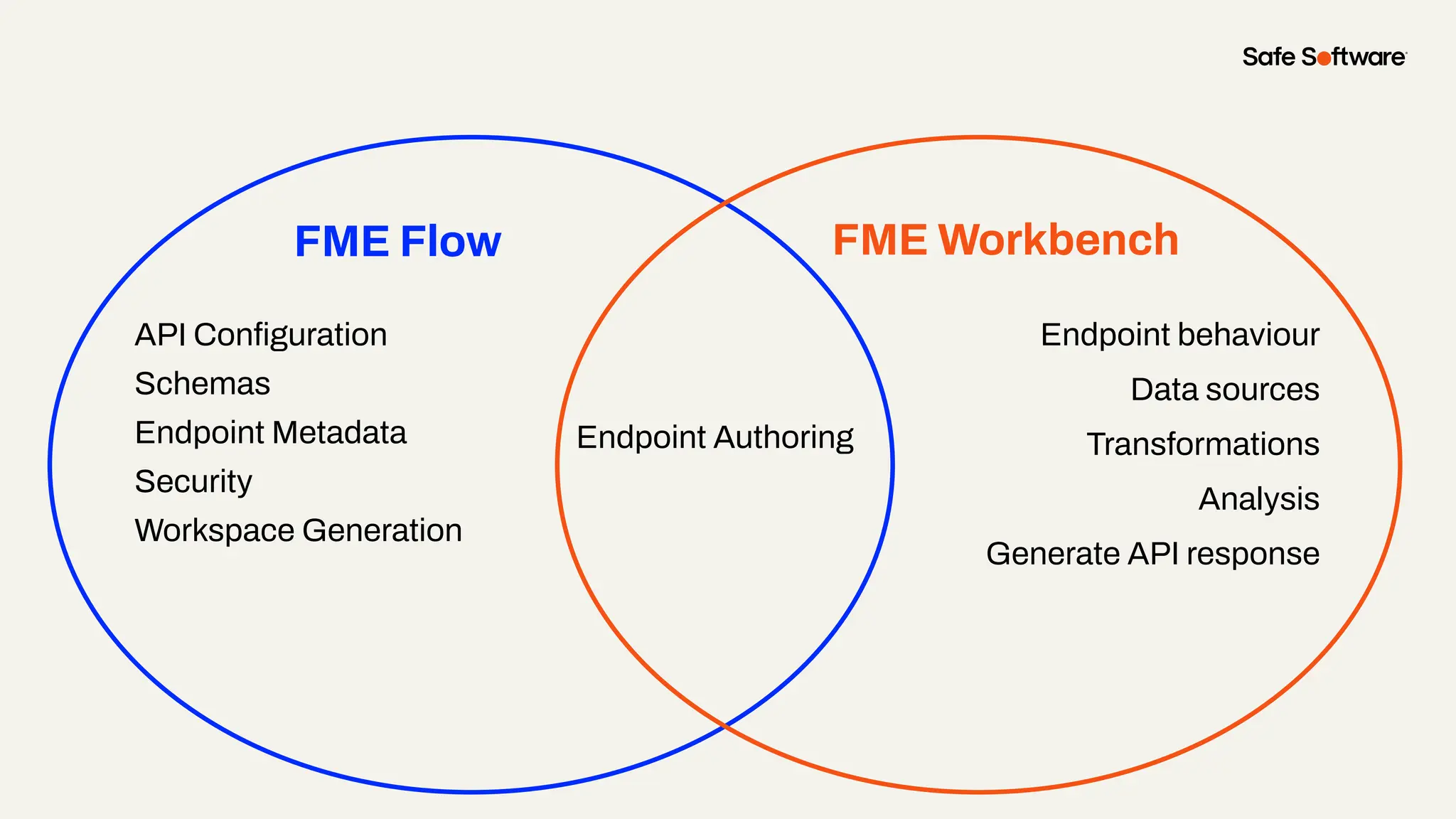
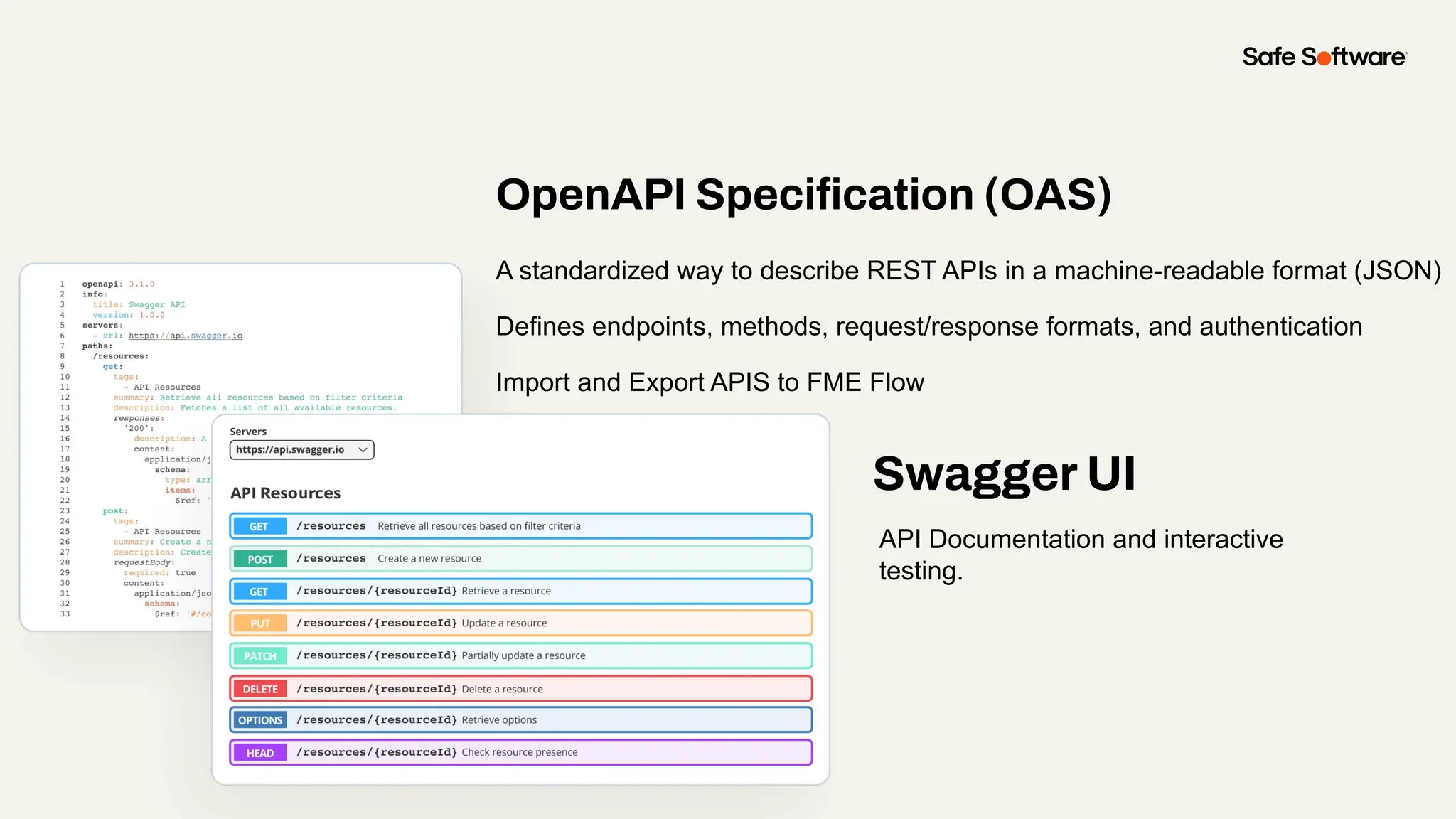
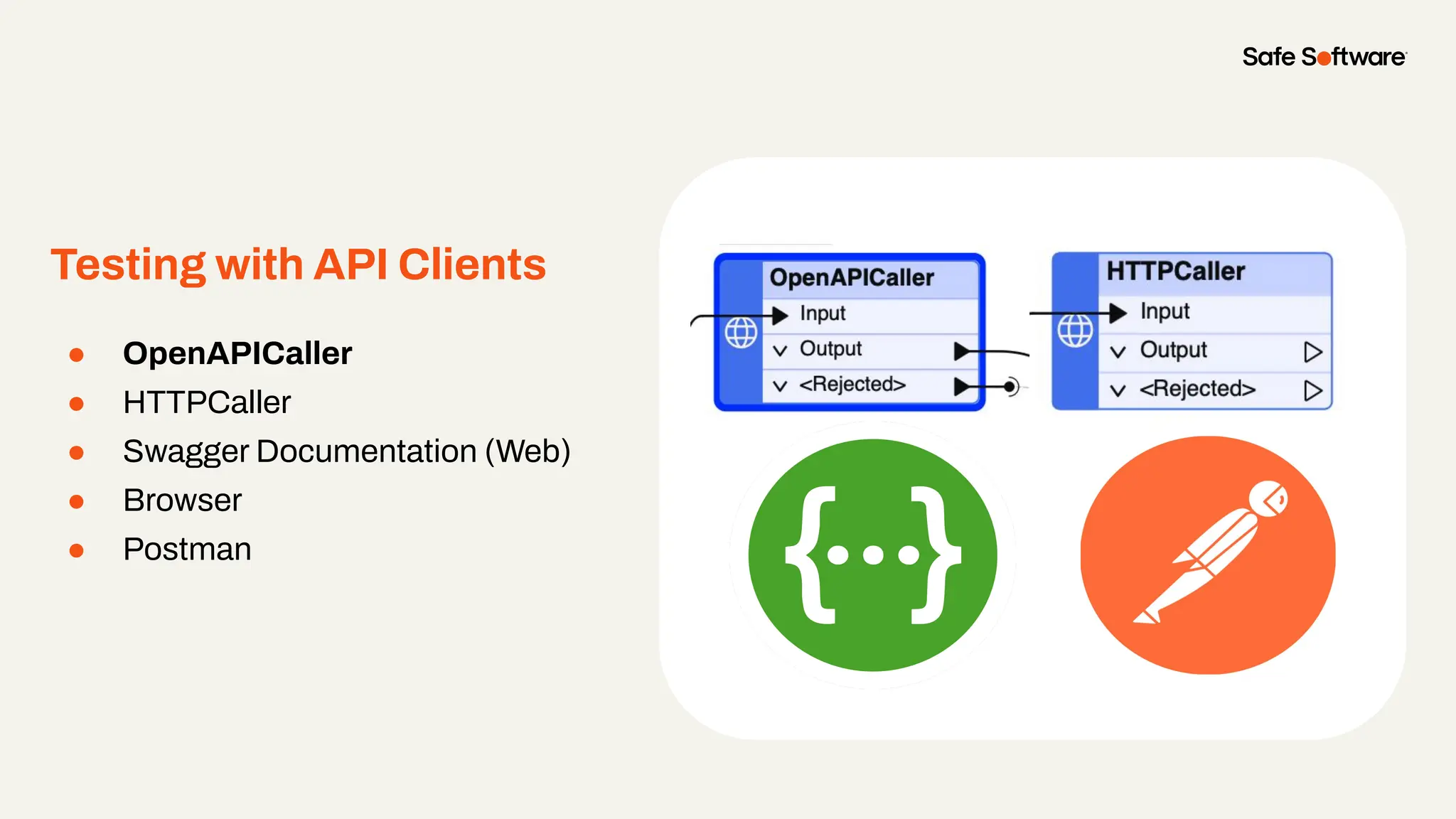
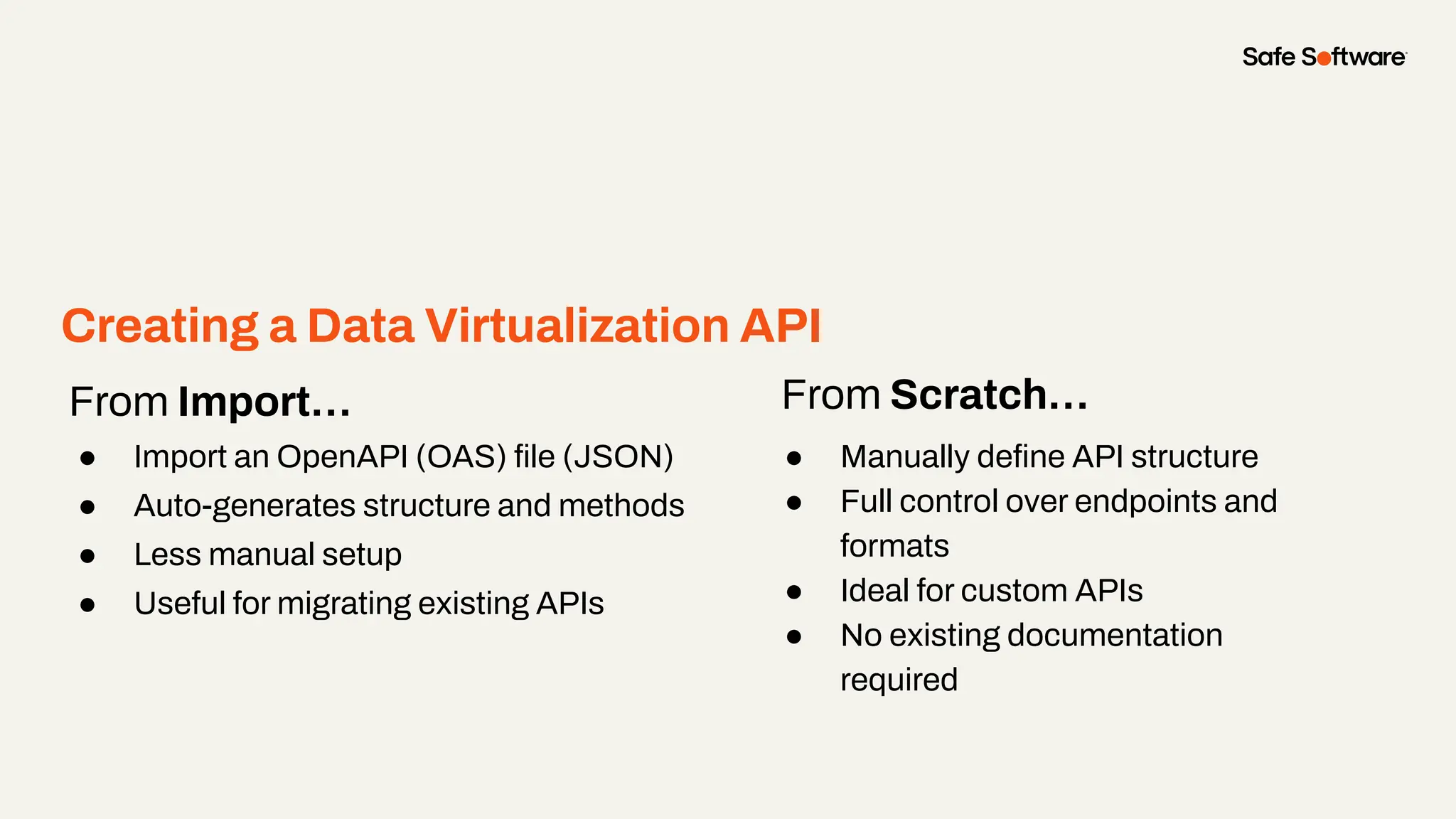
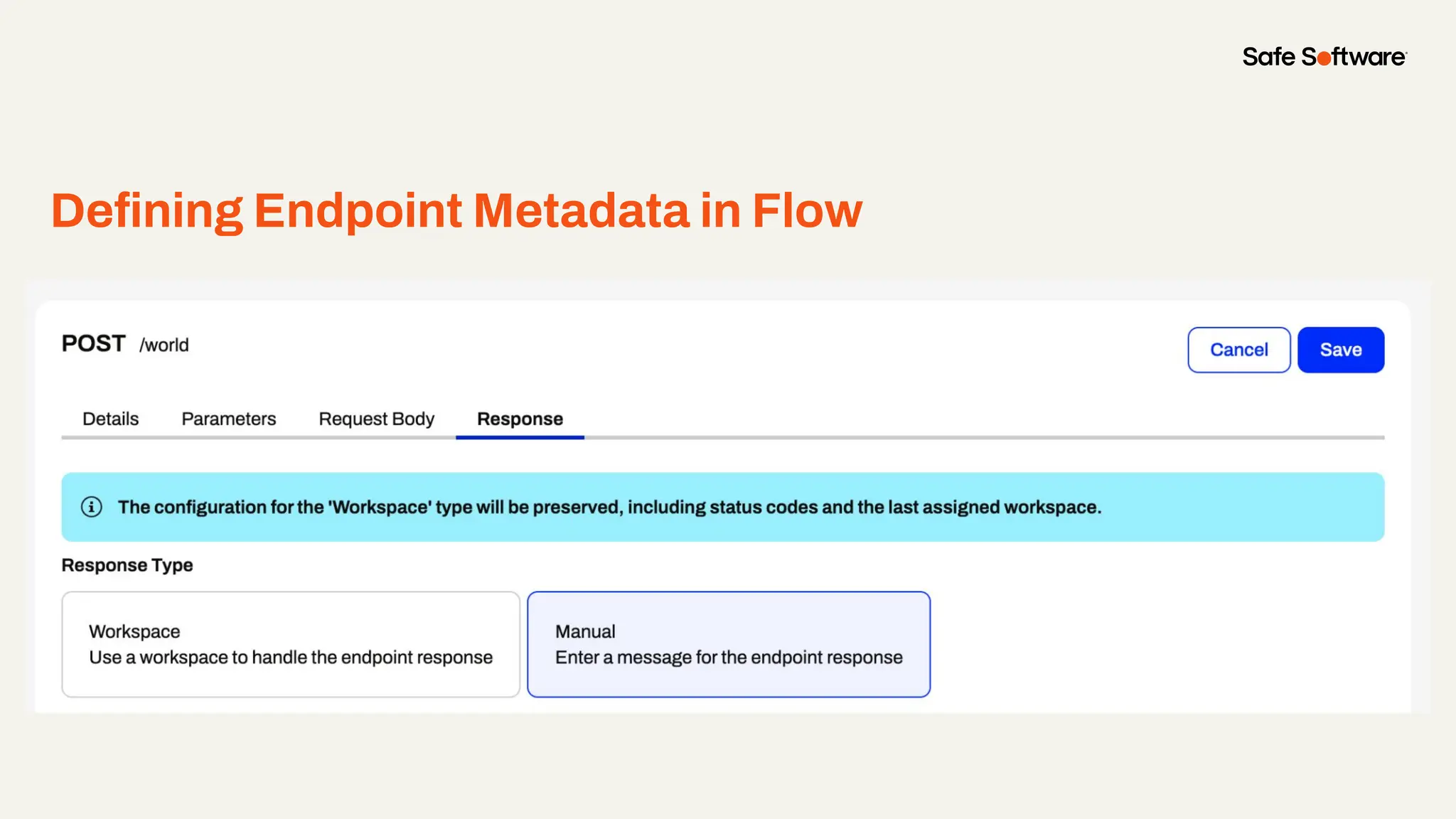
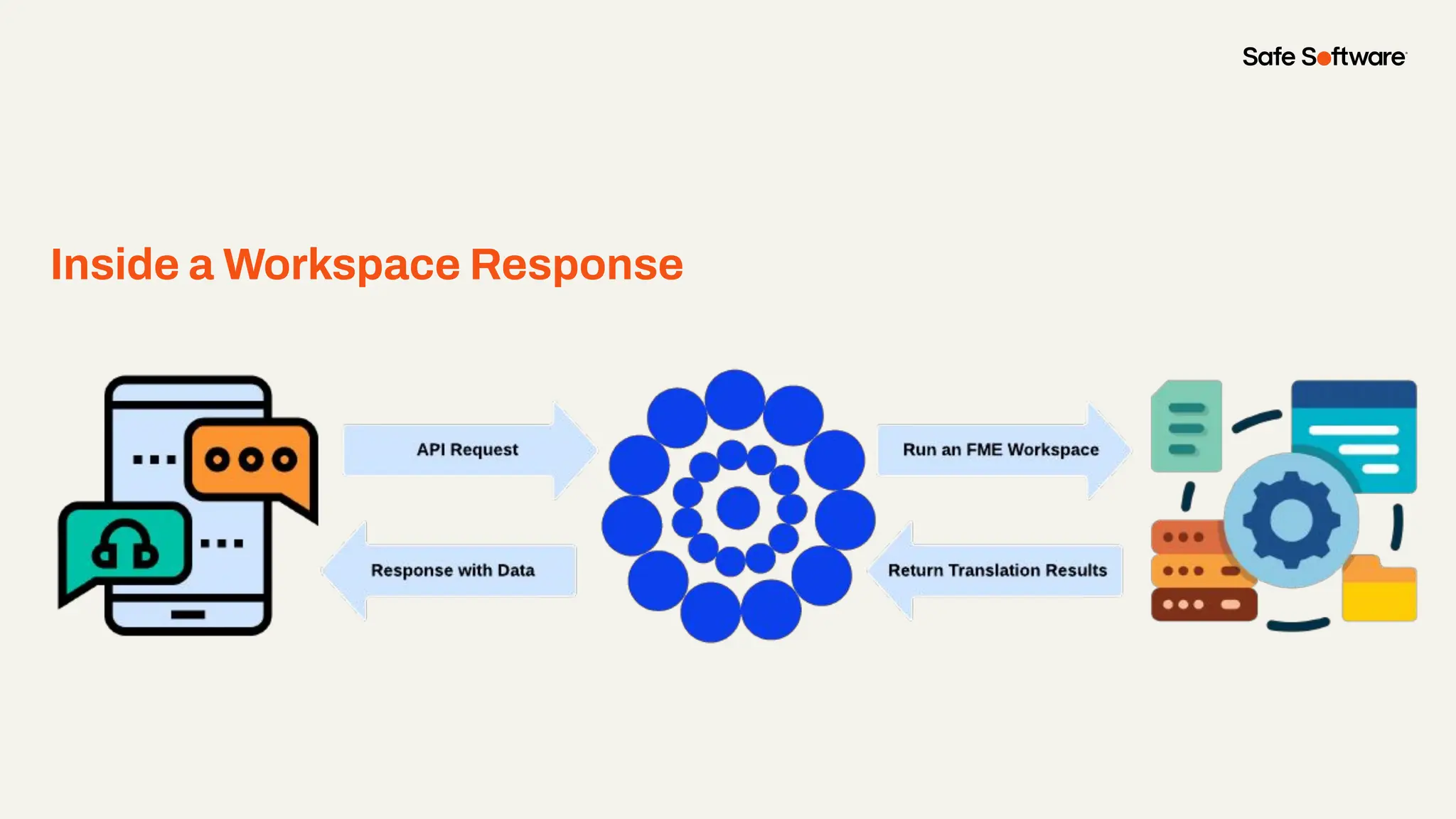
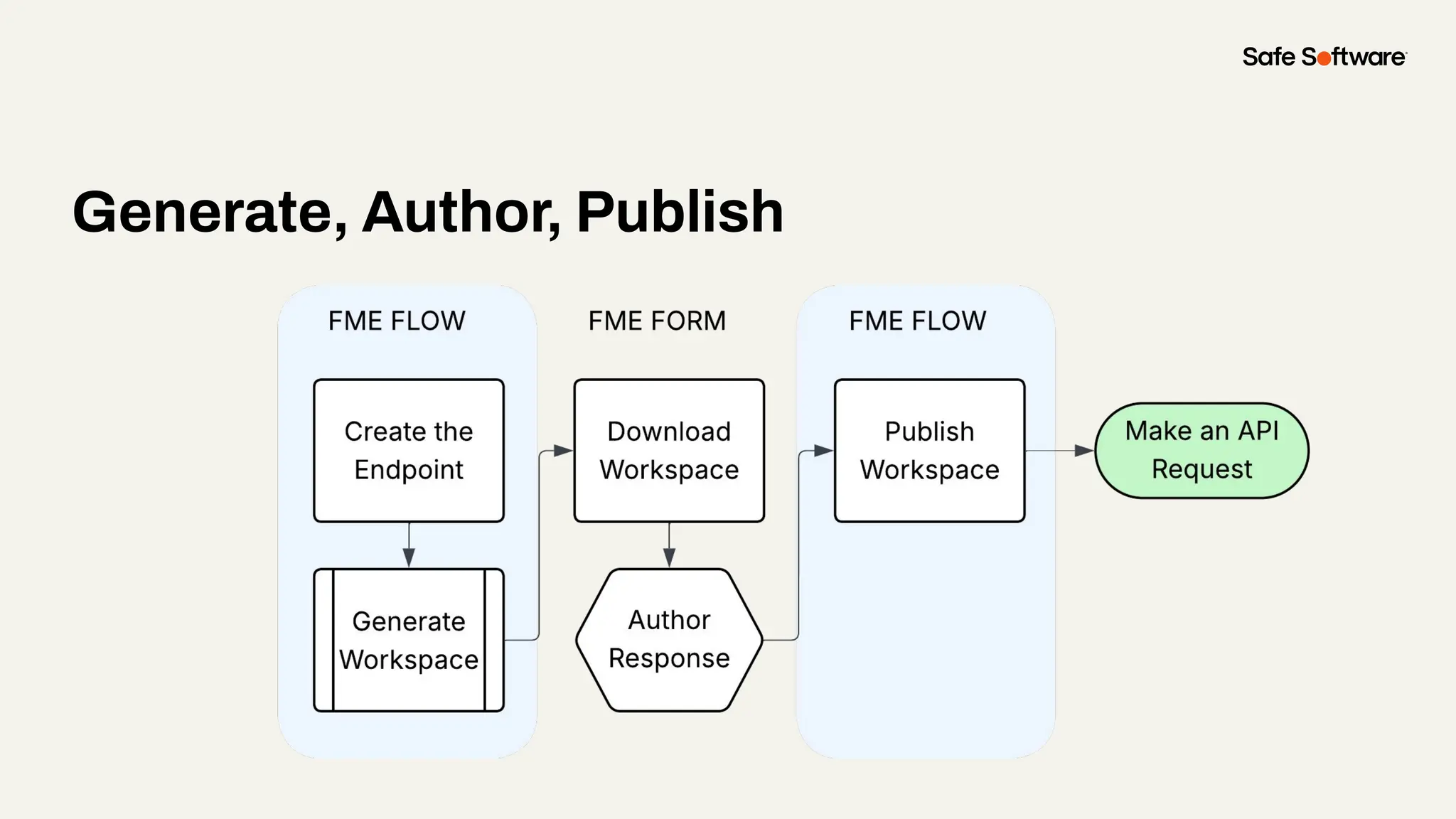
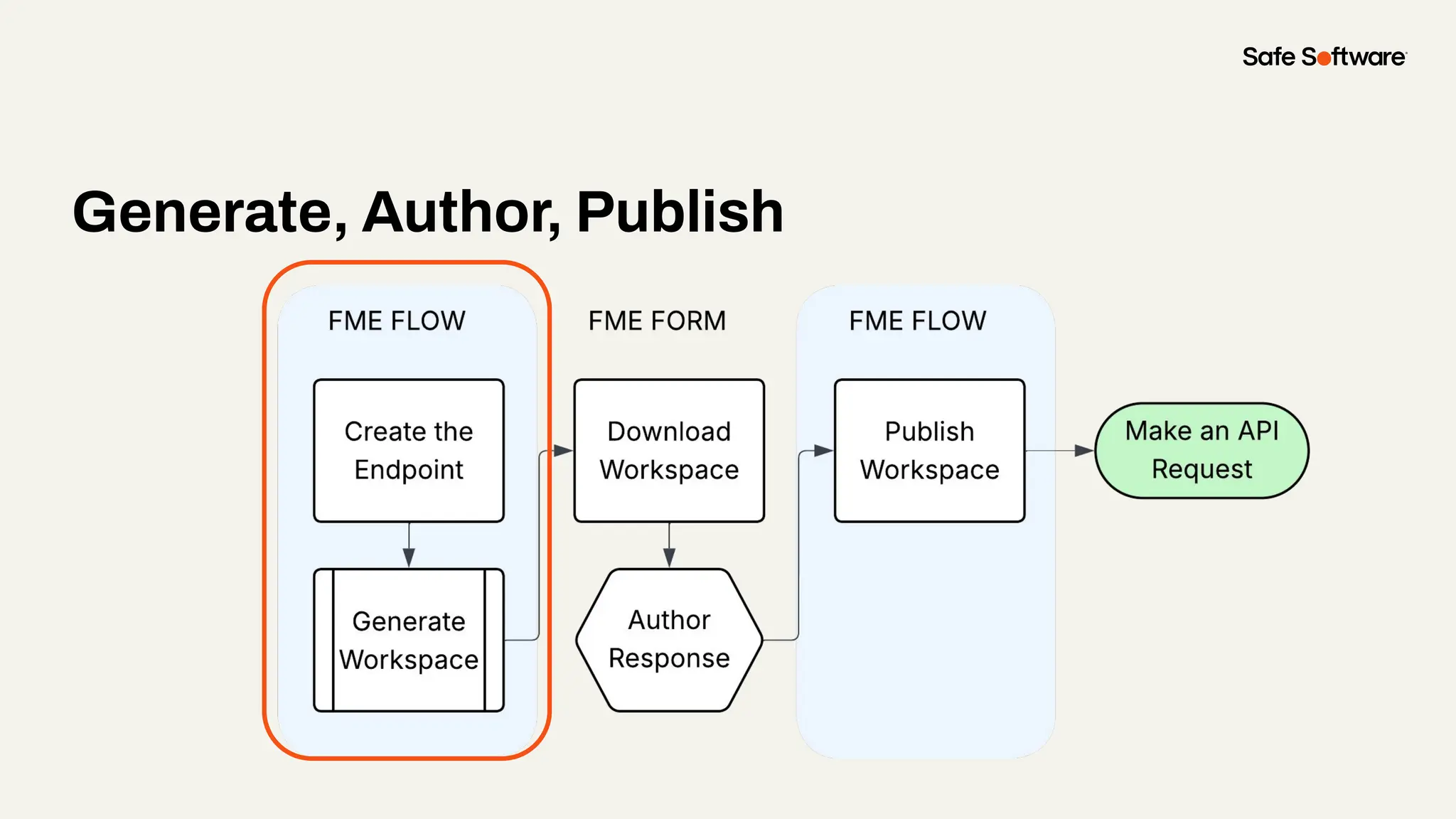
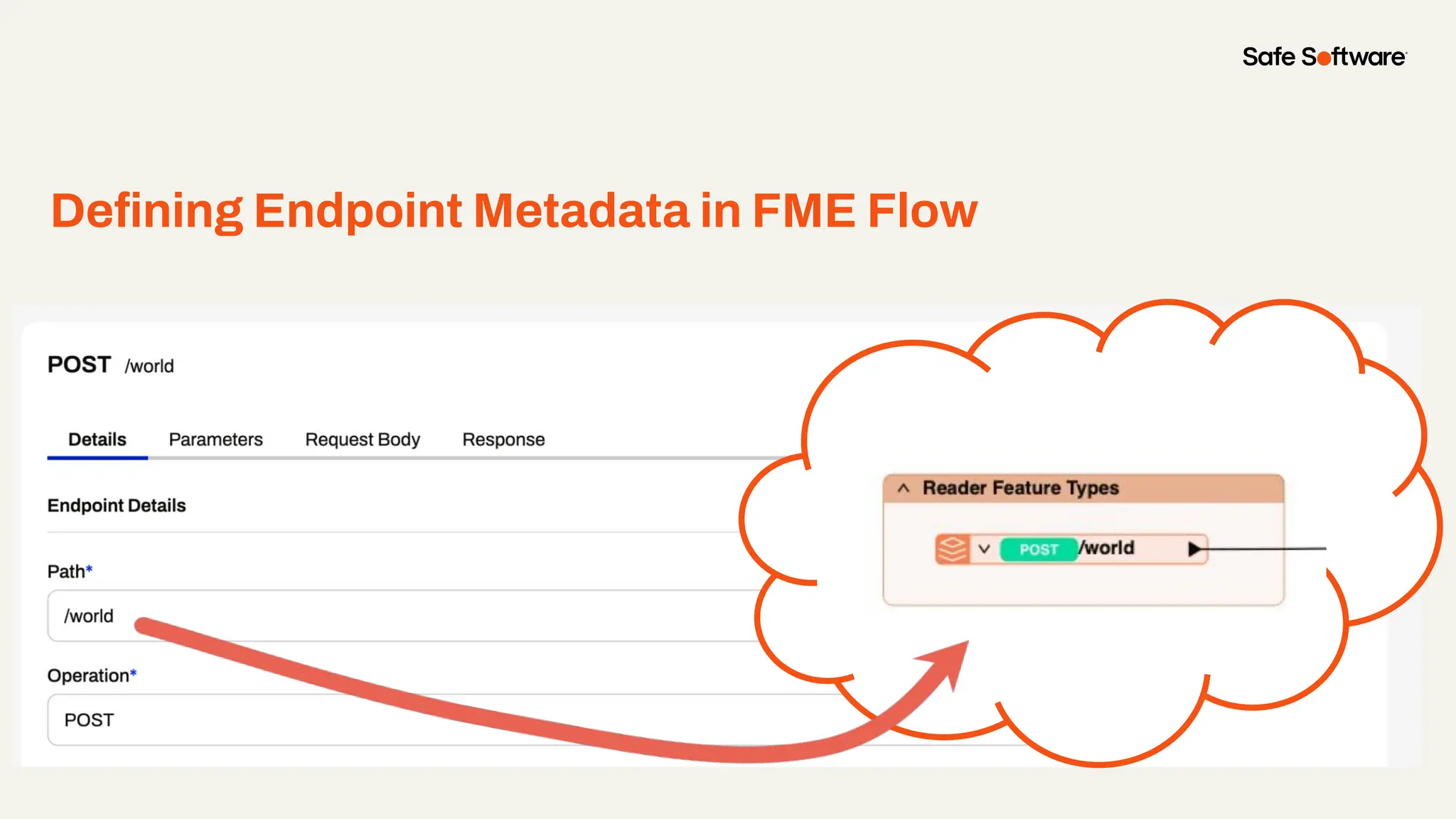
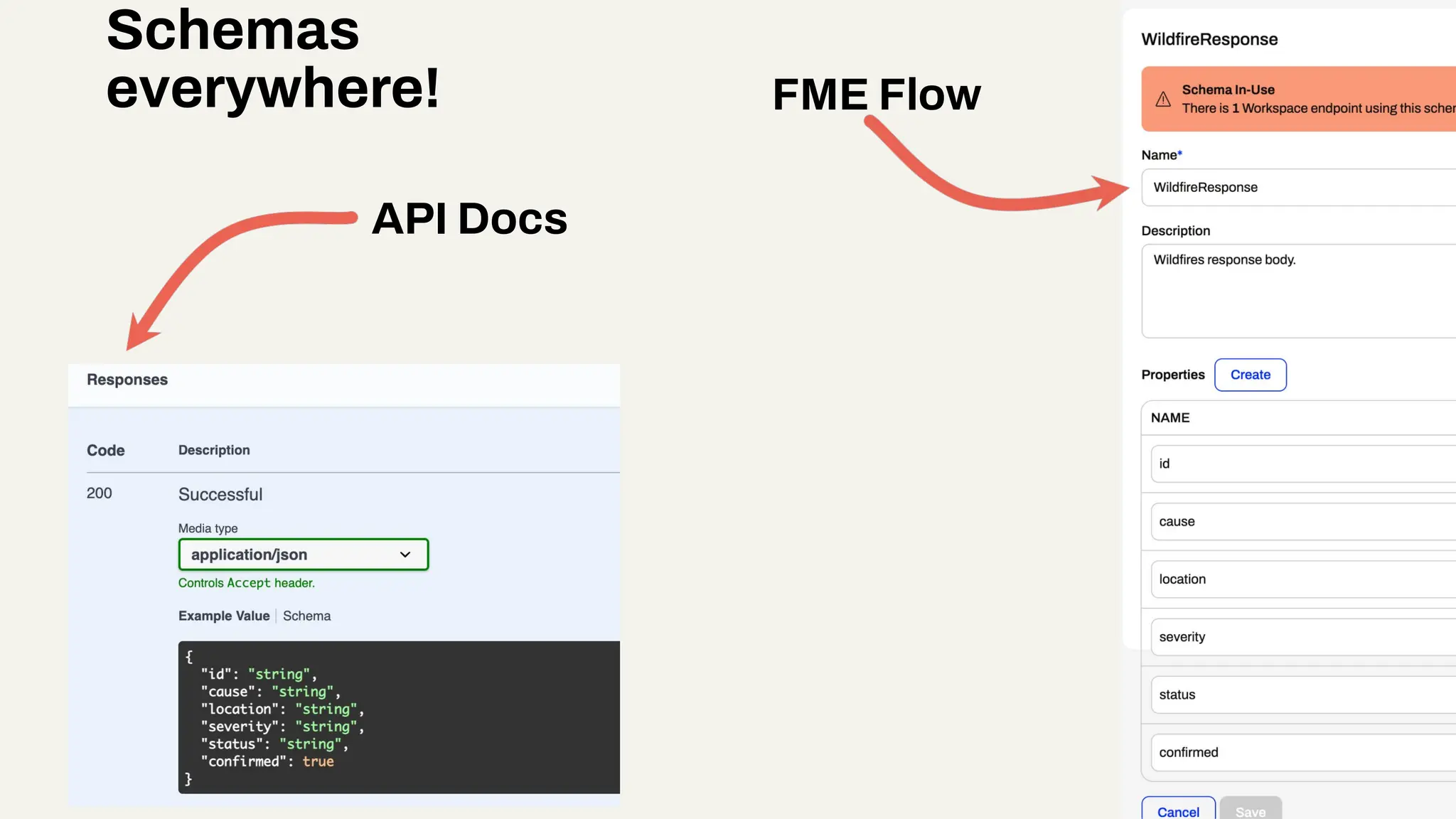
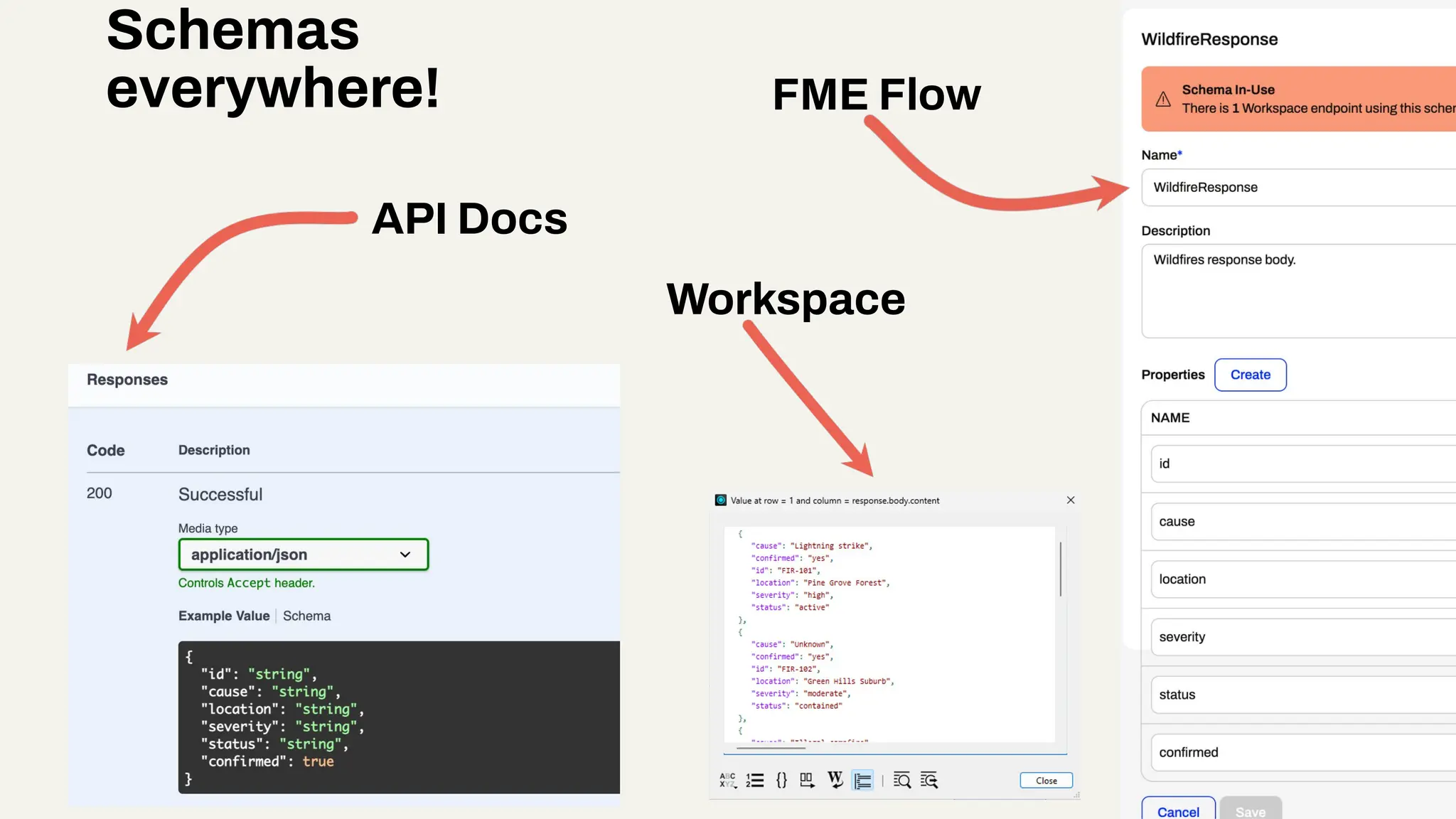
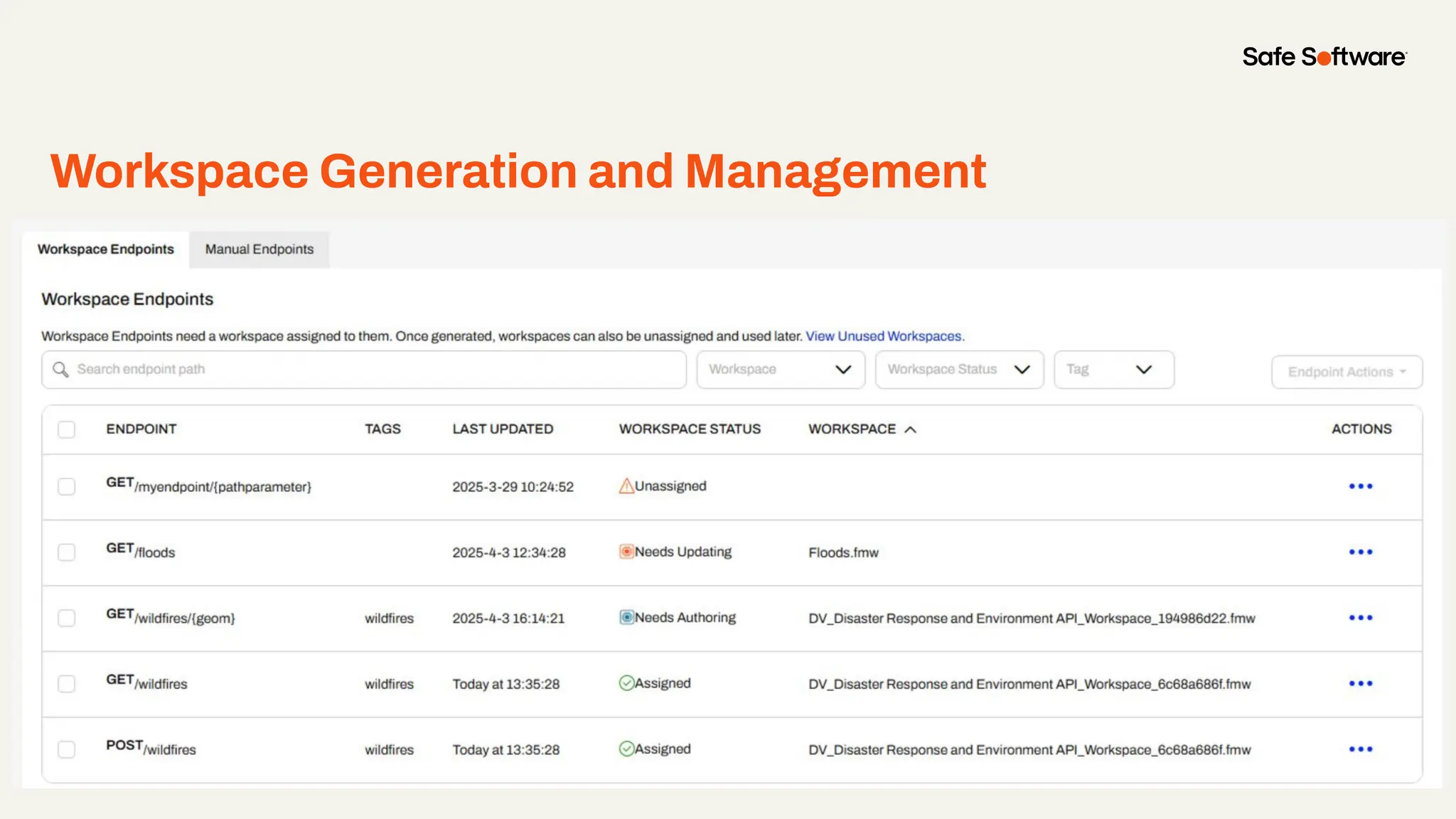
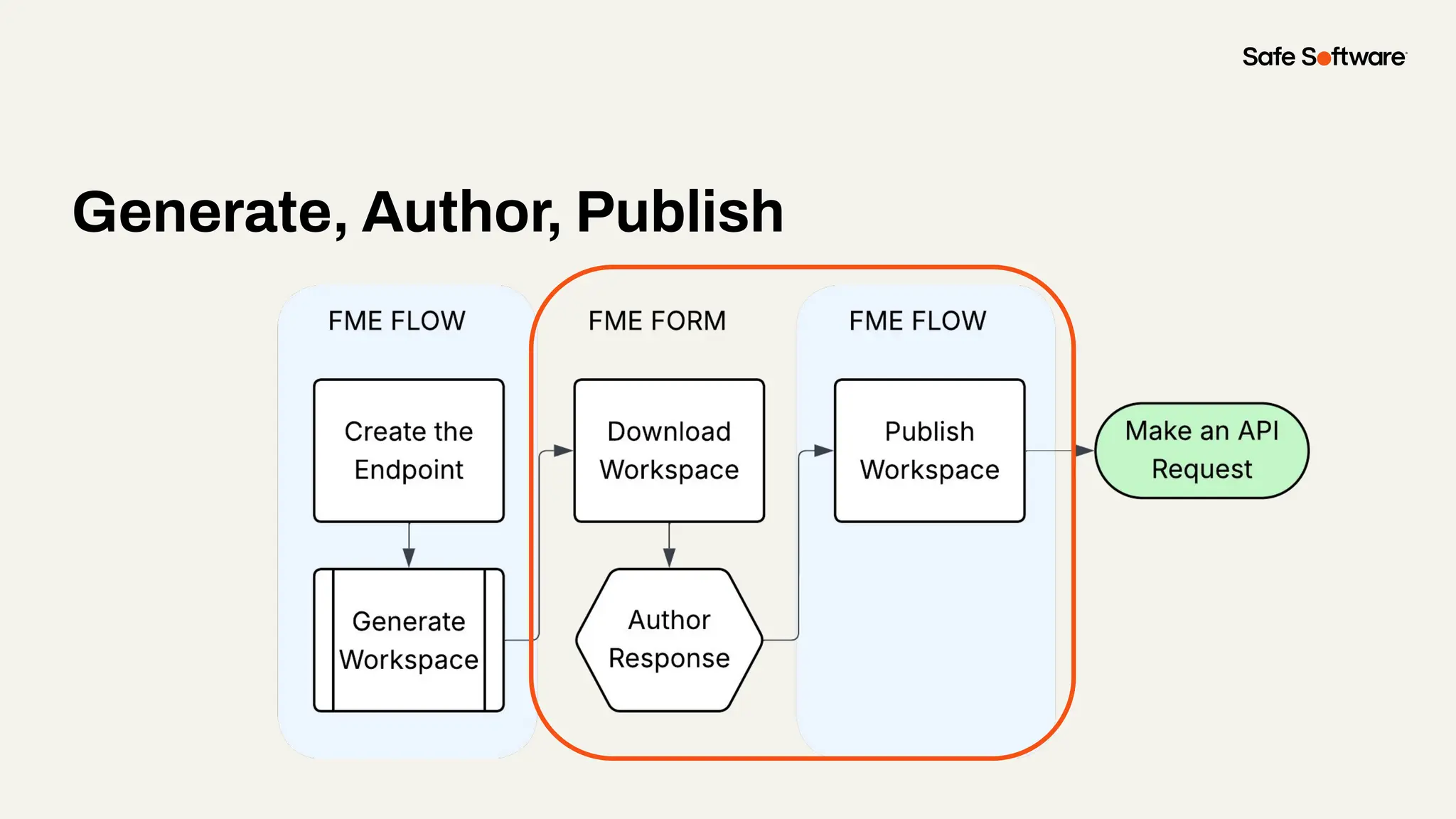
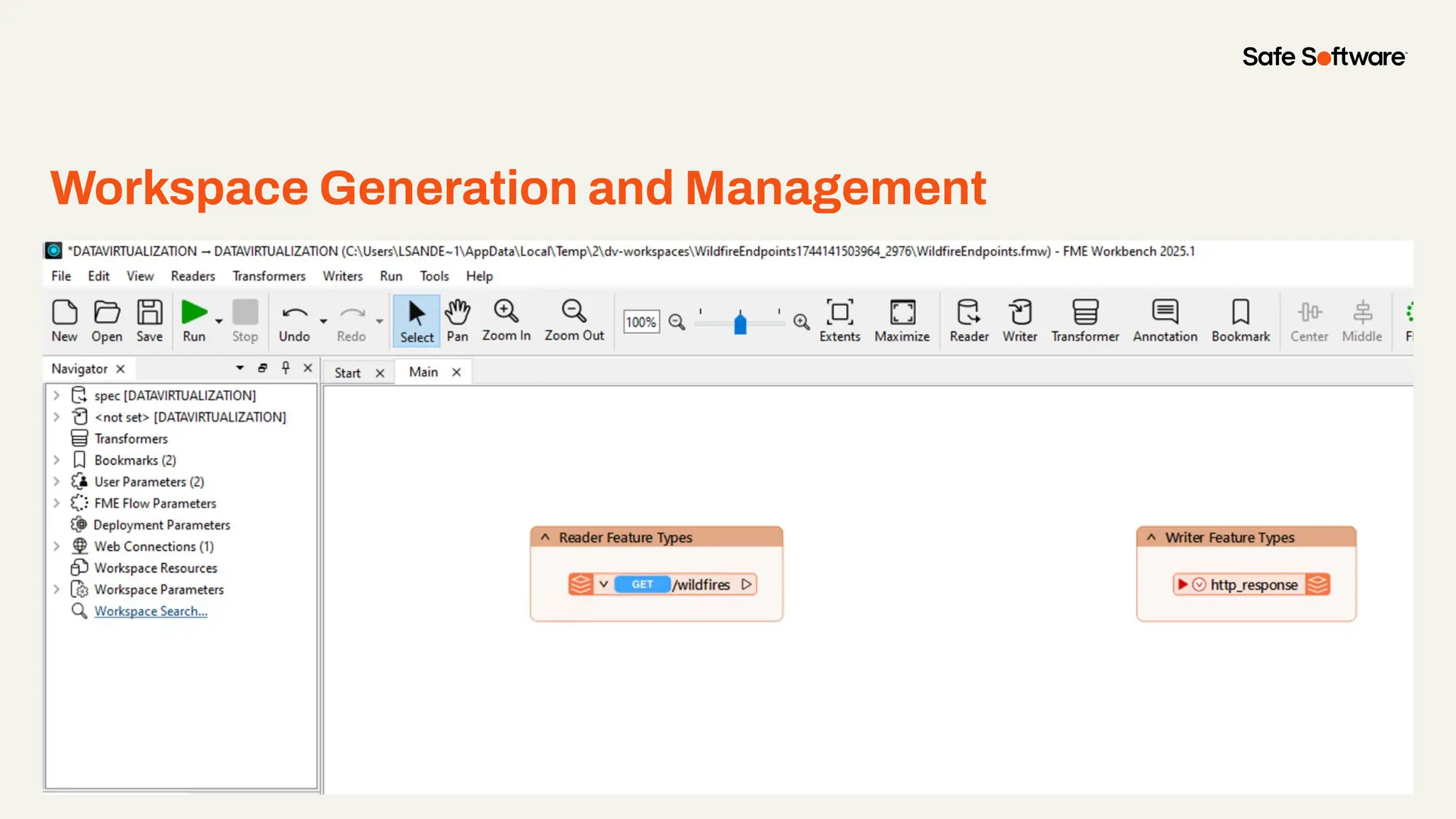
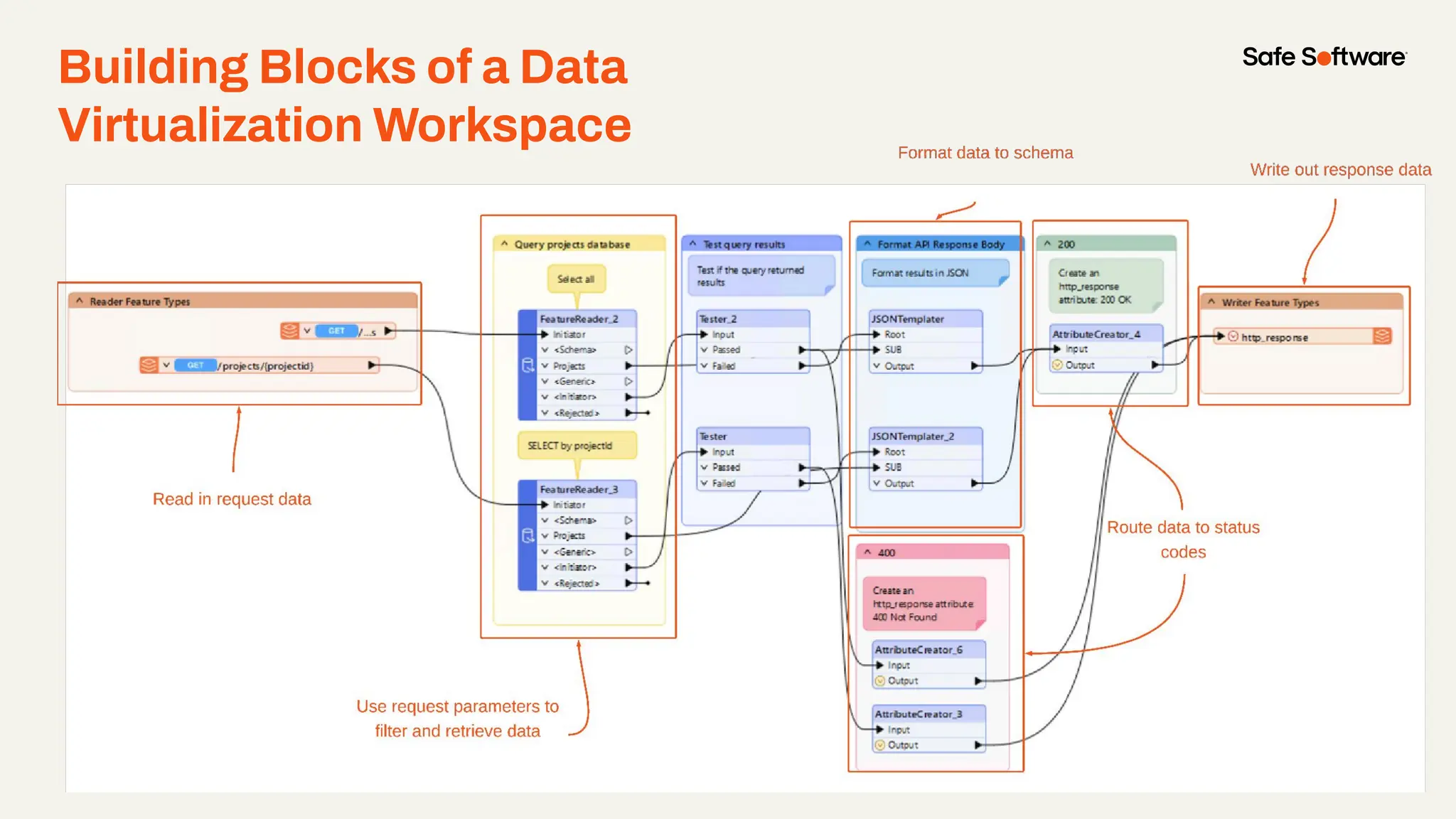
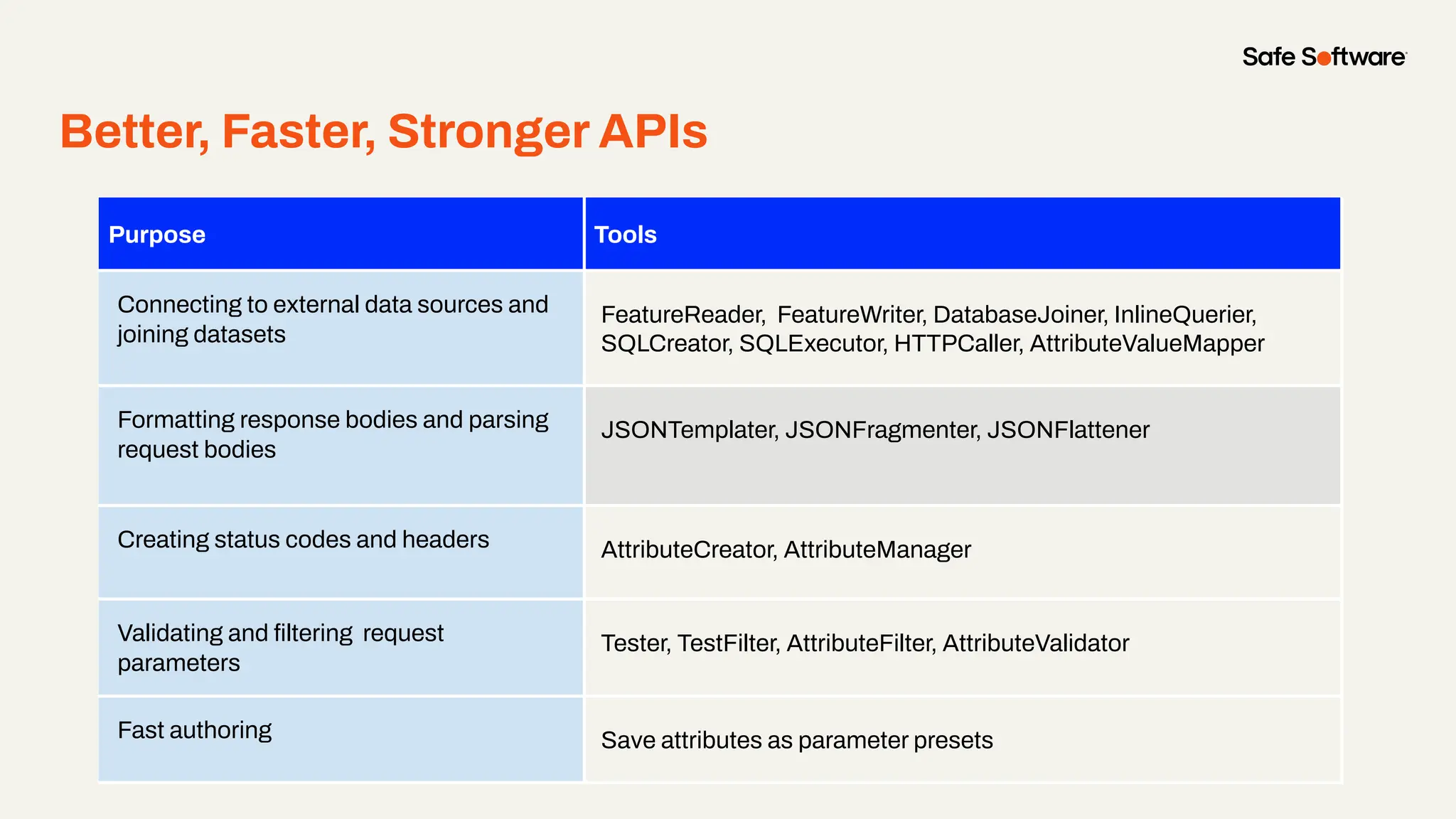
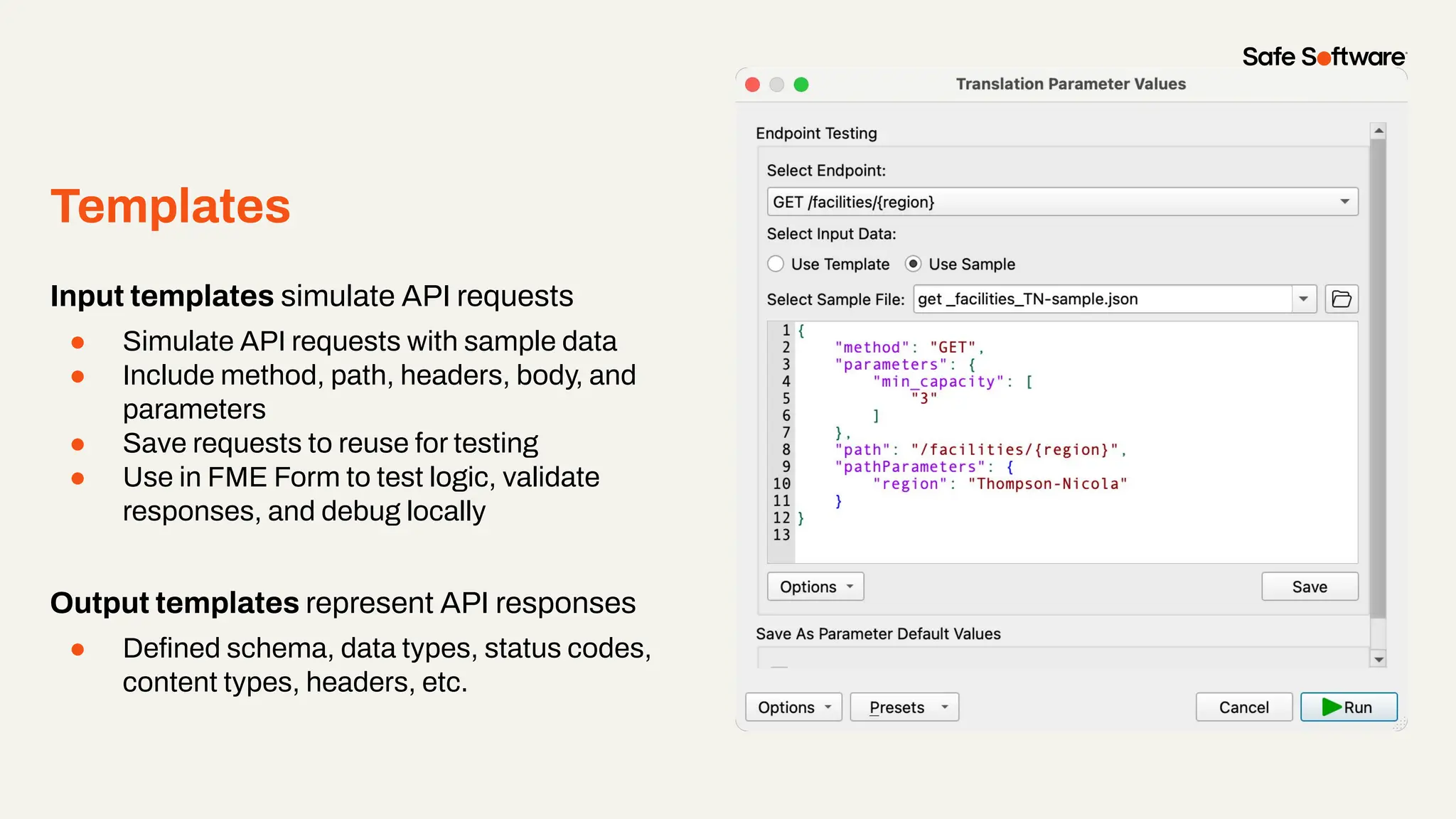
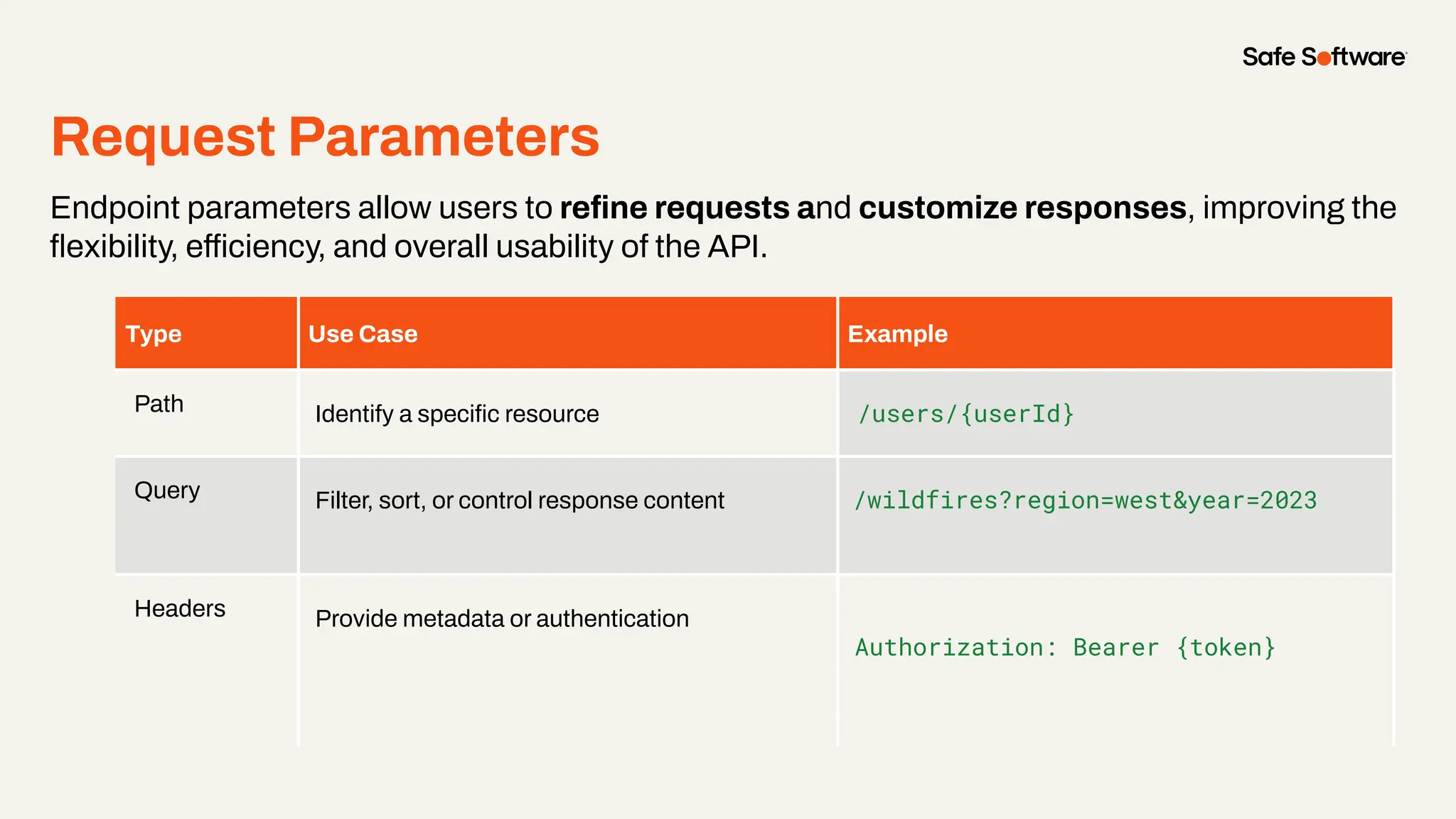
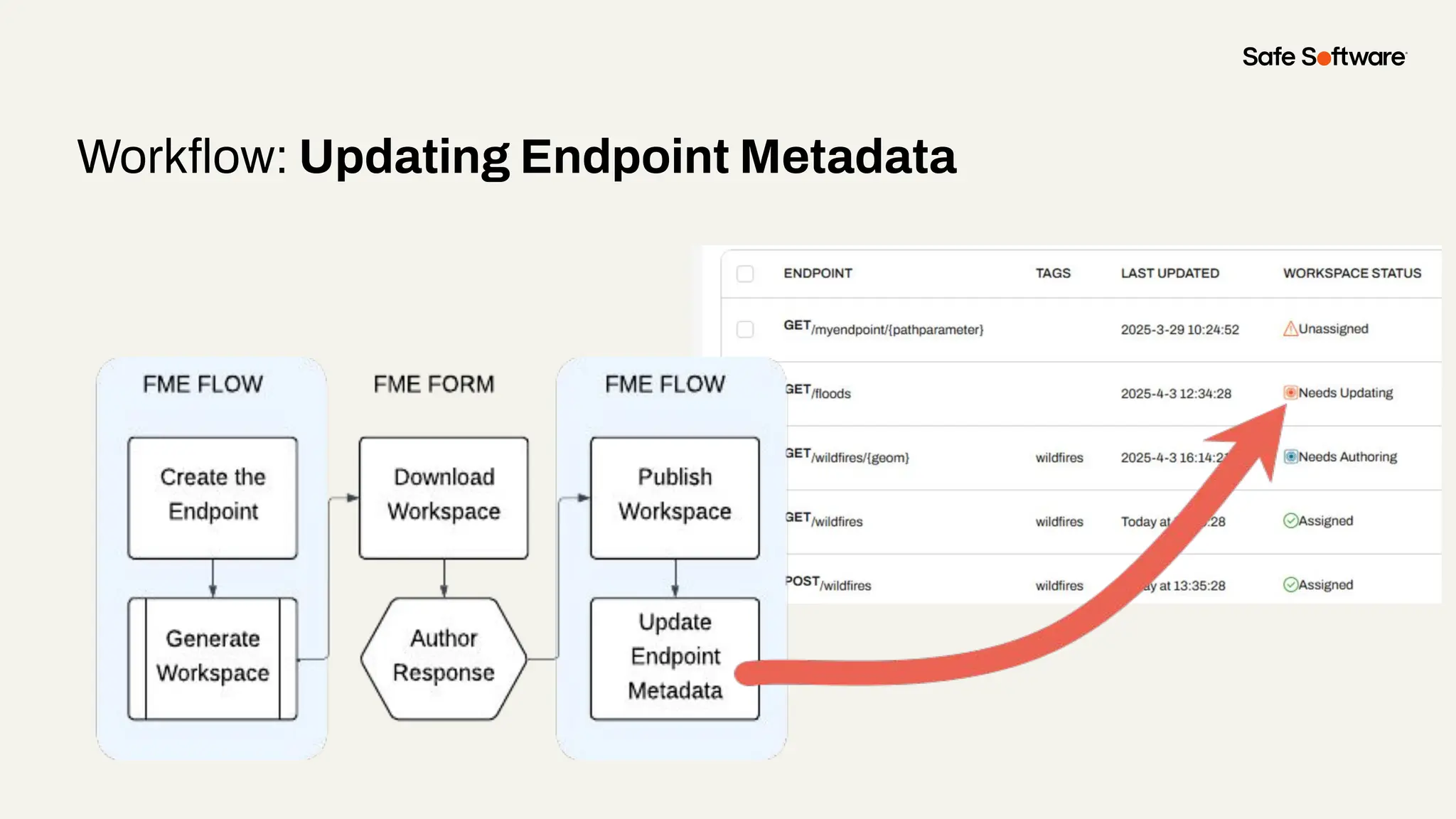
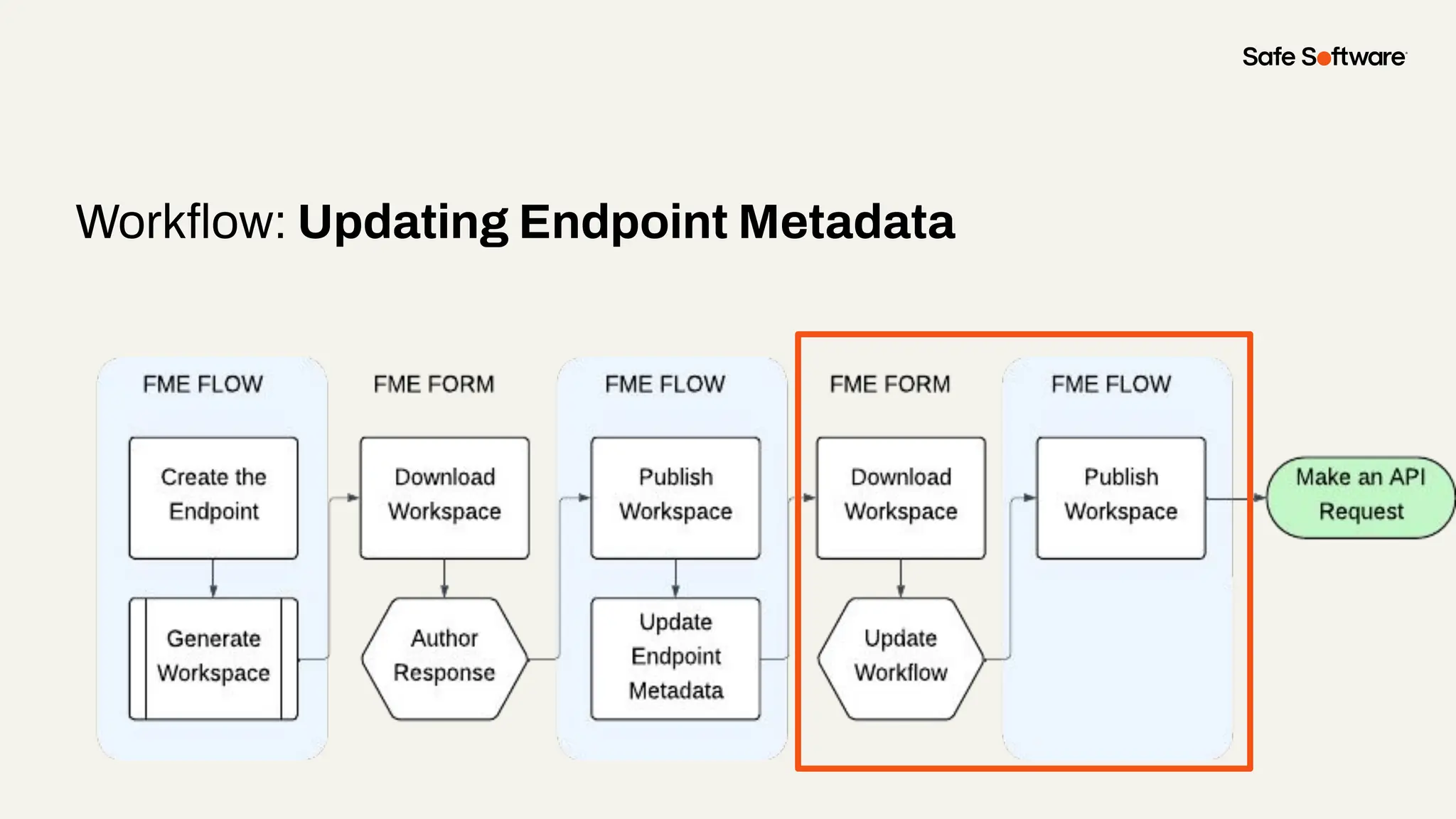
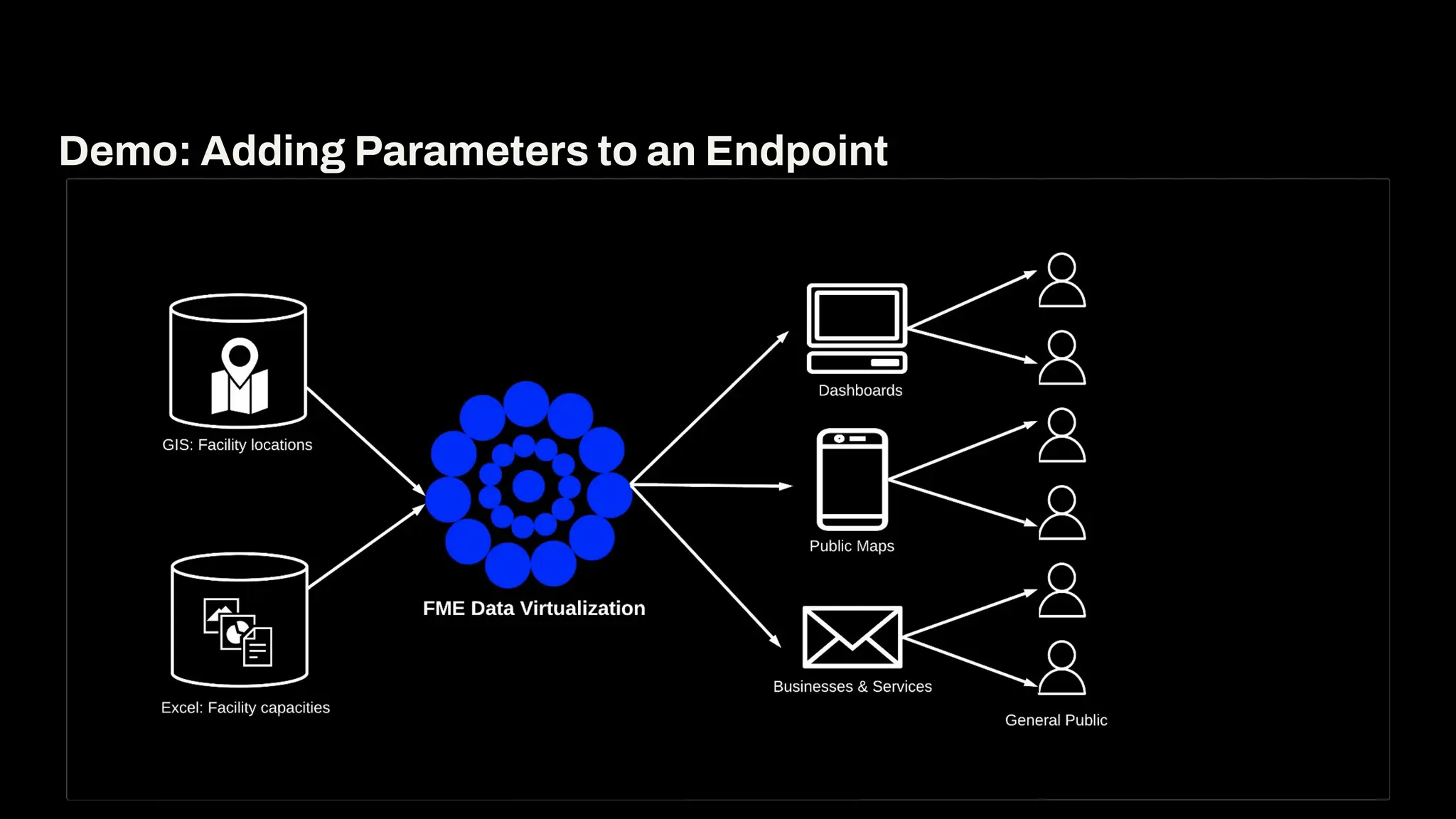
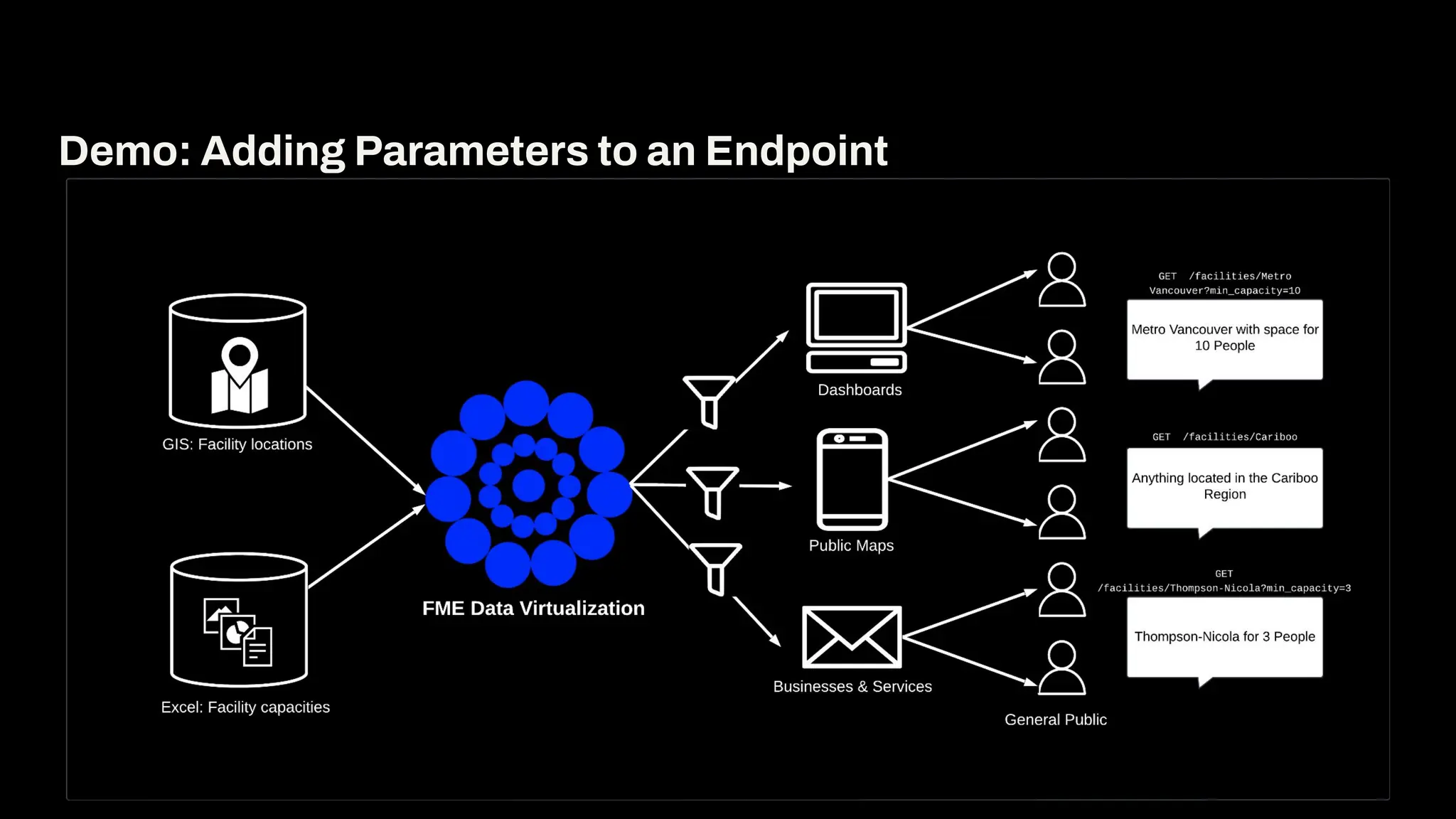
Imagine building web applications or dashboards on top of all your systems. With FME’s new Data Virtualization feature, you can deliver the full CRUD (create, read, update, and delete) capabilities on top of all your data that exploit the full power of FME’s all data, any AI capabilities. Data Virtualization enables you to build OpenAPI compliant API endpoints using FME Form’s no-code development platform.
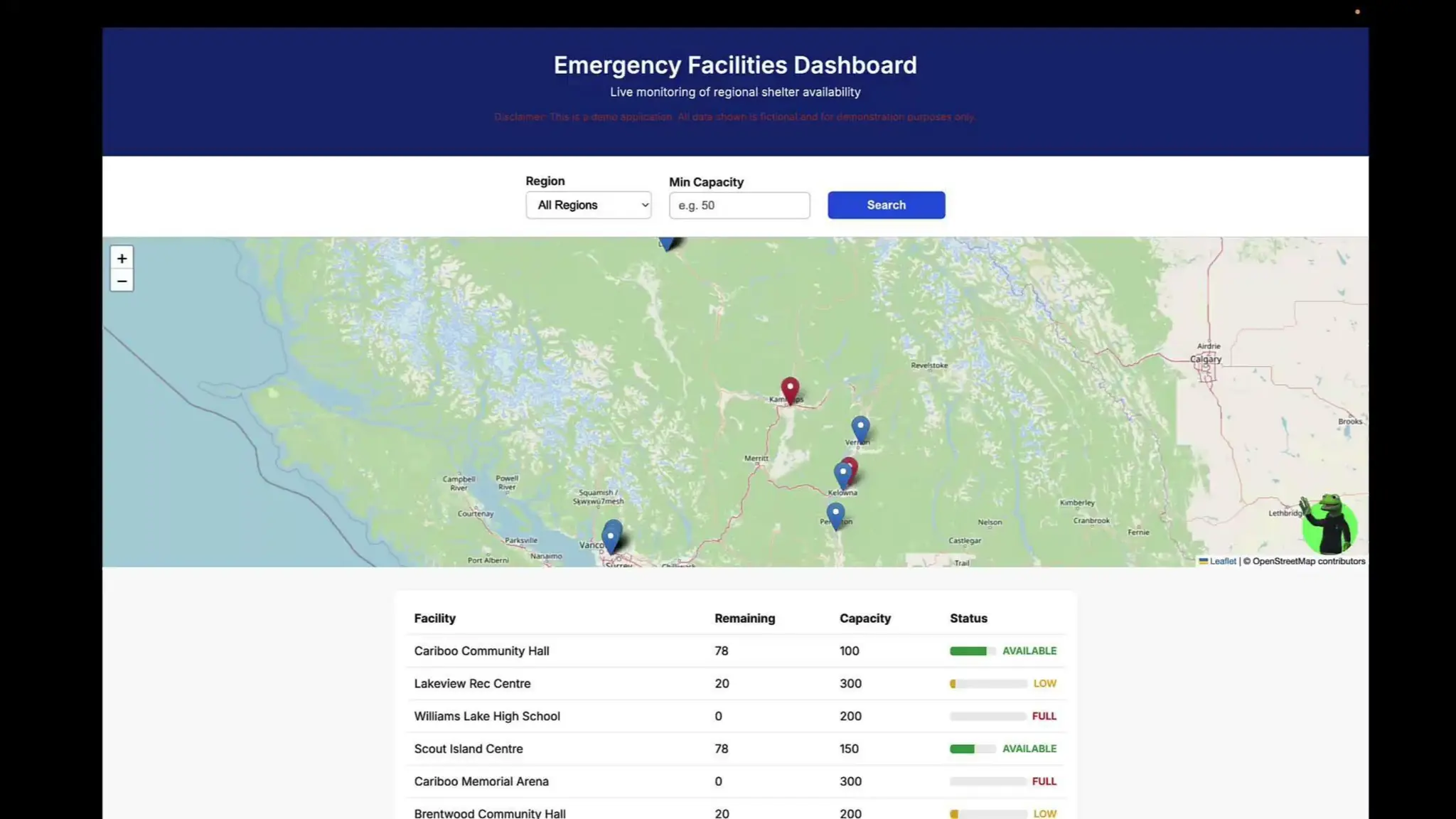
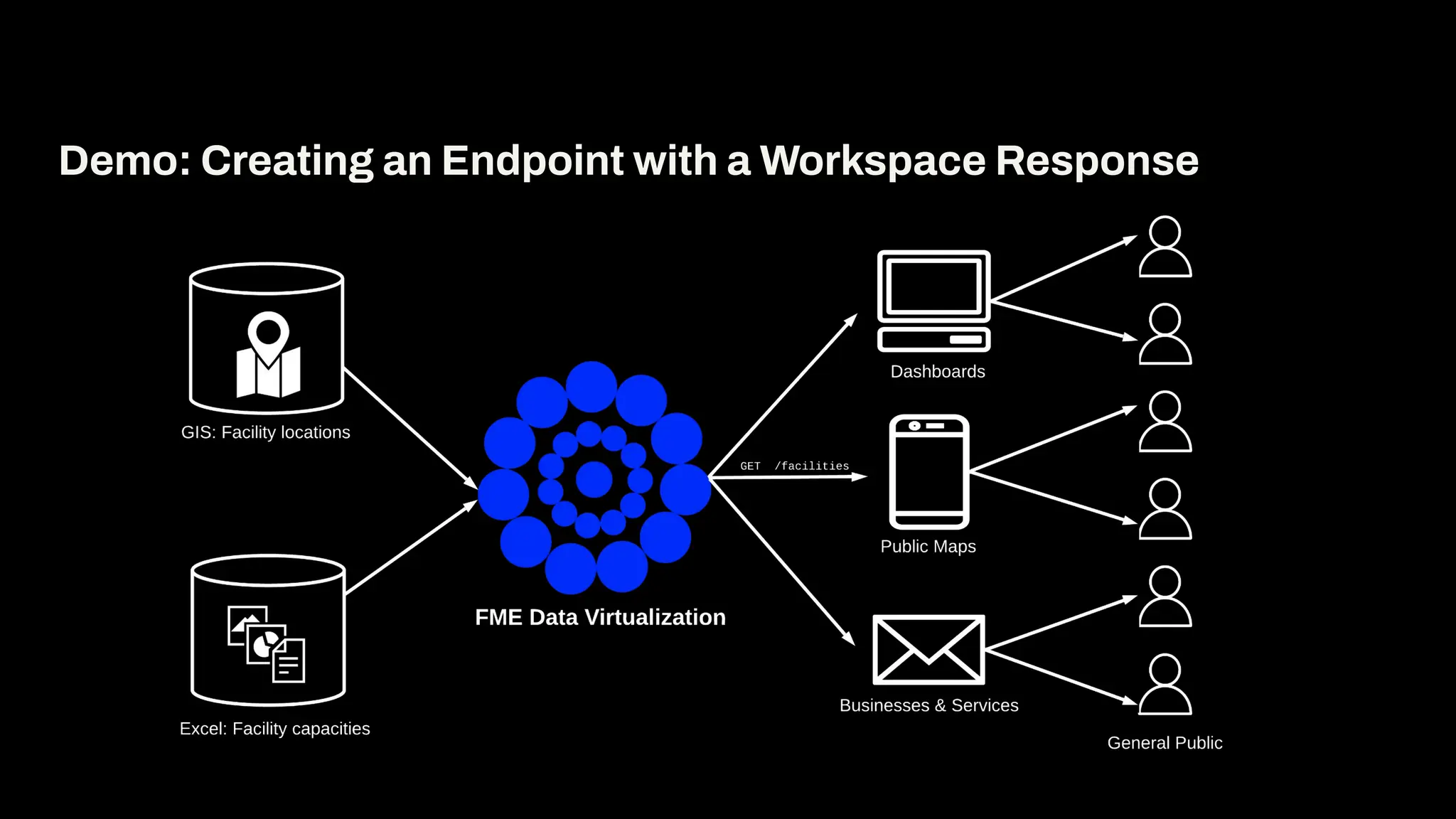
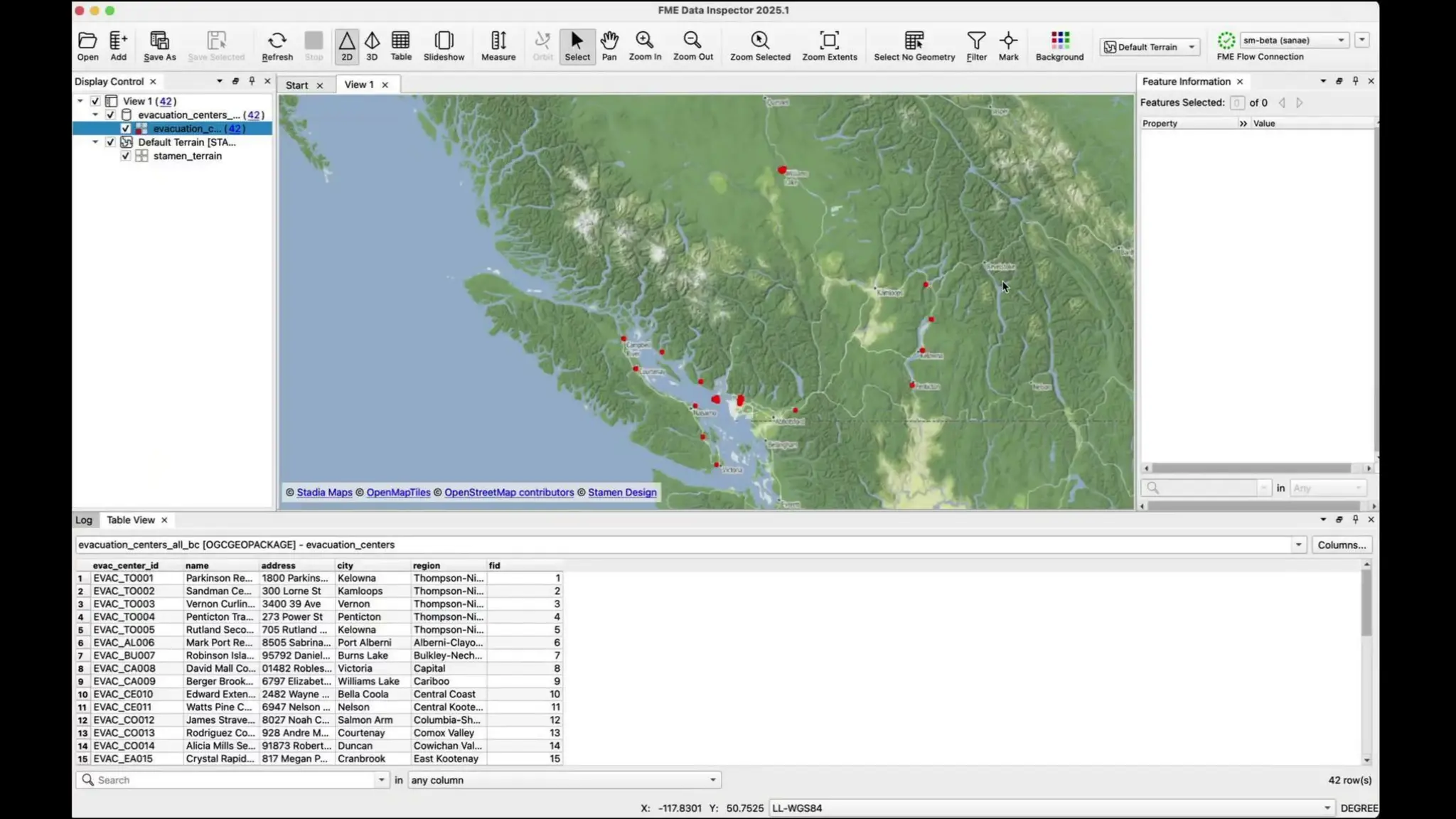
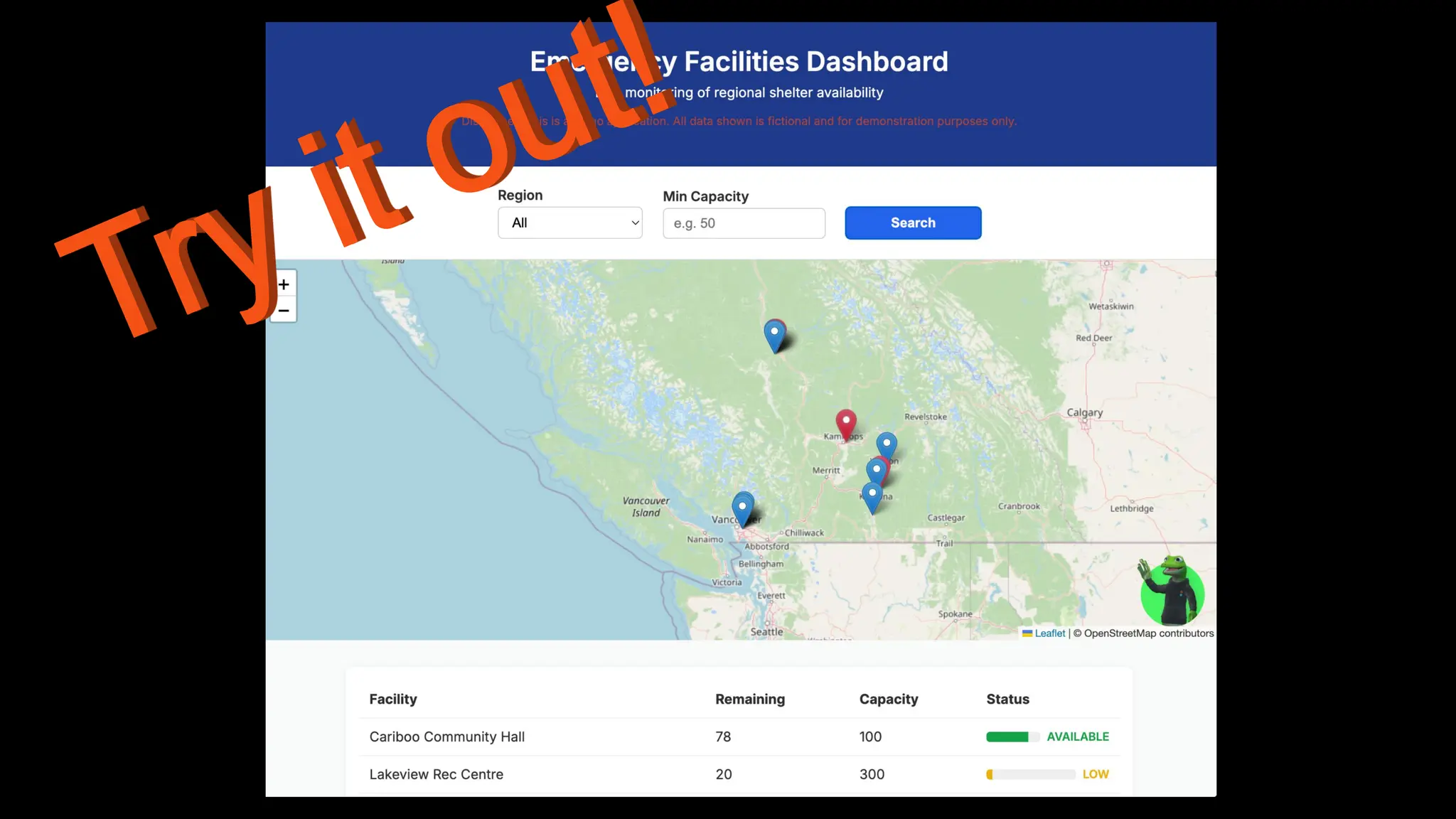
In this webinar, you’ll see how easy it is to turn complex data into real-time, usable REST API based services. We’ll walk through a real example of building a map-based app using FME’s Data Virtualization, and show you how to get started in your own environment – no dev team required.
What you’ll take away:
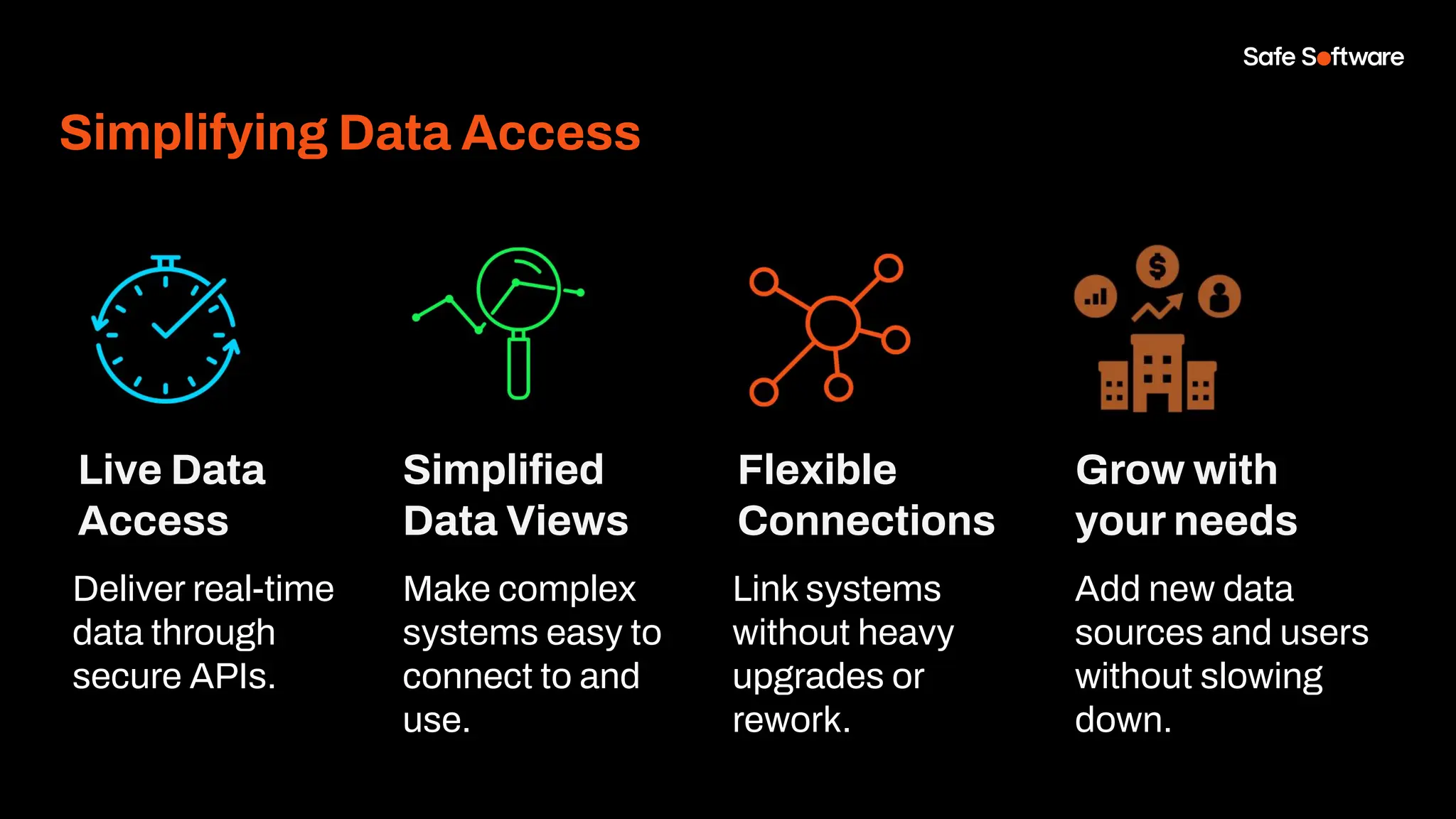
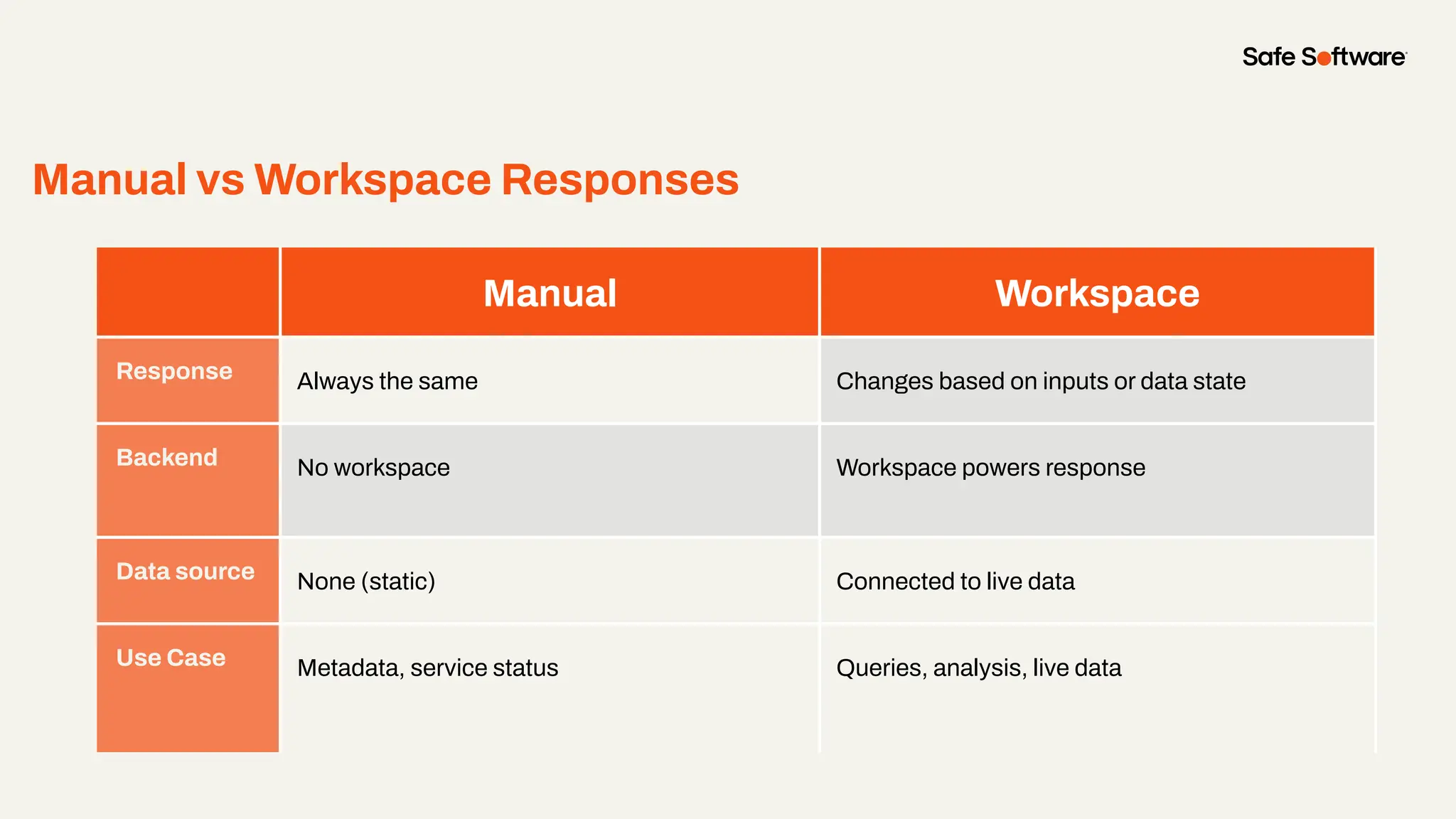
-How to build live applications and dashboards with federated data
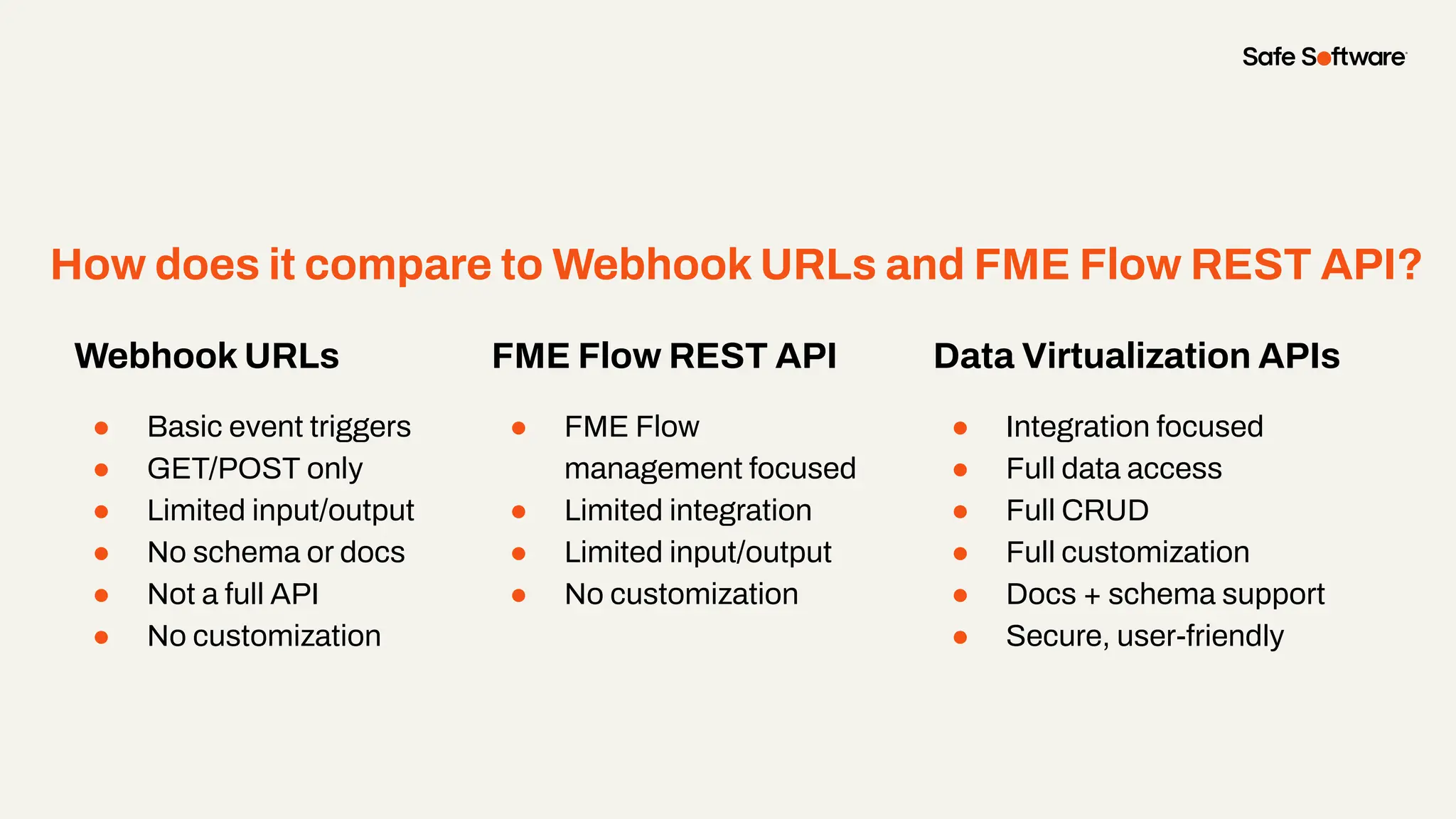
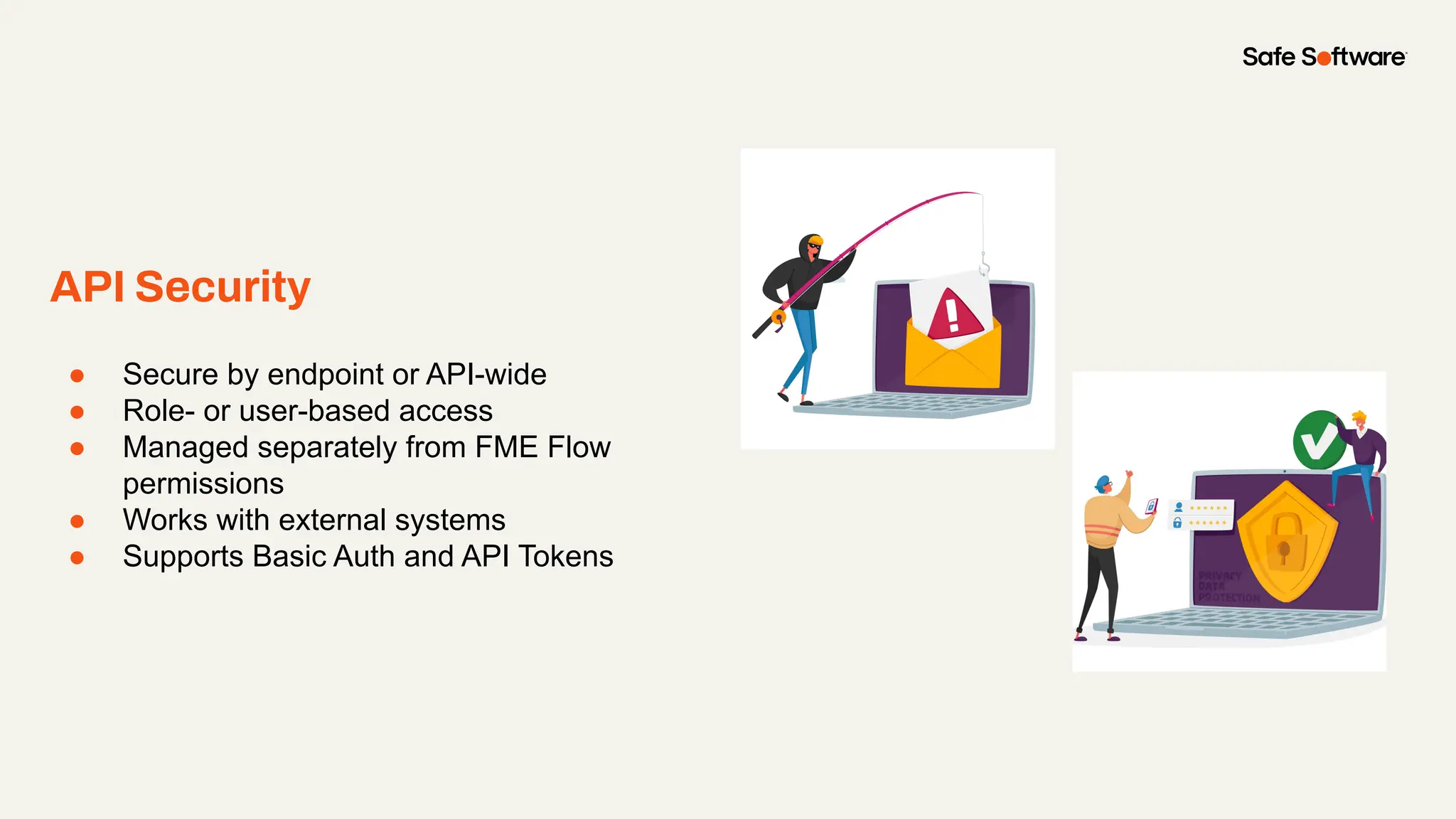
-Ways to control what’s exposed: filter, transform, and secure responses
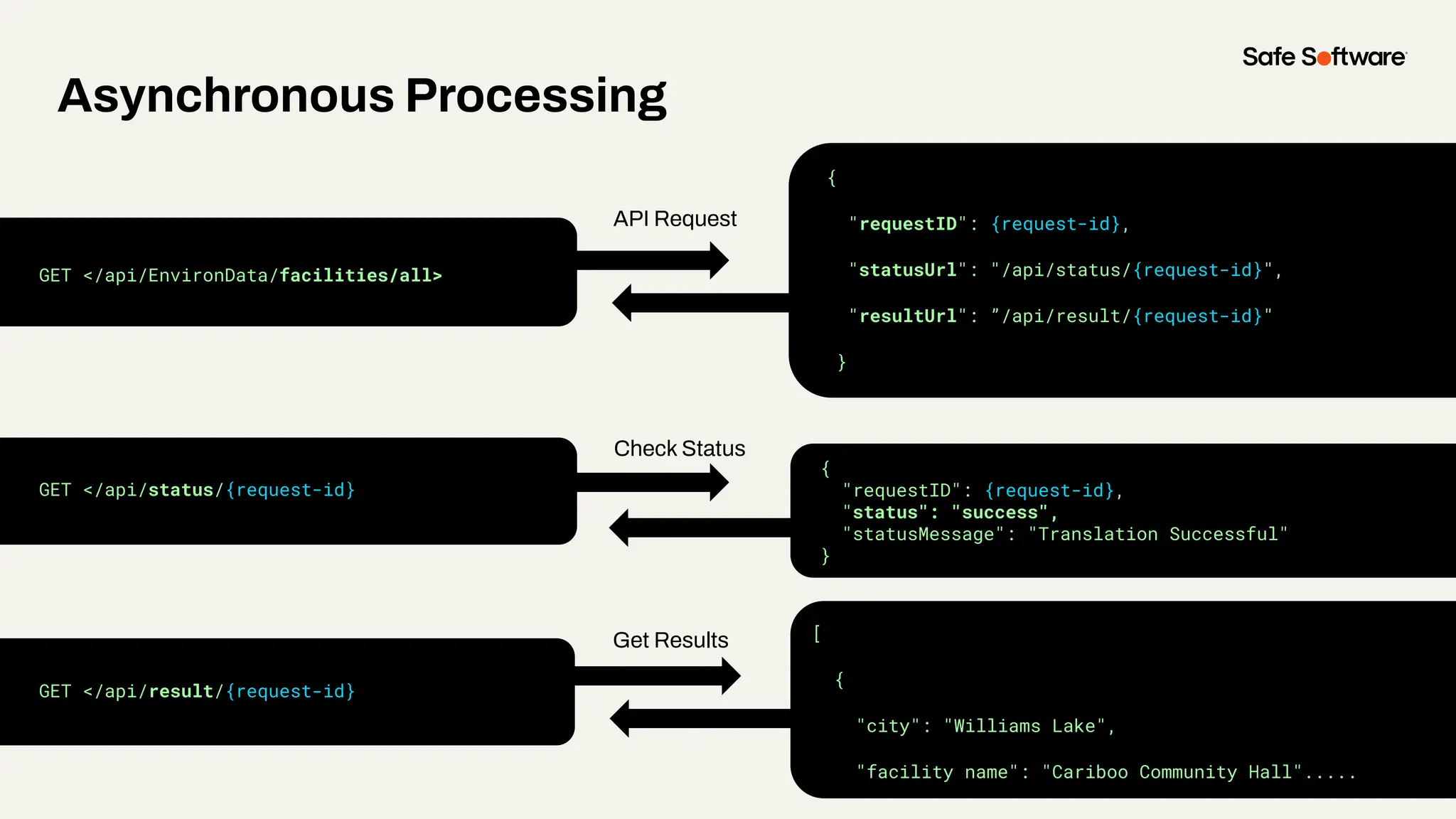
-How to scale access with caching, asynchronous web call support, with API endpoint level security.
-Where this fits in your stack: from web apps, to AI, to automation
Whether you’re building internal tools, public portals, or powering automation – this webinar is your starting point to real-time data delivery.