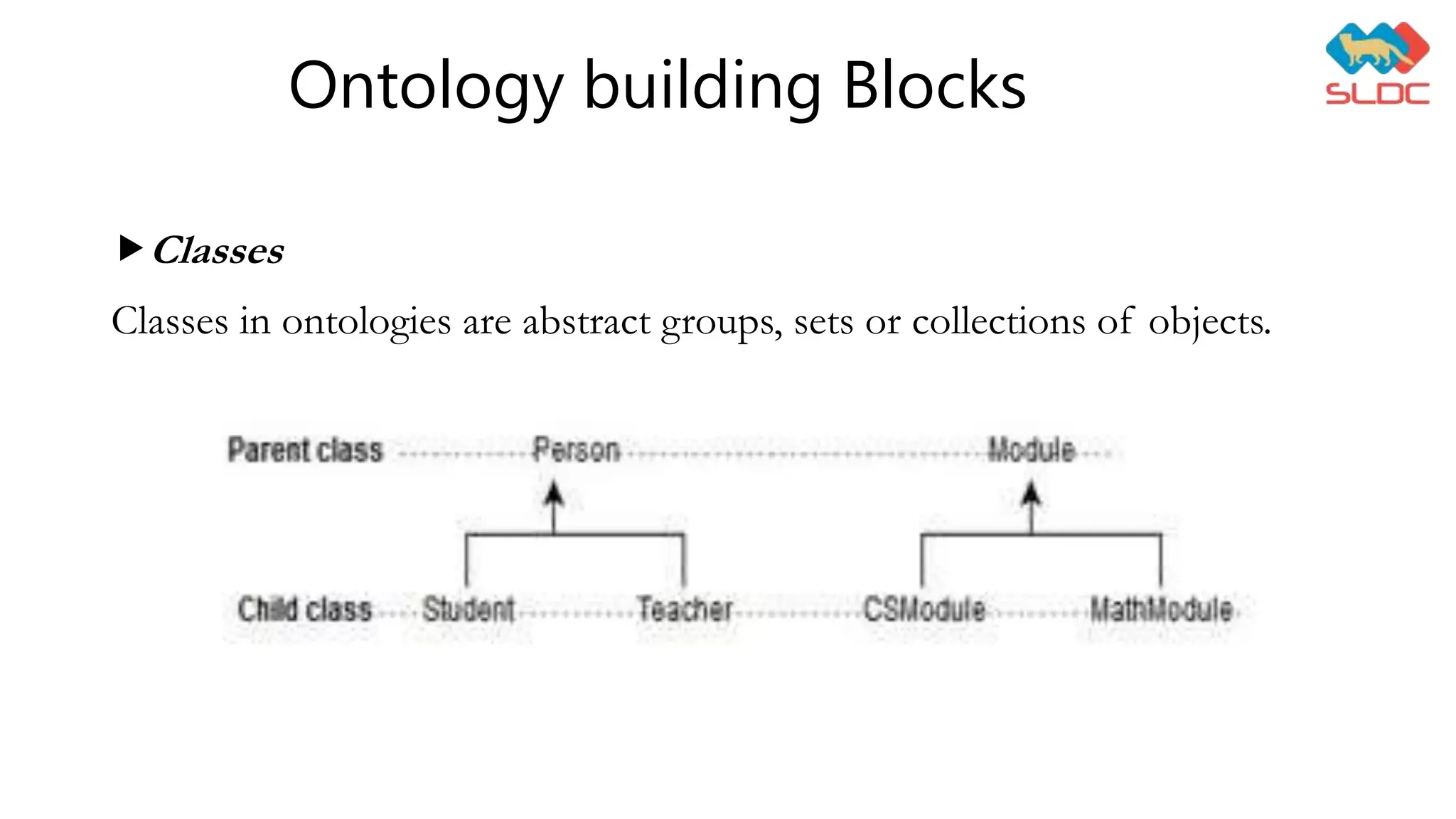
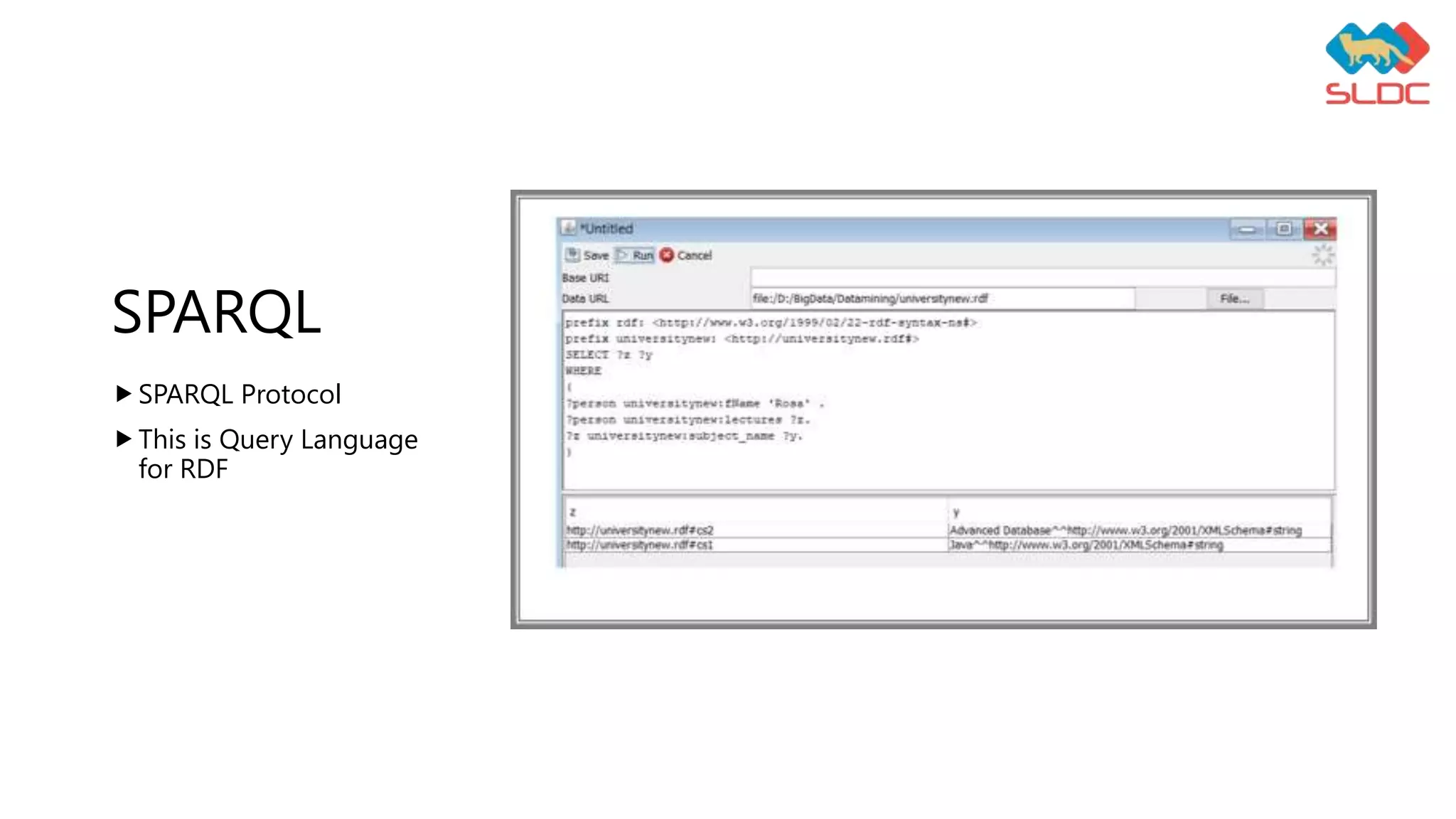
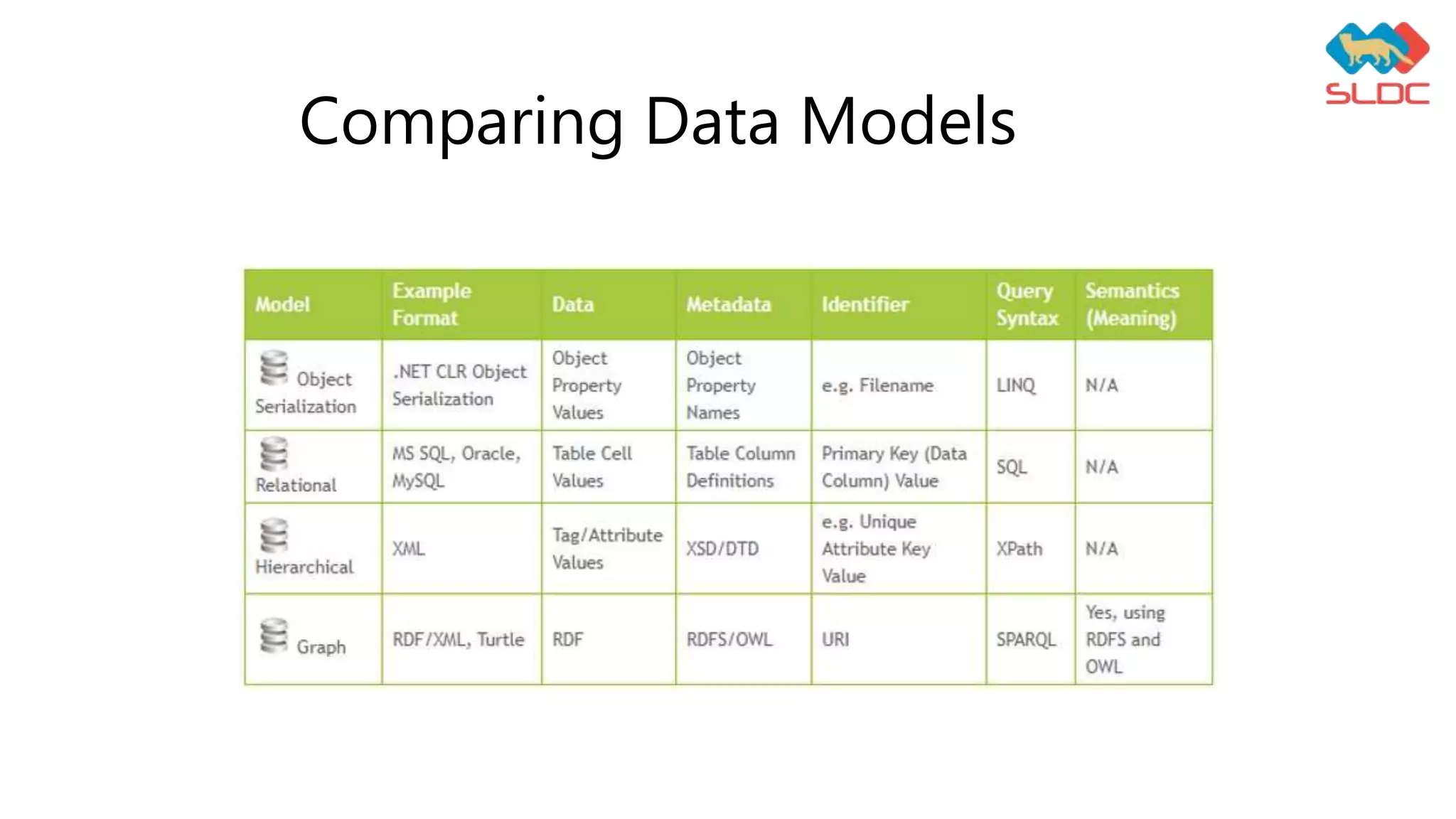
This document discusses data representation using ontology. It defines ontology as a formal description of knowledge as concepts and relationships within a domain. It lists tools for ontology visualization including Protégé, Graphviz, PCL, VOWL, and YEd. It provides examples of ontology building blocks like classes, object properties, data properties, and individuals. It also mentions SPARQL as a query language for RDF and discusses benefits of using ontology like making data more accessible, enabling easier modification of data models, allowing analysis of domain knowledge, and facilitating reuse of domain knowledge.