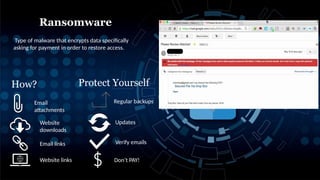
The document discusses the key aspects of cyber security, including concepts, legal acts, and the impact of cyber crimes across various sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government. It identifies major issues related to hacking, fake news, and identity theft, outlining their consequences and challenges in information integrity. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of cyber awareness and provides tips for individuals to protect themselves from cyber threats.