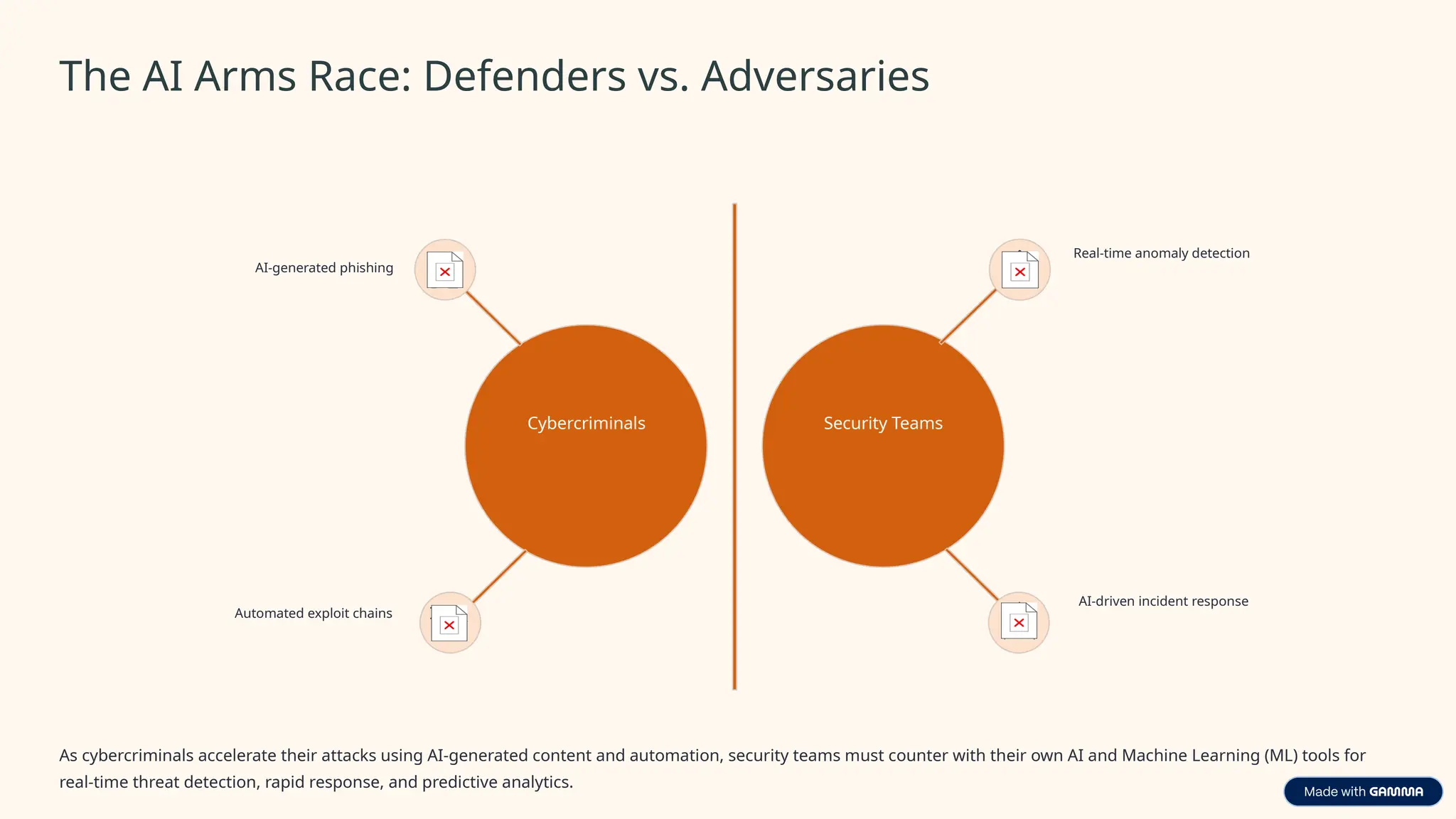
Cybersecurity involves the practices and technologies designed to protect computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, damage, or theft. Its primary goal is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information against digital threats.