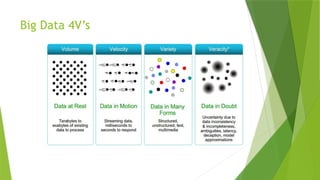
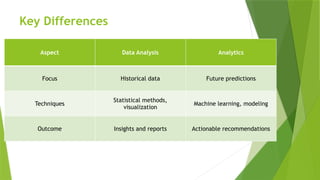
The document contrasts data analytics and data analysis, emphasizing their distinct functions where data analysis focuses on historical data insights while data analytics predicts future trends. It outlines the process of big data generation and management, the evolution of data usage, and the critical role both fields play in decision-making for businesses. Additionally, it highlights the growing demand for data professionals in India, reflecting the market opportunities in the big data and analytics sectors.