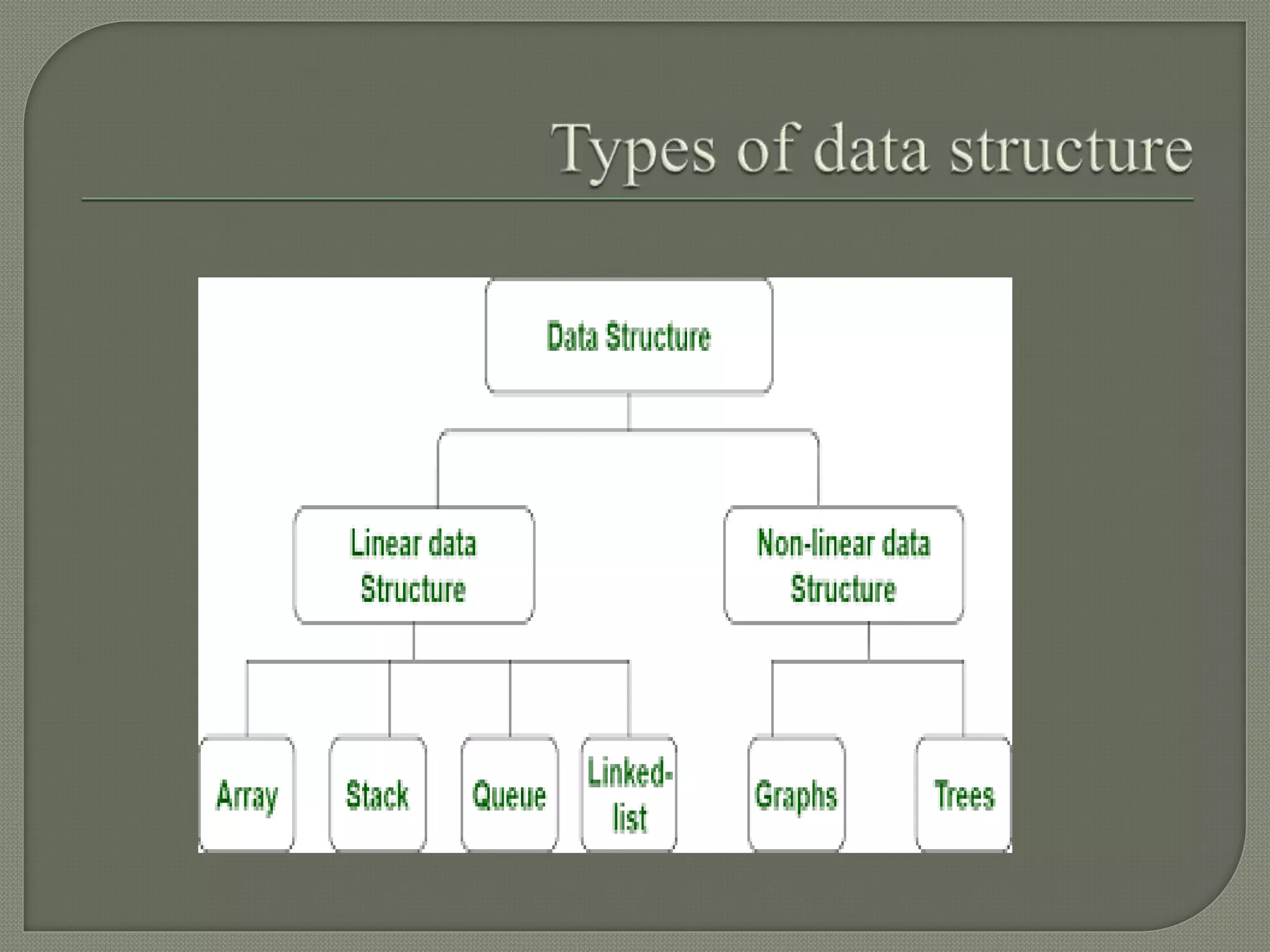
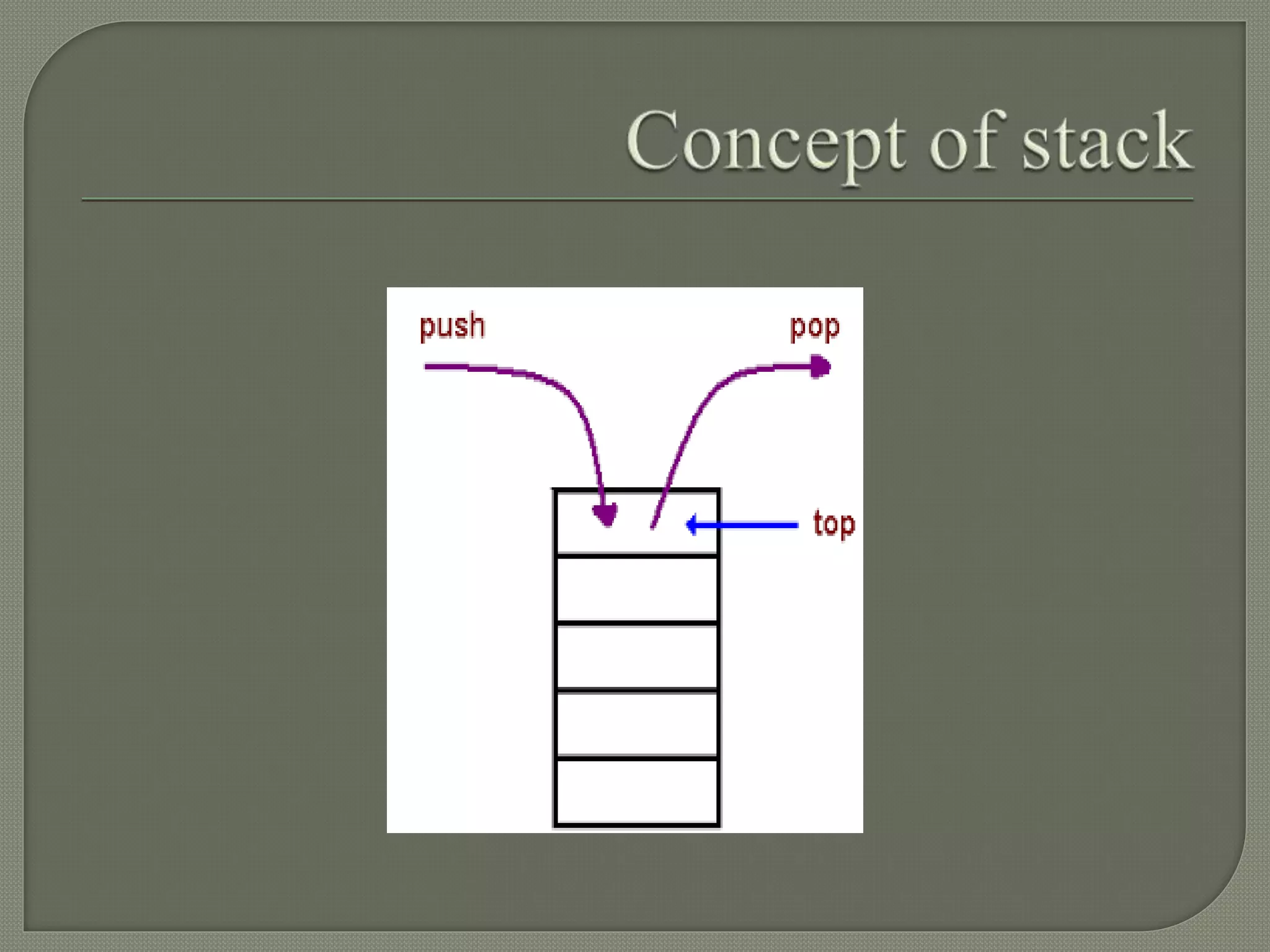
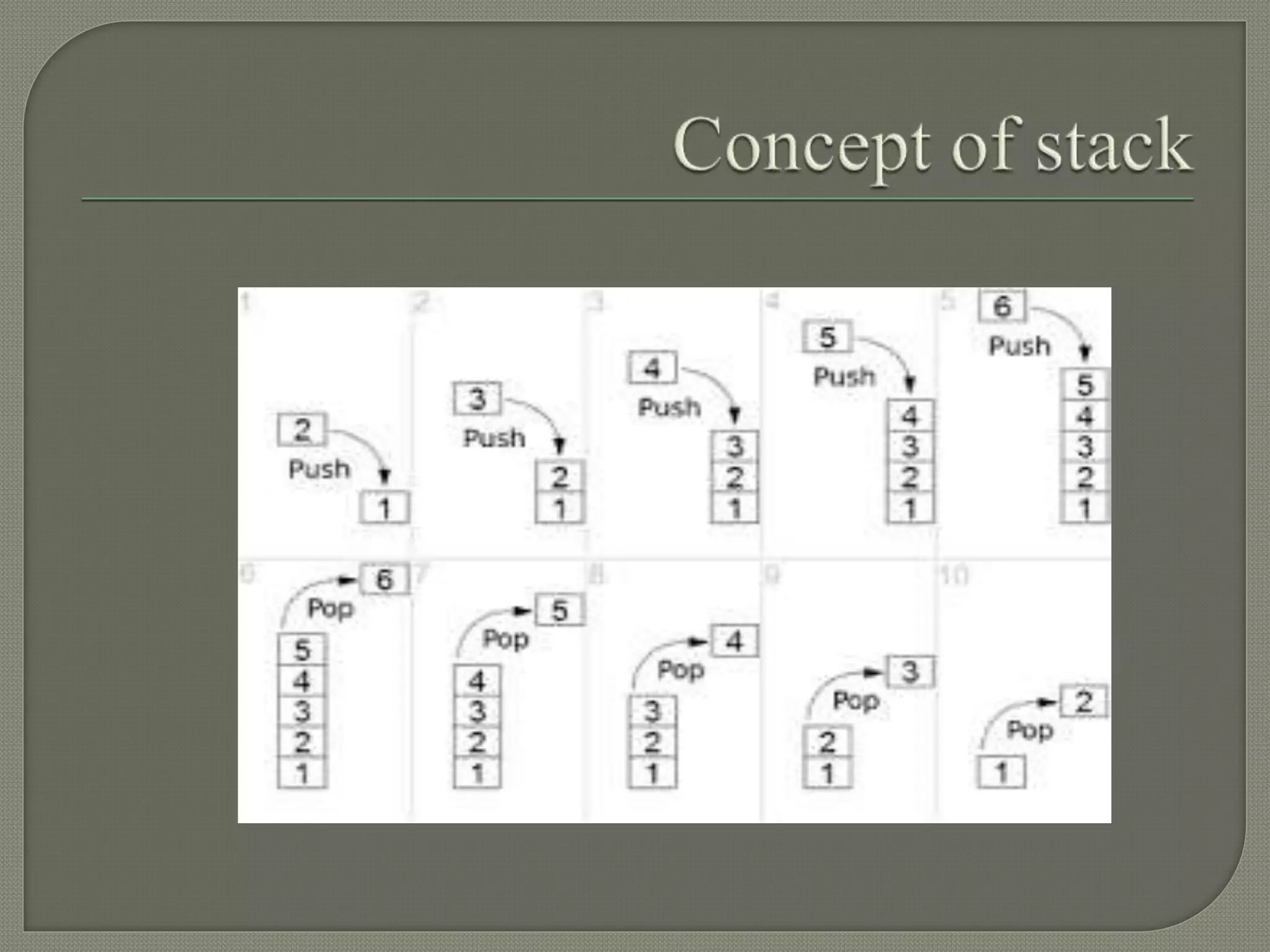
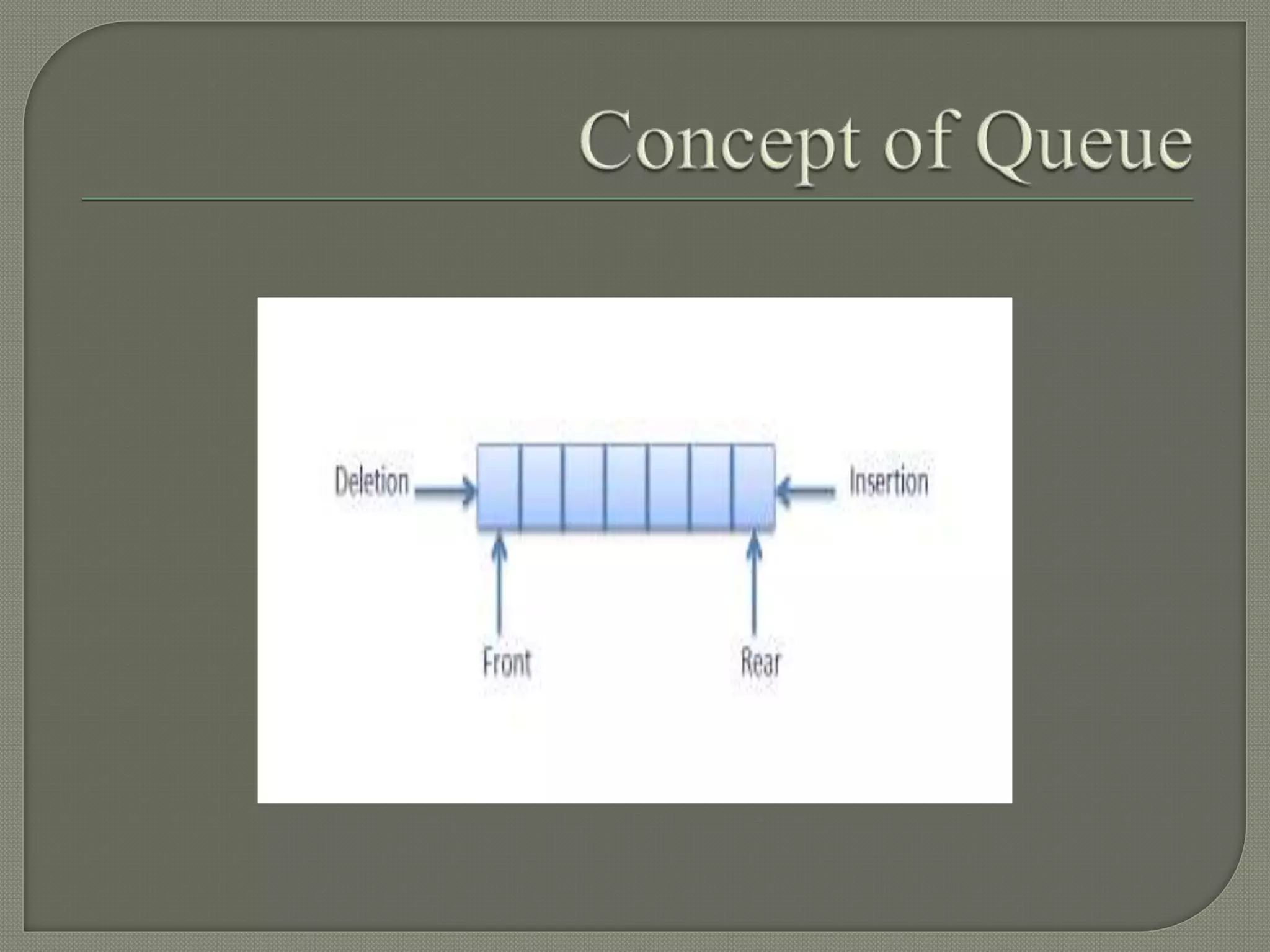
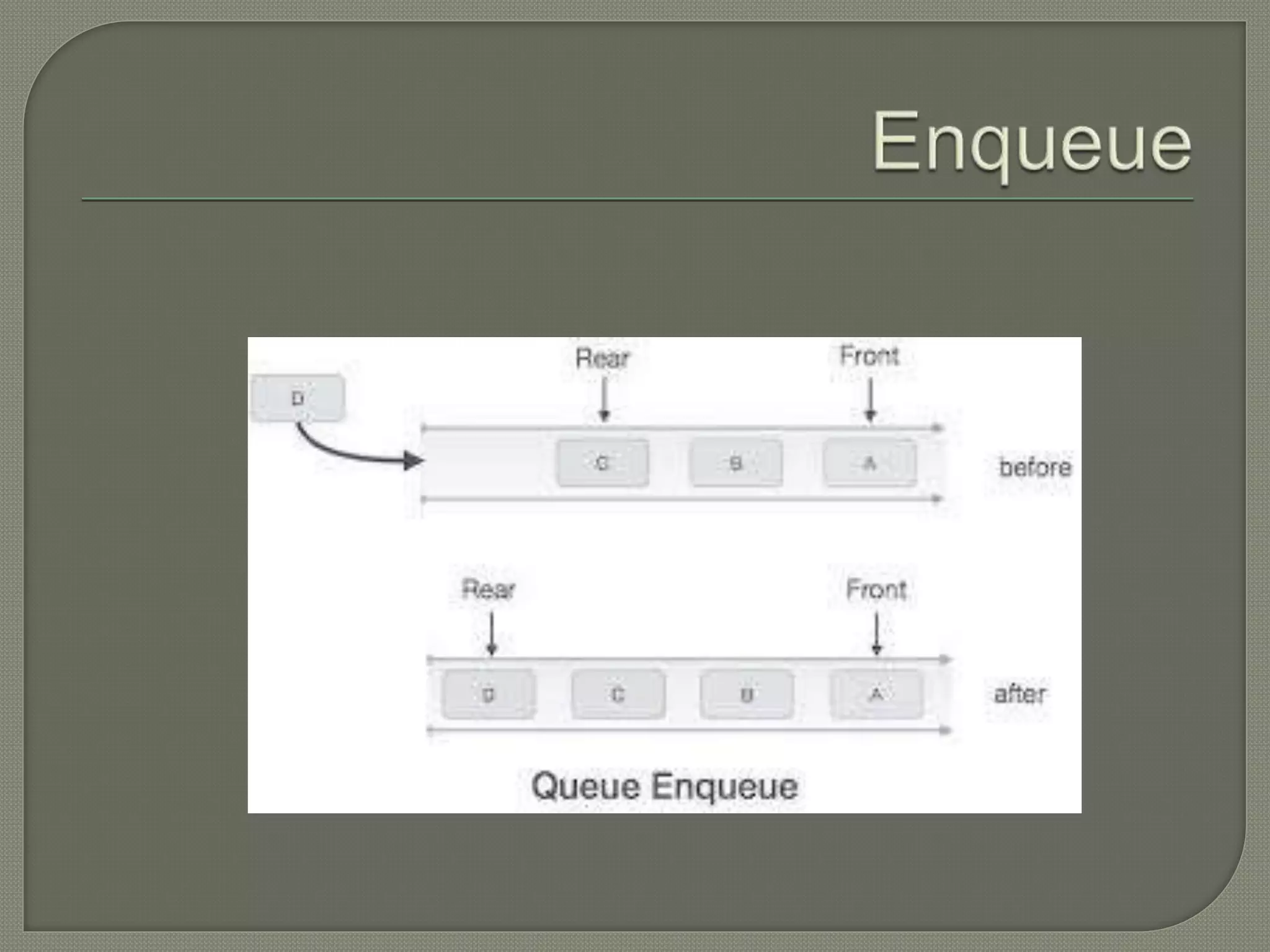
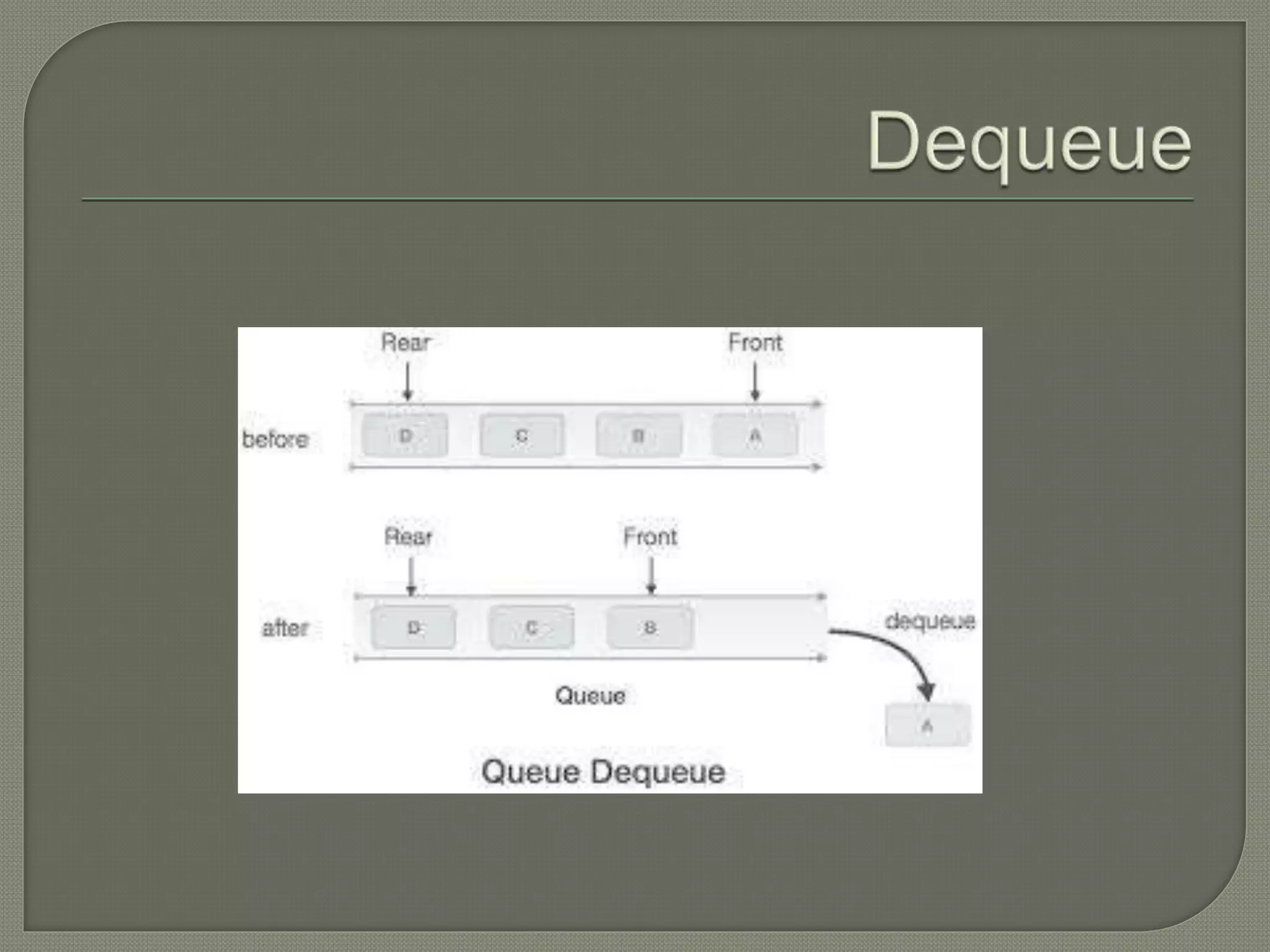
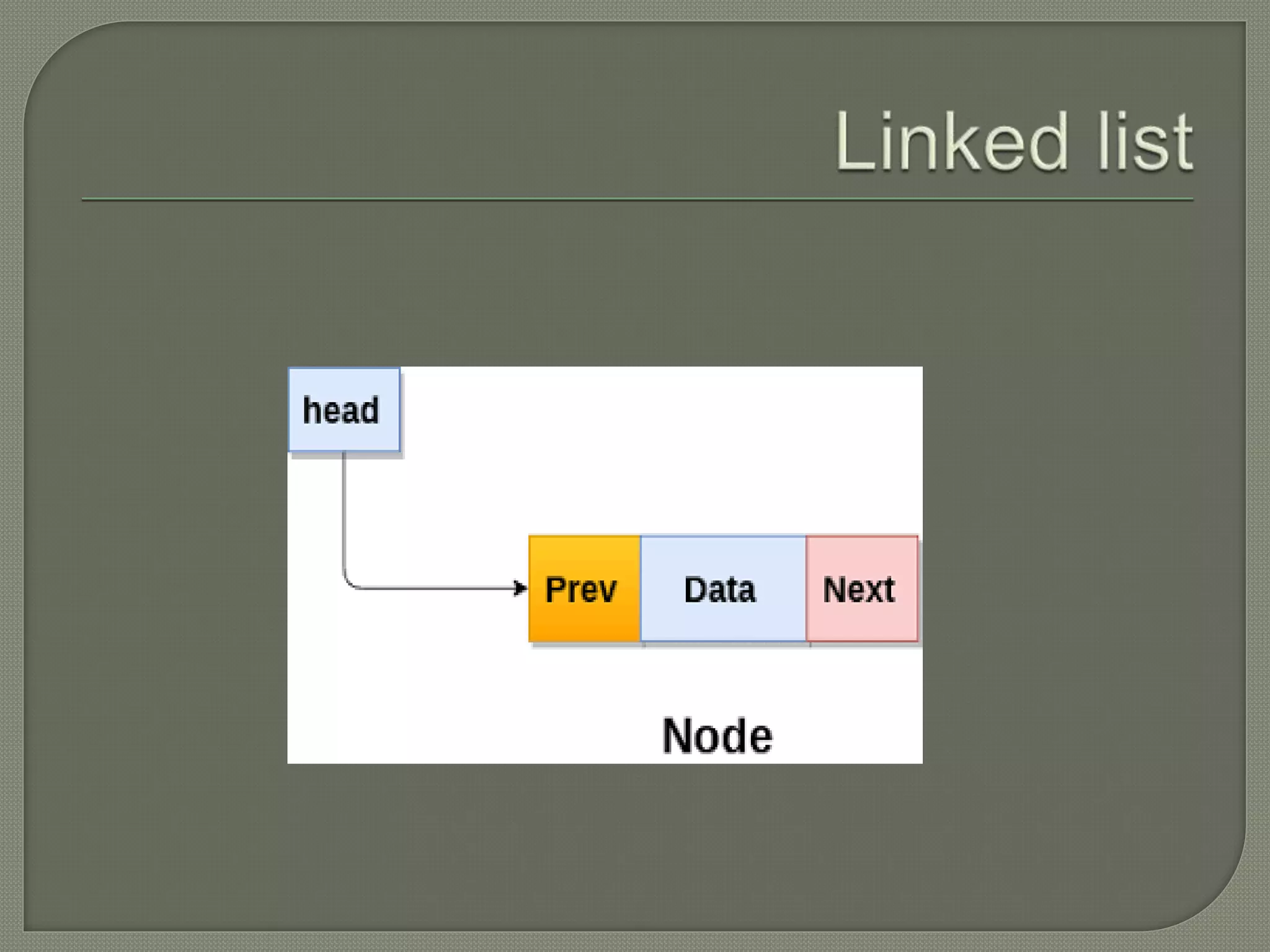
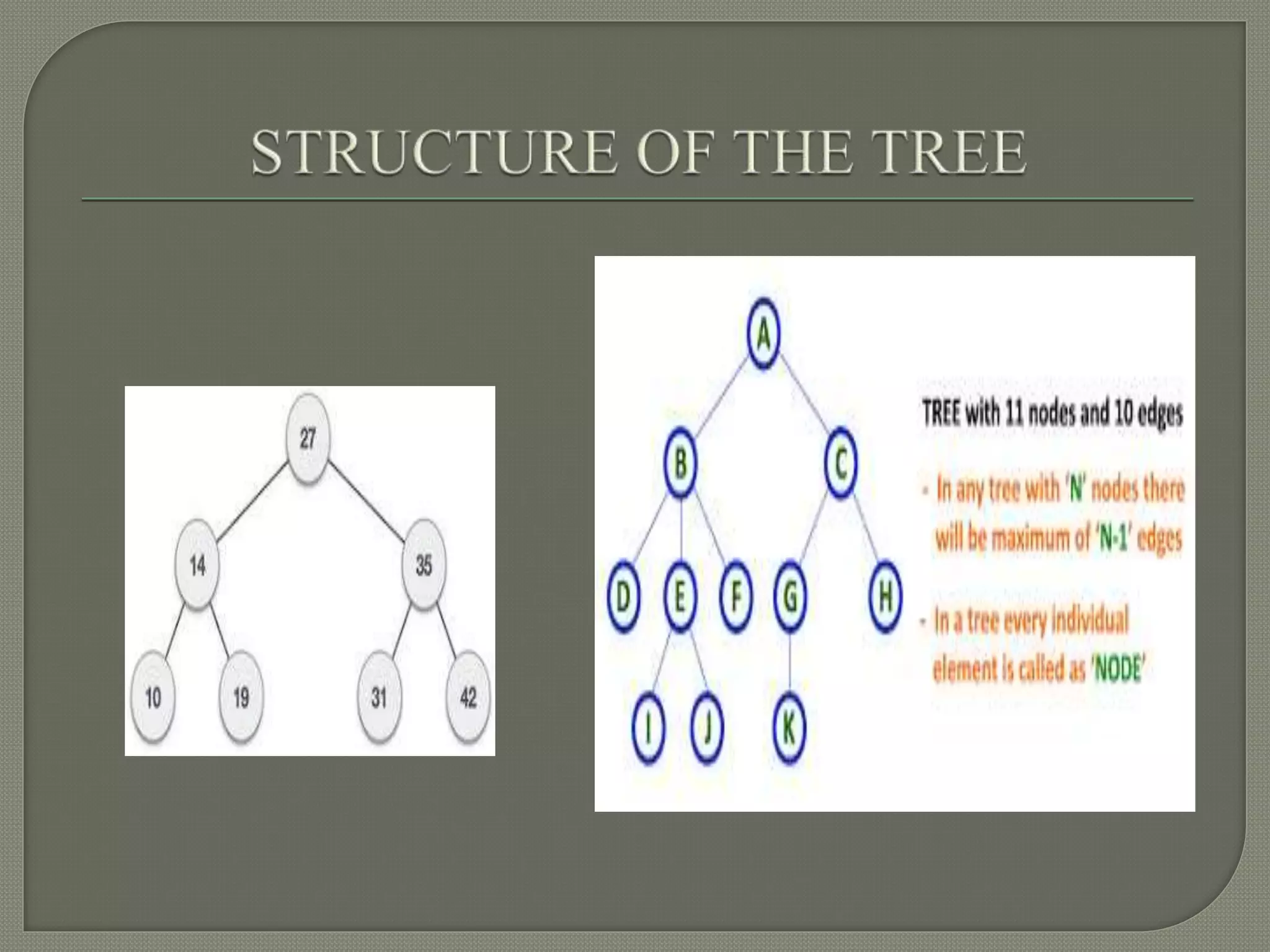
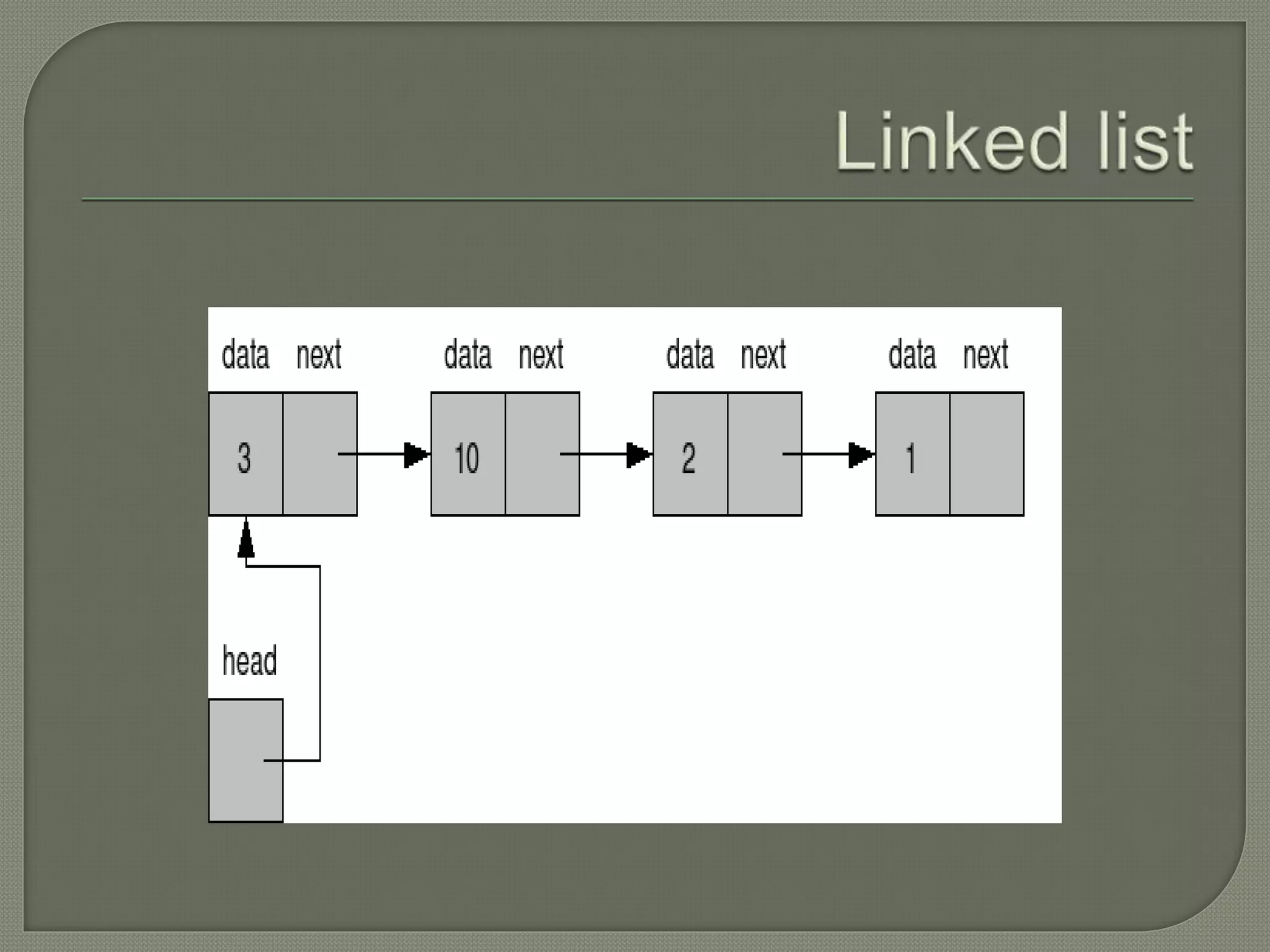
The document discusses a lecture on data structures and algorithms given on June 6, 2022 from 10:00-10:45 AM. It covers 5 units: arrays and sequential representations, trees and graphs, algorithms like heap sort and binary search, greedy methods and the knapsack problem, and backtracking techniques like the 8 queens problem. Key data structures discussed include arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, trees, and graphs.