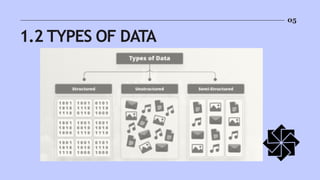
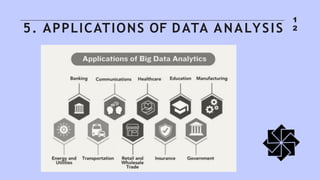
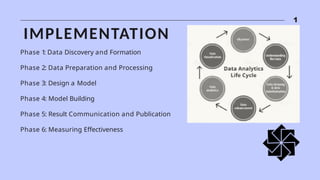
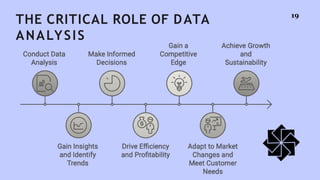
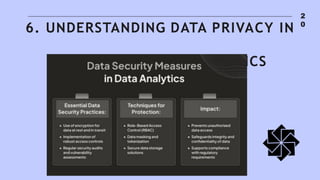
The document discusses the significance and evolution of data analysis, outlining various techniques, tools, and applications. It emphasizes the impact of data analysis on decision-making processes across sectors like healthcare, finance, marketing, and education. Additionally, it addresses the importance of data visualization and privacy considerations in the realm of data analytics.