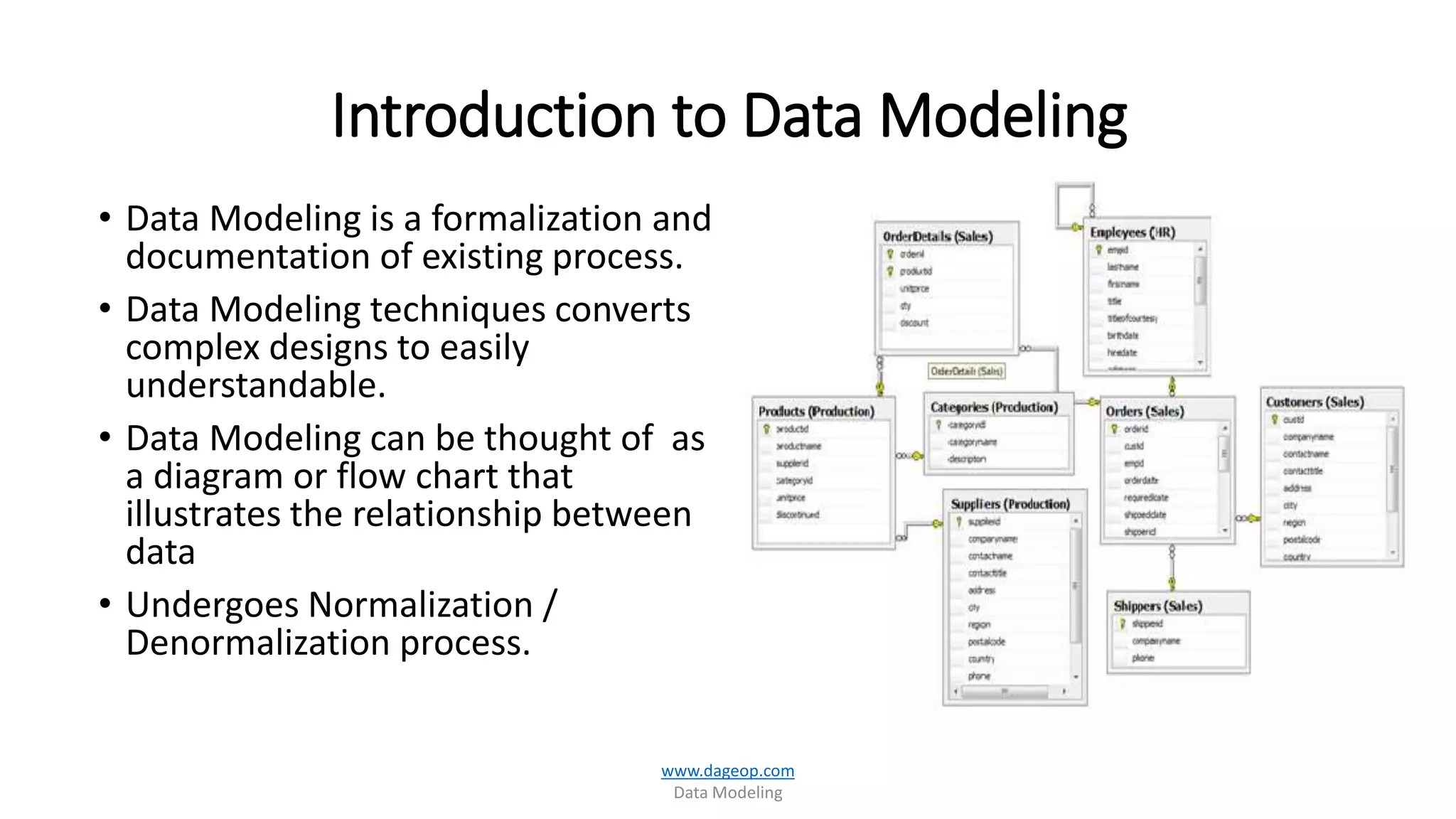
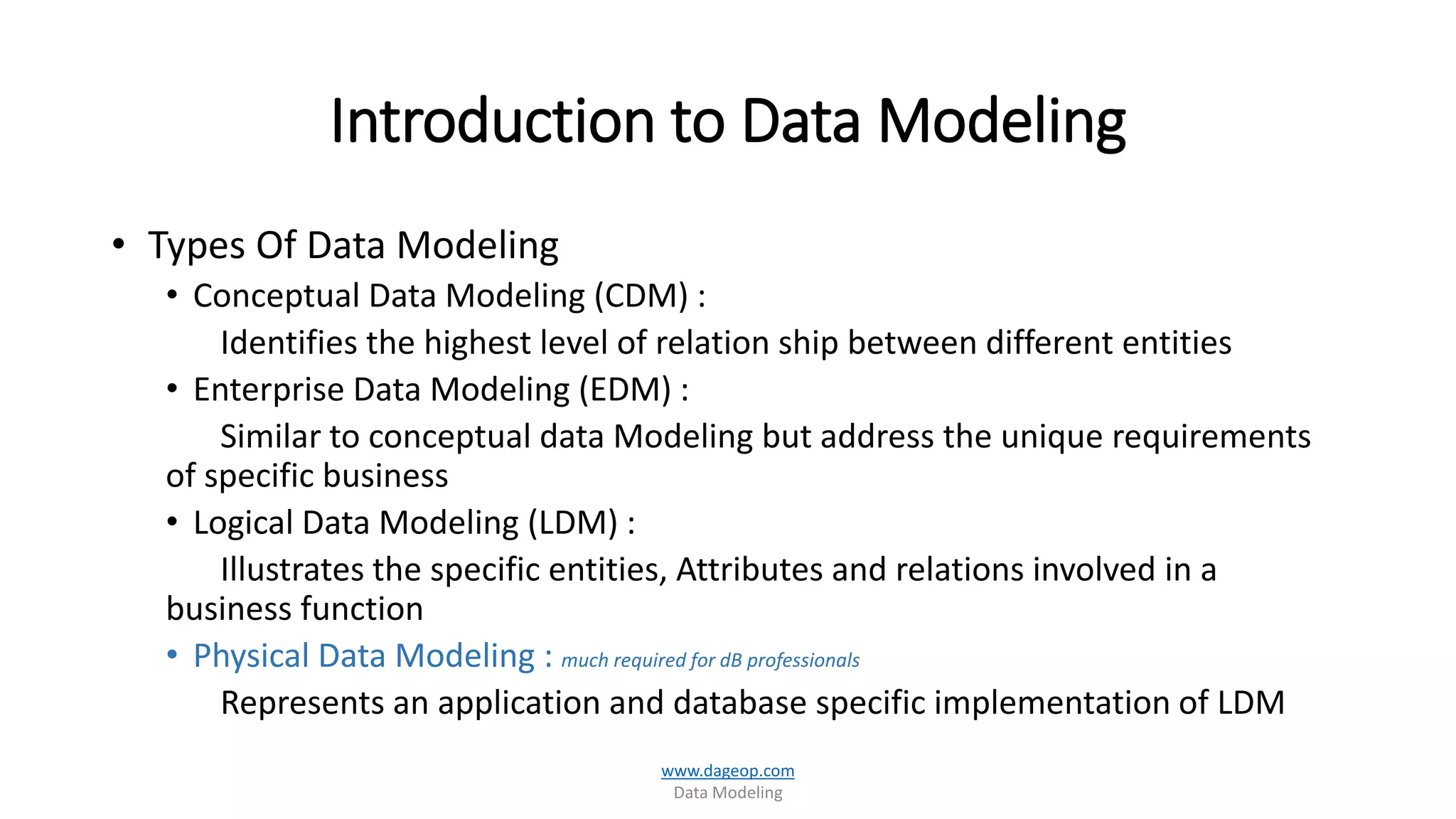
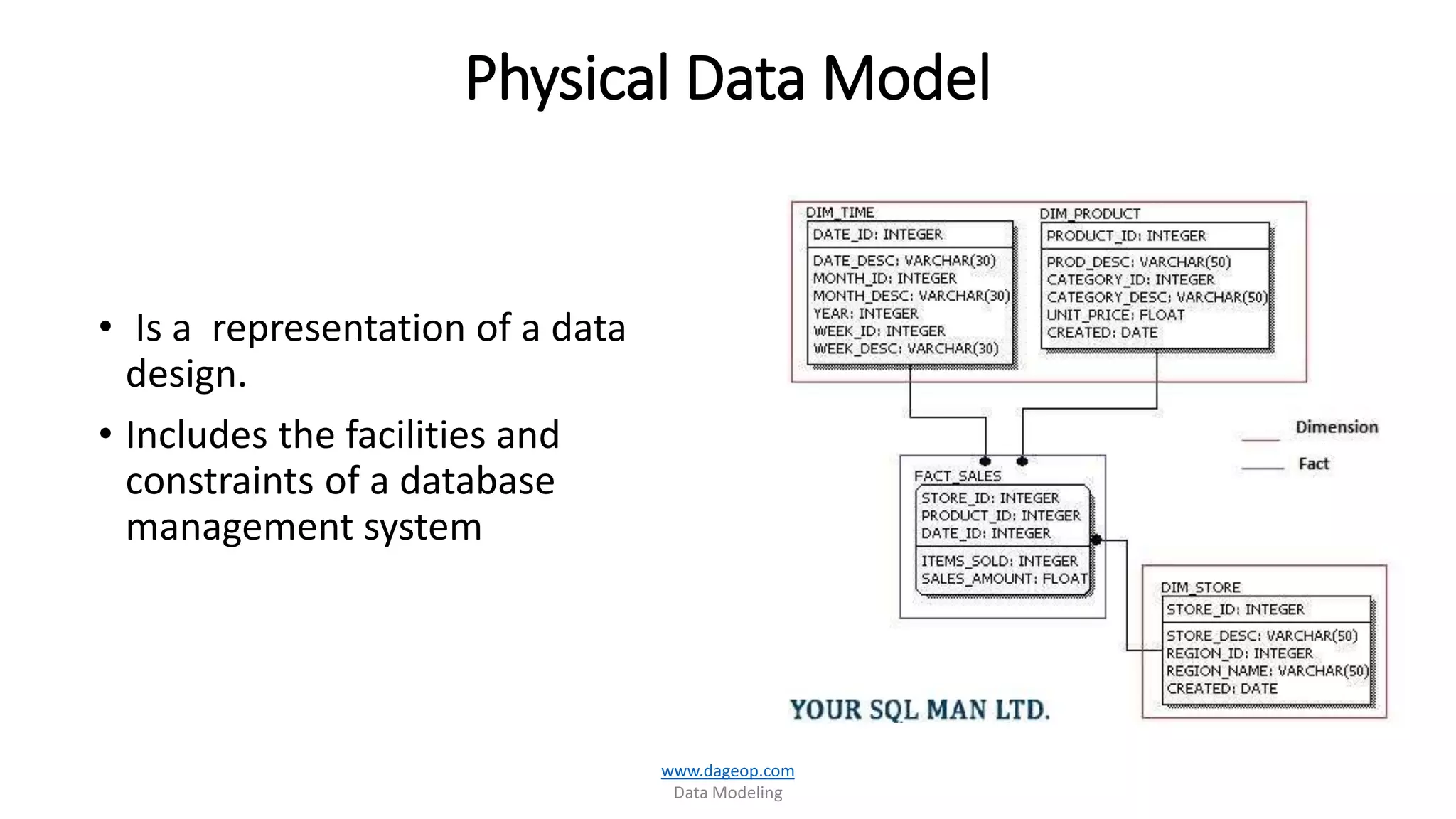
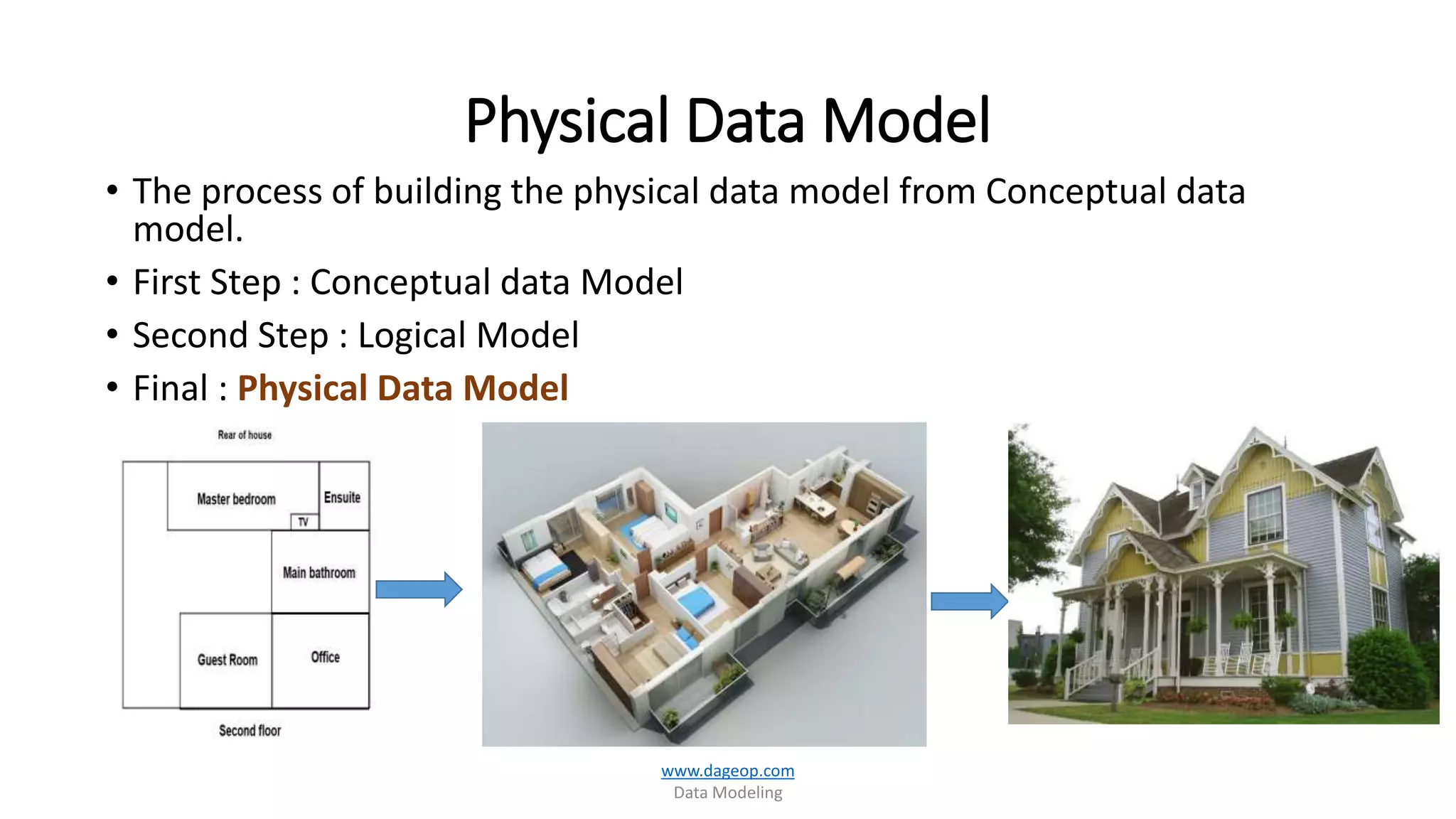
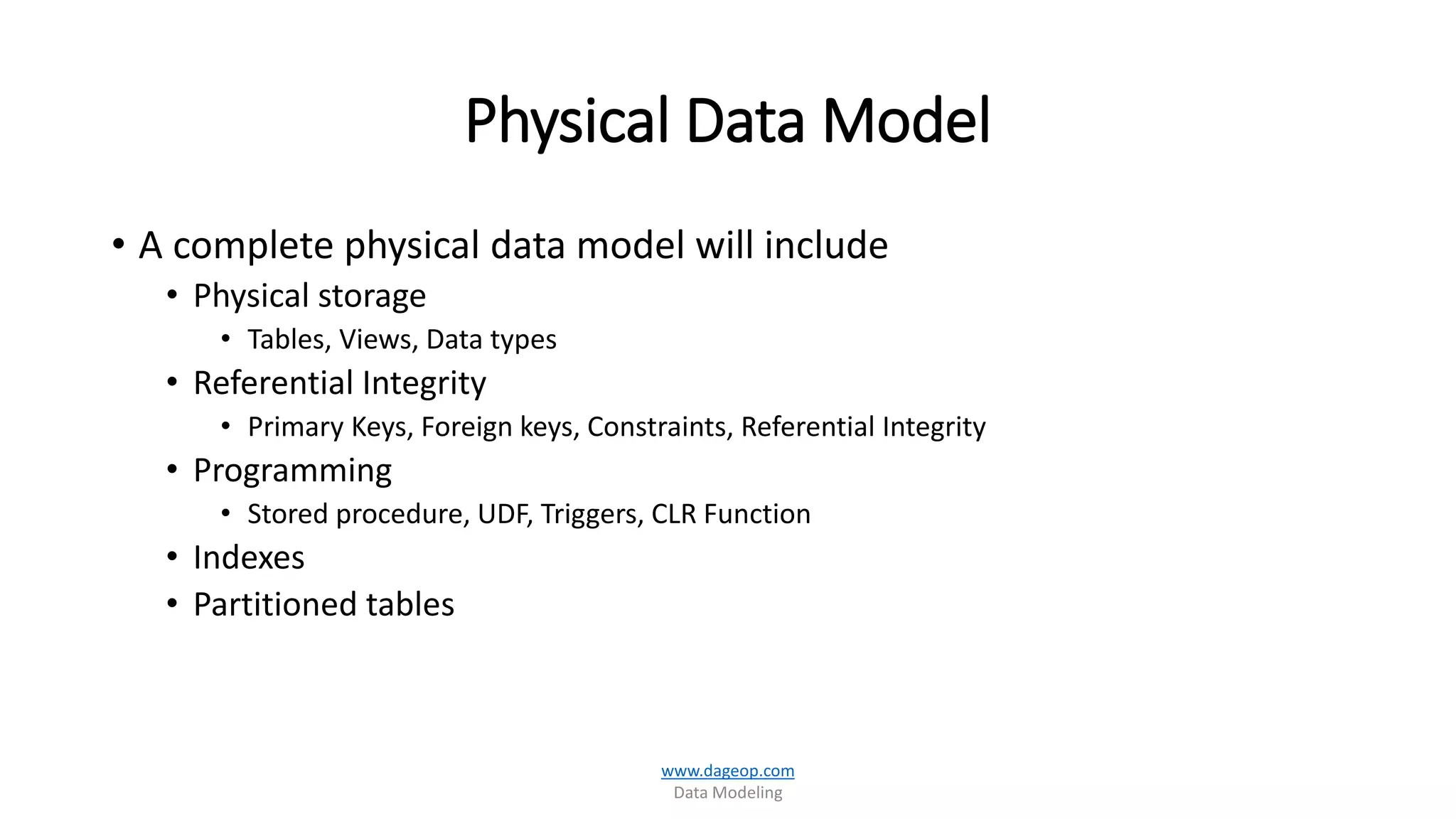
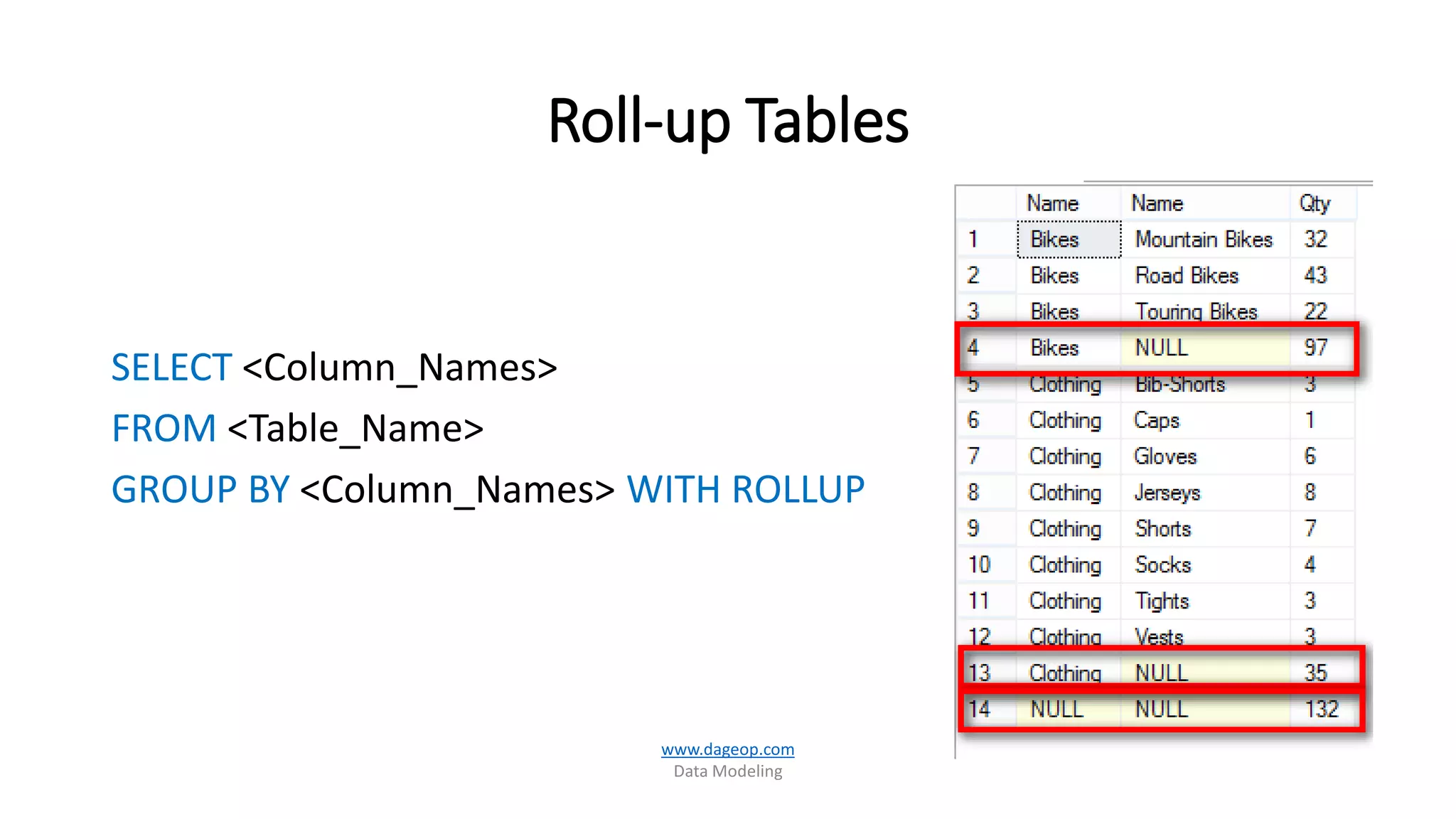
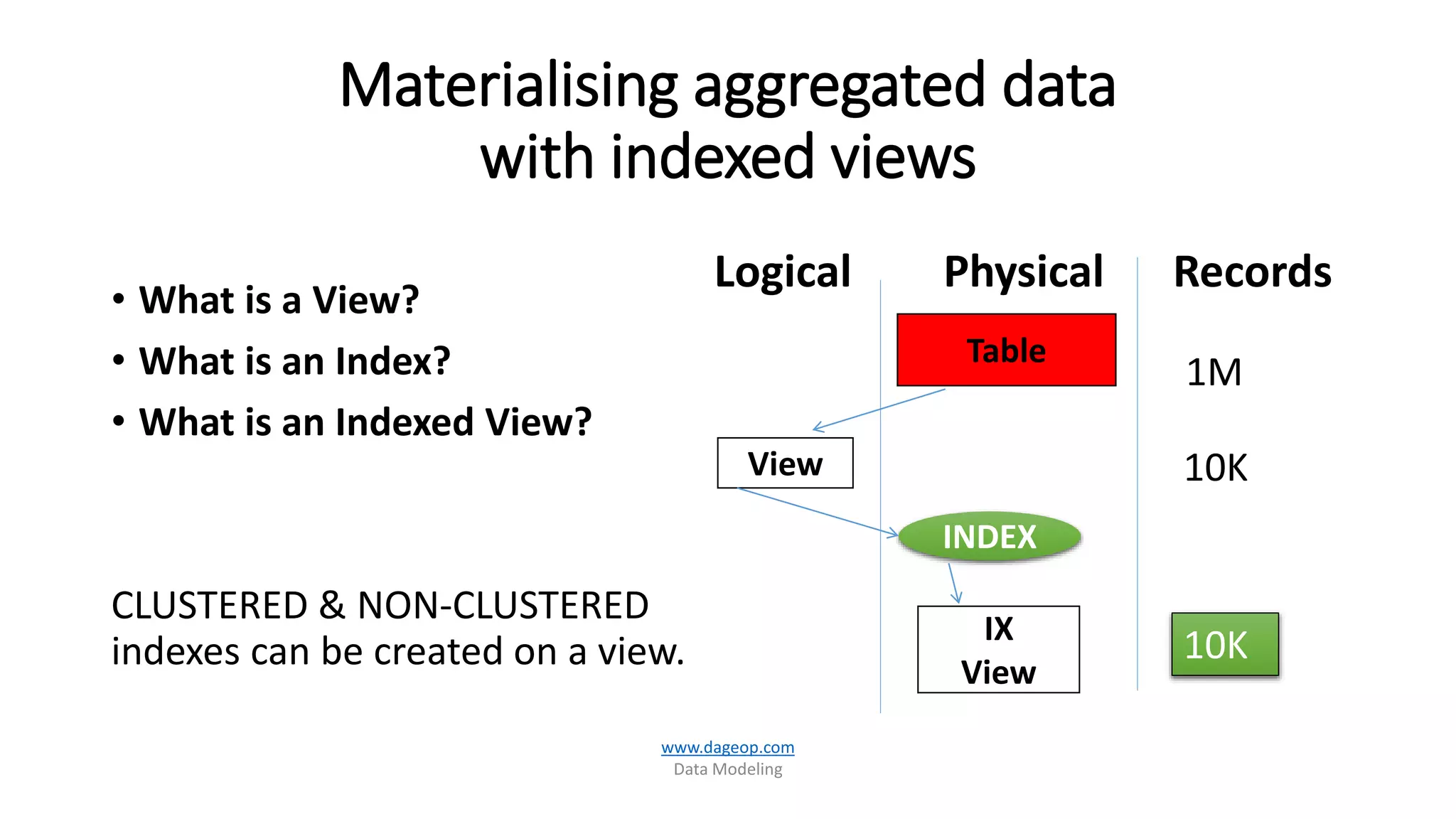
This document discusses techniques for storing summarized data efficiently. It introduces roll-up tables, which use the GROUP BY clause to calculate subtotals and grand totals in a single query. Indexed views are also covered, which allow indexes to be created on views to materialize aggregated data and improve performance. The document promotes the use of SQL Server tools like SSIS, SSAS, rollups and compute functions to generate summaries over complex, multi-dimensional analysis.