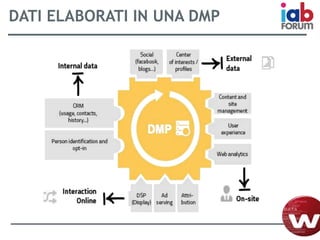
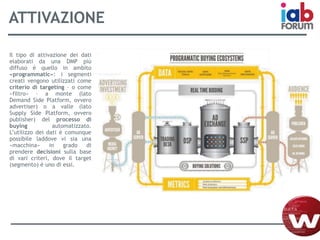
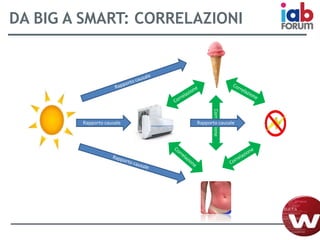
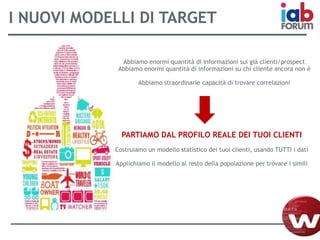
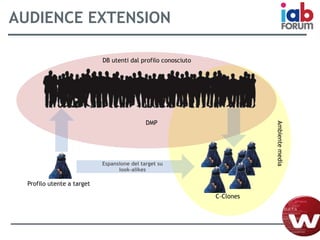
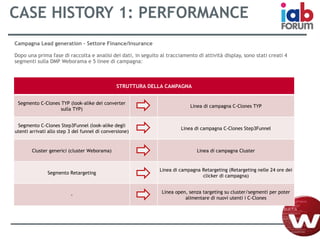
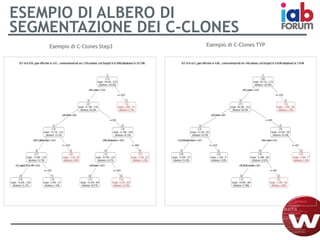
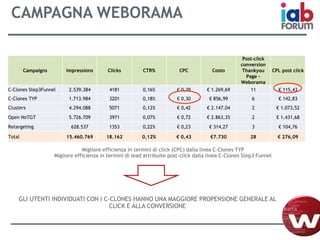
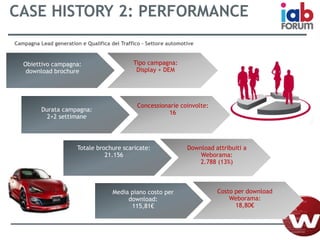
Il documento descrive l'evoluzione dei big data e il loro utilizzo nella pubblicità e nella gestione dei dati attraverso la piattaforma Weborama, evidenziando la capacità di raccogliere ed elaborare enormi quantità di dati per identificare modelli e ottimizzare strategie di marketing. L'importanza di correlazioni e modelli statistici è sottolineata, insieme all'efficacia delle campagne pubblicitarie personalizzate basate su dati analizzati in tempo reale. Infine, si enfatizza che i big data devono essere supportati dalla scienza dei dati per essere realmente efficaci.